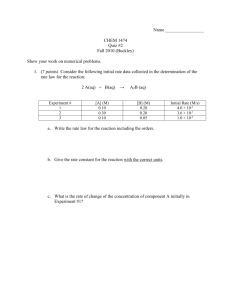
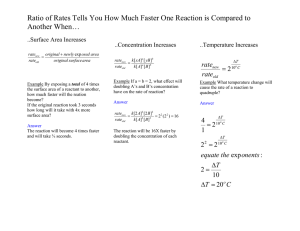
Chemical Kinetics Practice question set 1 1) Given the following balanced equation, determine the rate of reaction with respect to [O2]. 2 SO2 (g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) 1 Δ[O 2 ] 2 Dt 1 Δ[O 2 ] B) Rate = 2 t Δ[O 2 ] C) Rate = Dt 2 Δ[O 2 ] D) Rate = t E) It is not possible to determine without more information. A) Rate = 2) Given the following balanced equation, determine the rate of reaction with respect to [SO3]. 2 SO2 (g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) 1 Δ[SO3 ] 2 Dt 1 Δ[SO3 ] B) Rate = 2 t Δ[SO3 ] C) Rate = Dt 2 Δ[SO3 ] D) Rate = t E) It is not possible to determine without more information. A) Rate = 3) Write a balanced reaction for which the following rate relationships are true. Rate = 1 Δ[N 2 ] Δ[O 2 ] 1 Δ[N 2O] = = 2 t t 2 t 1 1 N2 + O2 → N2O 2 2 B) 2 N2O → 2 N2 + O2 C) N2O → N2 + 2 O2 1 1 D) N2O → N2 + O2 2 2 E) 2 N2 + O2 → 2 N2O A) 4) Given the following balanced equation, determine the rate of reaction with respect to [NOCl]. If the rate of Cl2 loss is 4.84 × 10-2 M/s, what is the rate of formation of NOCl? 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2 NOCl(g) A) 4.84 × 10-2 M/s B) 2.42 × 10-2 M/s C) 1.45 × 10-1 M/s D) 9.68 × 10-2 M/s E) 1.61 × 10-2 M/s 5) Give the characteristic of a first order reaction having only one reactant. A) The rate of the reaction is not proportional to the concentration of the reactant. B) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of the reactant. C) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square root of the concentration of the reactant. D) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the natural logarithm of the concentration of the reactant. E) The rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant. 6) Give the characteristic of a zero order reaction having only one reactant. A) The rate of the reaction is not proportional to the concentration of the reactant. B) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of the reactant. C) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square root of the concentration of the reactant. D) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the natural logarithm of the concentration of the reactant. E) The rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant. 7) Give the characteristic of a second order reaction having only one reactant. A) The rate of the reaction is not proportional to the concentration of the reactant. B) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of the reactant. C) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square root of the concentration of the reactant. D) The rate of the reaction is proportional to the natural logarithm of the concentration of the reactant. E) The rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant. 8) What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate law? 2X+3Y → 2Z Rate = k[X]1[Y]2 A) 3rd order B) 5th order C) 2nd order D) 1st order E) 0th order 9) What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate law? X+2Y →4Z Rate = k[X][Y] A) 3rd order B) 5th order C) 2nd order D) 1st order E) 0th order 10) What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate law? NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) Rate = k[NO][O3] A) 1st order B) 2nd order C) 3rd order 1 D) 1 order 2 E) 0th order 11) What are the units of k in a zero order reaction? M A) s B) Ms C) M-1s-1 M2 D) s s E) M2 12) Given the following rate law, how does the rate of reaction change if the concentration of Y is doubled? Rate = k [X][Y]2 A) The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 2. B) The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 4. C) The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 5. D) The rate of reaction will decrease by a factor of 2. E) The rate of reaction will remain unchanged. 13) Given the following rate law, how does the rate of reaction change if the concentration of X is doubled? Rate = k [X][Y]2 A) The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 2. B) The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 4. C) The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 5. D) The rate of reaction will decrease by a factor of 2. E) The rate of reaction will remain unchanged. 14) What data should be plotted to show that experimental concentration data fits a zeroth-order reaction? A) ln[reactant] vs. time B) 1/[reactant] vs. time C) ln(k) vs. 1/T D) ln(k) vs. Ea E) [reactant] vs. time 15) Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The average rate of a reaction decreases during a reaction. B) It is not possible to determine the rate of a reaction from its balanced equation. C) The rate of zero order reactions are not dependent on concentration. D) The half life of a first order reaction is dependent on the initial concentration of reactant. E) None of the statements are FALSE.