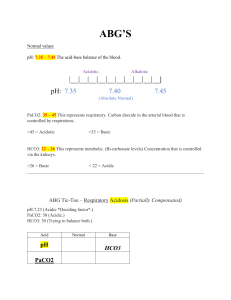
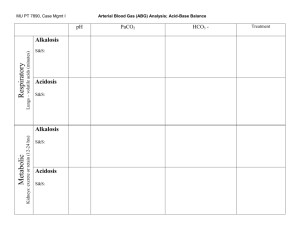
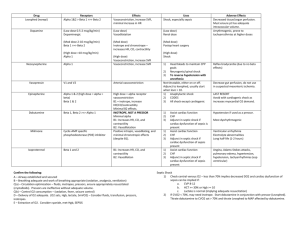
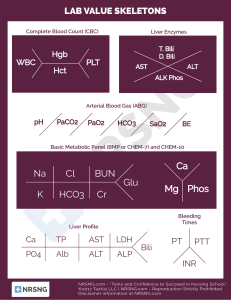
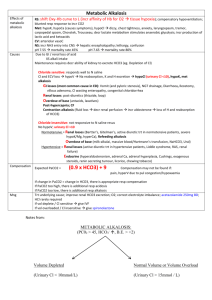
Let’s Play…. Values: pH (acid): < 7.35 pH (normal): 7.35 – 7.45 pH (base): > 7.45 ABG Tic-Tac-Toe PaCO2 (acid): PaCO2 (normal): PaCO2 (base): > 45 35 – 45 < 35 ABG values: pH______________ PaCO2__________________ Acid/Normal/Base: pH_________ PaCO2__________________ HCO3 (acid): HCO3 (normal): HCO3 (base): < 22 22 – 26 > 26 HCO3_____________________ HCO3_____________________ Now plug in your values: Acid Normal Base (Alkaline) pH PaCO2 HCO3 RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS: Respiratory acidosis uncompensated: Respiratory acidosis partially compensated: Respiratory acidosis totally compensated: pH acid () pH acid () pH normal PaCO2 acid () PaCO2 acid () PaCO2 acid () HCO3 normal HCO3 base () HCO3 base () RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS: Respiratory alkalosis uncompensated: Respiratory alkalosis partially compensated: Respiratory alkalosis totally compensated: pH base () pH base () pH normal PaCO2 base () PaCO2 base () PaCO2 base () HCO3 normal HCO3 acid () HCO3 acid () METABOLIC ACIDOSIS: Metabolic acidosis uncompensated: Metabolic acidosis partially compensated: Metabolic acidosis totally compensated: pH acid () pH acid () pH normal PaCO2 normal PaCO2 base () PaCO2 base () HCO3 acid () HCO3 acid () HCO3 acid () METABOLIC ALKALOSIS: Metabolic alkalosis uncompensated: Metabolic alkalosis partially compensated: Metabolic alkalosis totally compensated: pH base () pH base () pH normal PaCO2 normal PaCO2 acid () PaCO2 acid () HCO3 base () HCO3 base () HCO3 base () Interpretation: Uncompensated: pH and one other value (either PaCO2 or HCO3) are abnormal. Abnormal pH determines whether acidosis or alkalosis. Abnormal PaCO2 or HCO3 determines whether respiratory or metabolic. PaCO2 abnormal = respiratory; HCO3 abnormal = metabolic. Partial compensation: all values are abnormal. Two values “agree” (pH and either PaCO2 or HCO3 are BOTH acid or BOTH base), and the remaining value (either PaCO2 or HCO3) is the OPPOSITE of the pH. The value (PaCO2 or HCO3) that “agrees” with the pH is correct (determines whether respiratory or metabolic). Compensation: pH is normal, both PaCO2 and HCO3 are abnormal. One will be acidotic, the other base. The value that most closely matches the pH identifies the true (underlying) state. If the fully compensated pH is between 7.35-7.40, then the normal pH is closer to the acid end and the acidotic value (either PaCO2 or HCO3) is correct. If the pH is between 7.40-7.45, then the normal pH is closer to the alkalotic end and the base value (either PaCO2 or HCO3) is correct. Acid-Base Interpretation Table Values Acid Respiratory acidosis uncompensated pH PaCO2 HCO3 pH PaCO2 HCO3 pH PaCO2 HCO3 Respiratory alkalosis totally compensated pH PaCO2 HCO3 Metabolic acidosis uncompensated pH PaCO2 HCO3 Metabolic acidosis partially compensated pH PaCO2 HCO3 Metabolic acidosis totally compensated pH PaCO2 HCO3 Metabolic alkalosis uncompensated X Acid pH PaCO2 HCO3 X Normal Base Normal Base X X Acid Normal Base X X X Acid Normal Base X X X Acid Normal Base X X X Acid Normal Base X X Normal X Base X X Acid Metabolic alkalosis totally compensated X Base X Acid pH PaCO2 HCO3 Normal X X pH PaCO2 HCO3 Metabolic alkalosis partially compensated X Base X X Acid pH PaCO2 HCO3 Normal X pH PaCO2 HCO3 Respiratory alkalosis partially compensated Base X Acid Respiratory alkalosis uncompensated X Normal X X Acid Respiratory acidosis totally compensated Base X X Acid Respiratory acidosis partially compensated Normal Normal X Base X X X