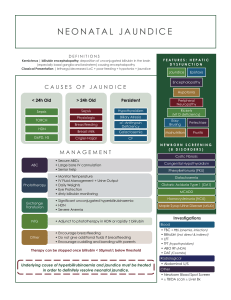
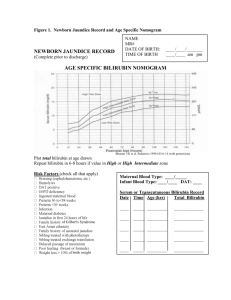
BILIRUBIN DETERMINATION (TOTAL, CONJUGATED AND UNCOJUGATED) JAMES ERRAN A. ALMODOVAR, RMT ACTIVITY DETERMINATION Evelyn-Malloy Modified Method Bile pigment is formed from the breakdown of hemoglobin molecule. It is the end product of hemoglobin metabolism and the principal pigment in bile. When initially formed, bilirubin is insoluble in water. This molecule must be carried through the circulation bound to albumin. This is called unconjugated bilirubin. When the protein/bilirubin complex reaches the liver, bilirubin passes into the liver cells where it is converted by UDP (uridine diphosphate)-glucoronyl tranferse. The formation of glucuronic conjugate now makes the bilirubin complex soluble in water. This is now the conjugated bilirubin that can be excreted in the bile and into the intestine. There are two forms of bilirubin that can exist in serum: conjugated, the major component of so called direct bilirubin (B2), and unconjugated bilirubin which is the major component of indirect bilirubin (B1). Bilirubin is measured by conjugating it to an appropriate diazonium salt, most often diazotized sulfanilic acid. This is known as the van den Bergh method. Bile - Comprises bile acids or salts, cholesterol and other substance extracted from the blood - It is intimately involved in the digestion and absorption of lipids - Primary bile acids: Cholic acid, Chenodeoxycholic acid - Bile salts – conjugated bile acids Bilirubin - principal pigment of the bile - 200-300 mg is produced daily - Derived mainly from the breakdown of hemoglobin (80%) - Also derived a small amount from myoglobin, catalase (20%) Indirect Bilirubin (B1) - Uncojugated bilirubin (attached to abumin) - Water insoluble - Pre- hepatic bilirubin Conjugation (esterification) - Enzyme Uridyldiphosphate Glucoronyl Transferase (UDP-T), converts bilirubin 1 into bilirubin diglucuronide ester (bilirubin 2). Direct Bilirubin - Conjugated bilirubin - Water soluble - Post hepatic bilirubin - Direct bilirubin is secreted into the bile ducts to intestine - In the colon, bilirubin is acted upon by the enzymes of intestinal bacteria - The 1st product is mesobilirubin mesobilirubinogen Urobilinogen (colorless). - The oxidation of urobilinogen produces the red-brown pigment Urobilin, which is excreted in the stool (Stercobilin). Delta Bilirubin – Bilirubin bound to protein, seen in bile duct obstruction. Jaundice (Icterus) – yellowish pigmentation of the skin or sclera. Prehepatic Jaundice - Excessive amount of bilirubin is presented to the liver for metabolism - “Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia” - Serum bilirubin rarely exceeds 5 mg/dL (liver is capable handling overload) - Ex. Hemolytic Anemia Hepatic Jaundice - More common type of jaundice - Gilbert Syndrome – impaired cellular uptake of bilirubin (impaired bilirubin transport). Increased B1, Normal B2 - Crigler-Najjar Syndrome – deficiency of the enzyme UDP-T - Dubin-Johnson Syndrome – hereditary disorder, defective excretion of bilirubin, “Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia”, lipofuscin positive. - Rotor Syndrome – hereditary disorder, commonly results from a viral infection, defective excretion of bilirubin, “Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia”, lipofuscin negative. Hepatic Jaundice - Lucey-Discroll Syndrome – there is conjugation inhibition, there is UDP-T but inhibits its reaction. (may due to genetic change in the UGT1A1 gene). Posthepatic Jaundice - Result from impaired excretion of bilirubin caused by mechanical obstruction of the flow of bile into the intestine. - Elevated Conjugated Bilirubin - Stool becomes “clay-colored” (loses uribilin pigmentation) - Urine findings: Conjugated bilirubin appears in the urine, Urine Urobilinogen is decreased. Principle: The procedure is based on the reaction of Diazo reagent. Which reacts with bilirubin to produce a colored chromophore. The diazotized sulfanilic acid reacts with bilirubin to form two molecules of azobilirubin. One molecule of bilirubin splits to produce two molecules of azobilirubin. The diazo product has a reddish-purple color in an acid pH with an absorption maximum in the region of 560 nm. Methanol serves as dissociating agent and will accelerate the diazotization reaction of unconjugated or direct bilirubin. Specimen: Strictly covered unhemolyzed serum, not lipemic and fasting serum. Reagents: Bilirubin reagent, Absolute methyl alcohol, Bilirubin accelerator (refrigerated). Procedure: Direct (Conjugated) Bilirubin Reagents Test/ Control Test/Control 0.2 mL Bilirubin Rgt 2.8 mL Bilirubin Accelerator 3 dorps Mix well. Stand for exactly one minute at room temperature then read %T and Absorbance against water blank at 550 nm. The absorbance has a logarithmic relationship to the transmittance; with an absorbance of 0 corresponding to a transmittance of 100% and an absorbance of 1 corresponding to 10% transmittance. Procedure: Total Bilirubin Use the same test tube (or mixture from the direct (conjugated) bilirubin). Reagent Test/Control Absolute Methyl Alcohol 3 mL Mix well. Stand for exactly five minutes at room temperature then read %T and absorbance against water blank at 550 nm. Calibration or Standardization Transfer the bilirubin calibrator directly into the cuvette and read %T and Absorbance against water blank at 550 nm. Calculation of Results Direct Bilirubin Value of test = Absorbance of Test / Absorbance of the standard multiplied by the Value of the Standard (Calibrator) X 17.10 =umol/L Calculation of Results Total Bilirubin Value of test = Absorbance of Test / Absorbance of the standard multiplied by the Value of the Standard (Calibrator) X 17.10 =umol/L Calculation of: Indirect Bilirubin Total Bilirubin – Direct Bilirubin = Indirect Bilirubin Reference range (Henry, 21st Ed.) Bilirubin Conventional Factor SI unit Direct <0.3 mg/dL 17.10 <5 umol/L Indirect 0.1 - 1 mg/dL 17.10 2-17 umol/L Total 0.1 – 1.2 md/dL 17.10 2-21 umol/L Newborns (total) 1.0 – 12 mg/dL 17.10 17-205 umol/L Methods: 1. Evelyn and Malloy - Diazo reagent: Diazotized Sulfanilic Acid - Coupling accelerator (dissociating rgt) : Methanol - ( + ) Pink/Red to purple azobilirubin - Uses ascorbic acid to stop reaction 2. Jendrassik and Groff - Most sensitive and widely used (discrete analyzers) - Coupling accelerator (dissociating rgt): Caffeine Sodium Benzoate - Buffer: Sodium Acetate - ( + ) Blue azobilirubin Nice to know: - Conjugated Bilirubin directly reacts with the Van den Bergh reaction - Unconjugated Bilirubin produces a color after alcohol is added to couple with diazo reagent. - For direct bilirubin comparison used in Muelengracht method with NSS is potassium dichromate - 0.01% potassium dichromate solution is the standard used in icterus index.