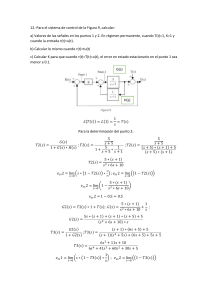
Hoja de referencia de probabilidad: distribuciones y conceptos
advertisement

Probability Cheat Sheet
Poisson Distribution
Distributions
notation
Unifrom Distribution
notation
U [a, b]
cdf
x
b
k
X
e
cdf
pmf
1
for x 2 [a, b]
b a
1
expectation
(a + b)
2
1
variance
(b a)2
12
etb eta
mgf
t (b a)
story: all intervals of the same length on the
distribution’s support are equally probable.
k!
Gamma Distribution
Gamma (k, ✓)
notation
✓ k xk
1e
(k)
Z
(k) =
pdf
✓x
1
k✓
variance
k 1
x
e
dx
i=1
ind. sum
n
X
i=1
k
for t <
Xi ⇠ Gamma
1
✓
n
X
ki , ✓
i=1
!
story: the sum of k independent
exponentially distributed random variables,
each of which has a mean of ✓ (which is
equivalent to a rate parameter of ✓ 1 ).
Geometric Distribution
notation
G (p)
cdf
1
pmf
(1
p)k
1
p
1
p
(1
p
p for k 2 N
pet
1 (1 p) et
story: the number X of Bernoulli trials
needed to get one success. Memoryless.
mgf
1
2⇡
2
e
✓
mgf
exp µt +
ind. sum
n
X
1
2
fX,Y (s, t) dsdt
ZBx Z y
FX,Y (x, y) =
fX,Y (s, t) dtds
1
1
Z 1 Z 1
fX,Y (s, t) dsdt = 1
1
Marginal Distributions
PX (B) = PX,Y (B ⇥ R)
PY (B) = PX,Y (R ⇥ Y )
Z a Z 1
FX (a) =
fX,Y (s, t) dtds
1
1
Z b Z 1
FY (b) =
fX,Y (s, t) dsdt
1
Marginal Densities
fX (s) =
fY (t) =
Z
Z
1
1
1
1
fX,Y (s, t)dt
fX,Y (s, t)ds
Joint Expectation
E (' (X, Y )) =
ZZ
R2
1
(x) = p
2⇡
2
1
p e x /2
2⇡
1
P (X x, Y y) = P (X x) P (Y y)
FX,Y (x, y) = FX (x) FY (y)
fX,Y (s, t) = fX (s) fY (t)
E (XY ) = E (X) E (Y )
Var (X + Y ) = Var (X) + Var (Y )
Independent events:
P (A \ B) = P (A) P (B)
Conditional Probability
P (A \ B)
P (B)
P (B | A) P (A)
bayes P (A | B) =
P (B)
P (A | B) =
µi ,
n
X
2
i
i=1
!
Z
x
e
t2 /2
dt
1
2
⇠ exp
minimum
✓
2◆
story: the amount of time until some specific
event occurs, starting from now, being
memoryless.
notation
Bin(n, p)
cdf
k ⇣ ⌘
X
n
i
1
mgf
1
1
1
\
1
[
P (lim sup An ) = lim P
n!1
P (lim inf An ) = lim P
n!1
1
\
m=1 n=m
An
n=m
1
\
An
n=m
Borel-Cantelli Lemma
1
X
P (An ) < 1 ) P (lim sup An ) = 0
p + pe
t n
lim P (|Xn
n!1
X| > ") = 0
Var (X)
n!1
X| ) = 0
p
!
)
p
Laws of Large Numbers
strong law
p
Xn ! E (X1 )
Xn
a.s.
! E (X1 )
Sn nµ D
! N (0, 1)
p
n
If ✓
tn ! t, then ◆
Sn nµ
P
tn !
p
n
t2 /2
(t)
1
X
1
X
n=0
P (Y > n) < 1 (Y
0)
P (X > n) (X 2 N)
ln X ⇠ exp (1)
Convolution
D
!
If Xn ! c then Xn ! c
p
If Xn ! X then there exists a subsequence
a.s.
nk s.t. Xnk
!X
weak law
Var (X)
"2
for ' a convex function, ' (E (X)) E (' (X))
X ⇠ U (0, 1) ()
!
+
D
")
Jensen’s inequality
n=0
Lp
)
E (X)|
P (X E (X) > t (X)) < e
Simpler result; for every X:
P (X a) MX (t) e ta
E (X) =
)
E (|X|)
t
E (Y ) < 1 ()
p
n!1
q>p 1
t)
Miscellaneous
!X
Relationships
!
Inequalities
Let X ⇠ Bin(n, p); then:
Lp
lim E (|Xn
a.s.
⇣
⌘
MX (t) = E etX
Cherno↵ ’s inequality
Convergence in Lp
!
Cov (X, Y )
X, Y
Moment Generating Function
P (|X
n!1
meaning
E (Y )))
Chebyshev’s inequality
a.s.
