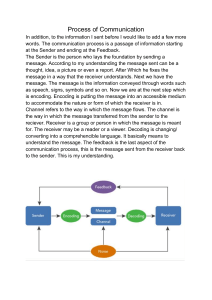
COMMUNICATIO N PREPARED BY: Sahad 1|Page TABLE OF INDEX PAGE 3 INTRODUCTION 03 Description of Topic of Study 03 Significance of Topic of Study 03 Overview of Research Strategies 03 PAGE 4 TO 7 PRESENTAION 04-07 What Is Communication 04 Types Of Communication 04 Communication Process 05 Communication Systems 06-07 PAGE 6 2|Page CONCLUSION 08 INTRODUCTION This topic gives you an overview of communication and introduces you to the main elements in the communication process. It also highlights the importance of writing clear, positive messages and offers you some basic tips and guidelines on this form of communication so that you may become more proficient in the kind of writing needed at home as well as in the college and workplace. You will also learn about some of the common pitfalls which may impede the effectiveness of written communication. Communication meaning has changed drastically throughout only a couple of years since the advent of technology. Earlier communication meant having to converse about feelings, emotions, views, and ideas all while sitting before one another or in a group. With technology, one can communicate via email where one can send a message to an entire group. The influx of smartphones has brought about an entirely different culture of communication. Smartphones have cameras that make it easier to communicate via video calls and conference calls between a group of people are also possible today. This generation of millennials is also adapting to social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram for business and personal communication as well. However, with the rapid changes in technology the fact that only good communication will get the job done remains unchanged. Before understanding the ways to better communicate with others we should understand the parts and types of communication. 3|Page PRESENTATION What is Communication? Communication is a process that involves sending and receiving of messages through a verbal and non-verbal method. The sender sends a message, the receiver receives a message and sends it back with the feedback to the sender again. Types of Communication The four main categories of communication are Verbal – It is a method that uses speech in the form of speaking to convey a message or information. It is the most popular and effective mode of communication, usually practiced during video conferences, phone calls, presentations, one-on-one conversations, and meetings. It supports both nonverbal and written communication. Nonverbal – It is basically a practice of gestures, facial expressions, and body language to send information. It can be implemented intentionally and unintentionally when communicating. For instance, a person can smile unintentionally when they hear an interesting piece of information or a pleasant idea. Written – It is all about typing, printing symbols, numbers, letters, and writing to send a piece of information. Sometimes used to record information for evidence or reference purpose. In general, the written style of communication is used in books, blogs, pamphlets, memos, and letters to share and spread information. In the workplace, e-mail is a common example of written communication. Visual – It uses art, photographs, sketches, graphs, charts, and drawings, to pass on the information. It is used especially during presentations to 4|Page present to give a visual effect and support written or verbal communication. Communication Process The communication is a process that starts with the development of thoughts by a sender who conveys the message using a various channel to the receiver, who then sends him a message as feedback. There are seven main components of the communication process: Sender – Here, the sender conceptualizes the idea or the conversation he wants to convey it to the recipient. Encoding – Now the sender starts the encoding process where he utilizes words or non-verbal means to translate the thought into a message. Message – After encoding, the sender receives the message that he wants to send. Communication Channel – The sender then decides through which medium or channel he/she wants to send the message to the recipient. They must choose the channel to have an effective and correct interpretation of a message to the recipient. Receiver – The receiver receives the message and tries to comprehend in the best possible way. Decoding – In this step, the receiver translates the sender’s information and tries to perceive it most suitably. Feedback – It is the last step of the communication process that assures the recipient, has received the information and understood correctly as the sender designed it. 5|Page Communication Systems The communication system is a system which describes the information exchange between two points. The process of transmission and reception of information is called communication. The major elements of communication are the Transmitter of information, Channel or medium of communication and the Receiver of information. Types Of Communication Systems Depending on Signal specification or technology, the communication system is classified as follows: (1) Analog Analog technology communicates data as electronic signals of varying frequency or amplitude. Broadcast and telephone transmission are common examples of Analog technology. (2) Digital In digital technology, the data are generated and processed in two states: High (represented as 1) and Low (represented as 0). Digital technology stores and transmits data in the form of 1s and 0s. 6|Page Depending on the communication channel, the communication system is categorized as follows: 1. Wired (Line communication) Parallel wire communication Twisted wire communication Coaxial cable communication Optical fiber communication 2. Wireless (Space communication) Ground wave communication Skywave communication Space wave communication Satellite communication Examples Of Communication Systems The following are a few examples of communication systems: 1. Internet 2. Public Switched Telephone network 3. Intranet and Extranet 4. Television 7|Page In this chapter we have reviewed why effective communication matters to organizations. Communication may break down as a result of many communication barriers that may be attributed to the sender or receiver. Therefore, effective communication requires familiarity with the barriers. Choosing the right channel for communication is also important, because choosing the wrong medium undermines the message. When communication occurs in the cross-cultural context, extra caution is needed, given that different cultures have different norms regarding nonverbal communication, and different words will be interpreted differently across cultures. By being sensitive to the errors outlined in this chapter and adopting active listening skills, you may increase your communication effectiveness. 8|Page