ISEN 310: Uncertainty Modeling for IE
Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
Texas A&M University
Fall 2023
Petar Momčilović
petar@tamu.edu
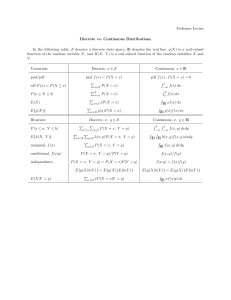
Expectation
Expectation
*
I E[X] is a number:
EX =
I Examples
(P
Reiki
x pX (x)
1 x fX (x) dx
R 1x
I Geometric X
I Exponential X -
I Geometry
*N1
,
I Random variable X
if X discrete
if X continuous
bat
2
Expectation of g(X)
g(X) Y
#g(X) EY
=
I Random variable X
=
I Function g
likelihood
I Random g(X)
E[g(X)] =
value
g(x) p (x)
(P
R 1x
1 g(x) fX (x) dx
I Examples
I E[X k ]: kth moment
I k = 1: mean
I E[(X
X
if X discrete
if X continuous
x
EX)k ]: kth centered moment
I k = 2: variance
I E[esX ]: moment generating function (MGF)
-
Expectation = Integral
/xx =() xxx)2
Saxdx
I In general
I Expectation is linear
Eg(X) 6= g(EX)
((=x b) &x
+
d
E[ag(X)] = aE[g(X)]
E[g(X) + h(X)] = Eg(X) + Eh(X)
I Variance
I Motivation
I Var(X) = E[X 2 ] (EX)2
I Example: Bernoulli r.v.
I Properties
Example
buy x amountprofit--ex+p min2x D3
-
E profit
I Newsvendor model
=
,
D1]
EL-4x
I Buy items for $c per unit
I Sell items for $p per unit
I Random demand D: CDF FD
I Maximize expected profit
I Optimal order quantity
,
qxD3
=
Elg
max E[g (D)]
,
Moment Generating Function
-
I
&
I MX (s) = E[esX ]
I Moments
Ms
-M
mi Is EX
M's -- EE(X]
I Examples
I Geometric r.v.
I Exponential r.v.
I MX (s) = 41 e 3s + 12 e2s + 14 e5s
ElesX]
:.
E
-
P(X 3) 4
5)
4(X 2) 1/2 4(X
=
-
=
=
E es D(=x )
:
*
E(Xes ]
*=
"
I MGF $ CDF
->
1E[-X es]
=
:
=
=
=
i
Expectation of g(X, Y )
I Random variables X and Y
(P
m
g(x,
y) pX,Y (x, y)
E[g(X, Y )] = R 1x
1 g(x, Y ) fX,Y (x, y) dx
vahie Likelihood
if (X, Y ) discrete
if (X, Y ) continuous
I Example: E[max{X, Y }] with X and Y random samples from
{1, 2, . . . , 310} without replacement
Covariance and Correlation
Cor(X X)
,
=
Var(X)
I Random variables X and Y
a number
Cov(X, Y ) = E[(X EX)(Y EY )] -Cov(X, Y )
- -1 , 1]
-> ⇢ = p
Var(X) Var(Y )
I Uncorrelated 6= Independent
I Example: Disk
I Data
I
Expectation = Integral
I Linearity
E[g(X) + h(Y )] = E[g(X)] + E[h(Y )]
en
I Even if X and Y are not independent E
F
I Example: Hypergeometric distribution
I n objects: k of them are faulty
I Goal: estimate k
I Sample m objects at random without replacement
I X = number of faulty objects in the sample
-
Total Expectation
I Conditional expectation (on an event)
~likelihood
(PValue
xp
(x)
E[X | A] = R 1x X|A
1 x fX|A (x) dx
if X discrete
if X continuous
I Events B1 , B2 , . . .: Bi \ Bj = ; and [i Bi = ⌦
I Total Expectation Theorem:
EX =
X
E[X | Bi ] P[Bi ]
M
I
/
B3
i
-
Examples
EX
/
I Geometric r.v.
I Branching process
:
1
.
definitio
I MGF
.
3
.
-
Conditional Expectation
I Event {Y = y}
-
value
d
Likelihood
(P Ne
xp
(x|y)
E[X | Y = y] = h(y) = R 1x X|Y
2
1 x fX|Y (x|y) dx
A
if X discrete
if X continuous
/
*
rv
I Random variable (!)
/
.
E[X | Y ] = h(Y )
->
-
-
-K
I Iterated expectation
vondim
variable
tower
-
E[X] = E[E[X | Y ]]
/
a
-
property
- -
Examples
I Stick
I Insurance claims
-
Sum of Independent R.V.s
I Recall: Independent r.v.s X and Y
FX,Y (x, y) = FX (x) FY (y)
I Implication
E[g(X) h(Y )] = E[g(X)] E[h(Y )]
en
I Examples
I Var(X + Y )
I Cov(X, Y )
MGF of a Sum
I Independent r.v.s X and Y
I MGF
dif
-get
MX+Y (s) = E[es(X+Y ) ] = E[esX esY ] = E[esX ] E[esY ]
-
I Example: Normal r.v.s
y My
MGF of a Random Sum
I Independent, identically distributed X1 , X2 , . . .
I N : r.v. independent of X1 , X2 , . . .
I Sum
S=
N
X
L
Xi
i=1
I MGF
definiti
⇥ ⇤
e Eles]
MS (s) = E esS
⇥
⇤
= E E[esS | N ]
⇥
⇤
= E (MX (s))N
MNs)
e
I Algorithm
I Find MX (s)
I Replace es by MX (s) in MN (s)
E([esN]
=
-
Examples
C
S
I Example 1
I Xi : exponential
I N : geometric
O
I Example 2
I Xi : geometric
I N : geometric
- >
=
NX
E
O
~exp
.
:
exercise