Xn
!X
⇣
⌘
P lim Xn = X = 1
Xn
E (x)) (Y
Var (X + Y ) = Var (X) + Var (Y ) + 2Cov (X, Y )
P (|X|
lim Fn (x) = F (x)
notation
E (X) E (Y )
Cov (X, Y ) = E ((X
Markov’s inequality
D
Xn ! X
Central Limit Theorem
meaning
p
(n)
Convergence
Xn ! X
(E (X))2
⌘
E (X))2
MaX+b (t) = etb MaX (t)
d
FX (x)
dx
fX (x) =
n=1
notation
g (x) fX xdx
E (X n ) = MX (0)
If Xi are i.i.d. r.v.,
p
1
Covariance
Z 1
FX (x) =
fX (t) dt
1
Z 1
fX (t) dt = 1
And if An are independent:
1
X
P (An ) = 1 ) P (lim sup An ) = 1
Convergence in Probability
1
⇢X,Y =
1
FX (t)) dt
xfX xdx
Correlation Coefficient
!
!
(1
Comulative Distribution Function
Lq
1
[
Z
1
0
E (aX + b) = aE (X) + b
(X) =
p)
• 8"9N 8n > N : P (|Xn X| < ") > 1 "
• 8"P (lim sup (|Xn X| > ")) = 0
1
X
• 8"
P (|Xn X| > ") < 1 (by B.C.)
An
1
E (g (X)) =
Z
Var (aX + b) = a2 Var (X)
i
n=1
m=1 n=m
1
[
lim inf An = {An eventually} =
lim inf An ✓ lim sup An
(lim sup An )c = lim inf Acn
(lim inf An )c = lim sup Acn
p)n
Criteria for a.s. Convergence
An
1
FX (t) dt +
Basics
meaning
lim sup An = {An i.o.} =
Z
1
Cov (X, Y ) = E (XY )
notation
Sequences and Limits
X ⇤ (p)dp
0
Var (X) = E X 2
⇣
Var (X) = E (X
i
Almost Sure Convergence
E (E (X | Y )) = E (X)
P (Y = n) = E (IY =n ) = E (E (IY =n | X))
1
0
story: the discrete probability distribution of
the number of successes in a sequence of n
independent yes/no experiments, each of
which yields success with probability p.
meaning
xfX|Y =y (x) dx
Z
Standard Deviation
np (1
Conditional Expectation
Z
p)n
pi (1
pi (1
Z
Variance
np
variance
notation
1
n=1
i
⇣n⌘
E (X) =
E (X) =
Convergence in Distribution
fX,Y (x, y)
fY (y)
fX (x) P (Y = n | X = x)
fX|Y =n (x) =
P (Y = n)
Z x
FX|Y =y =
fX|Y =y (t) dt
E (X | Y = y) =
i
i=1
!
Probability Density Function
t
2
story: normal distribution with µ = 0 and
= 1.
exp
mgf
k
X
FX (x) = P (X x)
1
variance
Xi ⇠ Gamma (k, )
i=1
expectation
i=1
N (0, 1)
' (x, y) fX,Y (x, y) dxdy
Independent r.v.
t
n
X
Xi ⇠ N
fX|Y =y (x) =
ZZ
2 2
◆
Standard Normal Distribution
pdf
t
Binomial Distribution
story: describes data that cluster around the
mean.
cdf
E (X ⇤ ) = E (X)
E (X) =
i=0
Conditional Density
Joint Density
ind. sum
pmf
i=1
FX ⇤ = FX
Expectation
k
X
(x µ)2 /(2 2 )
PX,Y (B) = P ((X, Y ) 2 B)
FX,Y (x, y) = P (X x, Y y)
1
i=1
0
0
2
Joint Distribution
1
i
2
expectation
p2
PX,Y (B) =
n
X
!
µ
notation
p)k for k 2 N
1
1
Xi ⇠ P oisson
N µ,
variance
✓t)
et
story: the probability of a number of events
occurring in a fixed period of time if these
events occur with a known average rate and
independently of the time since the last event.
expectation
(1
variance
n
X
pdf
0
2
mgf
expectation
ind. sum
notation
k✓
expectation
exp
for x
for x
2
mgf
Normal Distribution
Ix>0
x
mgf
x
1
variance
variance
The function ⇣
X ⇤ : [0, 1]⌘! R for which for any
p 2 [0, 1], FX X ⇤ (p)
p FX (X ⇤ (p))
1
expectation
expectation
pdf
x
e
e
pdf
for k 2 N
·e
1
cdf
i!
Quantile Function
exp ( )
notation
i
i=0
k
a
for x 2 [a, b]
a
Exponential Distribution
P oisson ( )
For ind. X,
Y, Z =X +Y:
Z 1
fZ (z) =
fX (s) fY (z s) ds
1
Kolmogorov’s 0-1 Law
If A is in the tail -algebra F t , then P (A) = 0
or P (A) = 1
Ugly Stu↵
cdf of Gamma distribution:
Z
t ✓ k xk 1 e ✓k
dx
(k 1)!
0
This cheatsheet was made by Peleg Michaeli in
January 2010, using LATEX.
version: 1.01
comments: peleg.michaeli@math.tau.ac.il