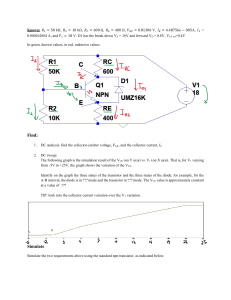
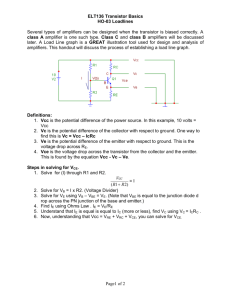
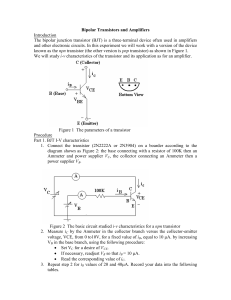
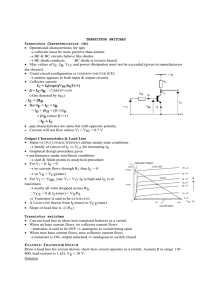
SSCP2313 Tutorial 7 IC RB IB VCE VBB VCC VBE IE Fig. 1(a) 1. Figure 1(a) shows an npn-transistor is biased in Common-Emitter connection. The transistor curves are shown in Figure 1(b). a) In normal operation of a transistor, the emitter-junction is (forward, reverse)* biased and the collector-junction is (forward, reverse)* biased. b) What is the relation between IE, IC and IB? c) Why IB is very much smaller than IC? dc d) Define dc and dc of a transistor and show that dc . 1 dc e) Calculate the value of dc and dc at point A, B and C. f) Define ac and ac of the transistor and calculate the value of ac and ac for the change from point B to point C. g) The collector current, IC is controlled by (IB, VCE)*. Explained why the transistor can be considered as a controlled current source. h) What is VCE,sat? What is ‘cutoff’ point? i) There is extremely small collector current when IB is zero, where is the current come from and what is it called? j) In transistor curves, what does ‘active regions’ means? Note: *(select the right answer) For all problems, the transistor is silicon with VBE = 0.7V. +15V RB 4k 600 Fig. 3 2. In the amplifier shown in Figure 3, βdc = 60. Draw the dc equivalent circuit for the amplifier and find the value of RB required to set VCE to 8V. Draw the dc load line and show the Q point, (IC,VCE). +VCC +30V RC 20k 4k RB dc = 50 10k Fig. 4 5k Fig. 5 3. For the voltage-divider bias circuit shown in Figure 4, determine the Q-point (IB, IC, VCE). Draw the dc load-line for the circuit. By assuming IC = IE, (IB 0), again determine the Q-point (IC, VCE). Are there any significant differences? 4. Circuit in Figure 5 shown the transistor is biased using collector-feedback. What is the V advantage of collector-feedback biased? What is the condition for VCE CC ? 2 If RC = 2k, RB = 330k and the transistor has dc = 150, what are the values of IC and VCE. 5. The biased circuit in Figure 6 is called ‘emitter-bias’. Show that the collector current is almost independent on dc. Show that VCE VCC - ICRC. If VCC = +20V, RC = 2.2k, RE = 3.9k, RB = 5.1k, find IC and VCE. +VCC RC RB -VEE Fig. 6