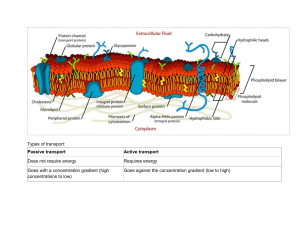
CHAPTER 3 MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF THE CELLS QUESTIONS 1 Look at the definition of diffusion in the Key words box. Explain what each of these words in the definition means: a. net movement b. concentration gradient c. random movement ANS: a. net movement – the overall result of some particles moving one way, but more moving in the other direction. b concentration gradient – a difference in concentration between two solutions; the gradient ‘slopes down’ from the high concentration to the lower concentration. c random movement – movement in any direction, just by chance. 2 When substances diffuse into and out of cells, which part of the cell must they move through? ANS: cell membrane 3 Describe three examples of diffusion in organisms. For each example, state whether the substance that is diffusing is a gas or a solute. ANS: Any three from (or other correct examples): • oxygen gas diffusing from outside a cell to inside • carbon dioxide gas diffusing from inside a cell to outside • oxygen gas diffusing from inside a photosynthesising cell to outside • carbon dioxide gas diffusing from outside a photosynthesising cell to inside • glucose or other solutes diffusing through the cytoplasm of a cell. 4 Where does the energy for diffusion come from? ANS: the kinetic energy of the particles 5 Using what you know about how diffusion happens, explain each of these statements: a Diffusion happens faster at higher temperatures. b The greater the difference in concentration between two solutions, the faster diffusion happens. c In a kidney dialysis machine, many small tubes containing dialysis fluid are used, rather than one big one d. In a kidney dialysis machine, the membrane separating the blood and the dialysis fluid is very thin. ANS: a At higher temperatures, particles have more kinetic energy and move faster. b The greater the diffusion gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion. c Many small tubes have a larger surface area than a single large tube, which speeds up diffusion. d This decreases the distance across which the particles have to travel, to get from the blood into the dialysis fluid, so it takes them less time. These questions are about the diagram in Figure 3.4 6 What is the solvent in the sugar solution? What is the solute? ANS: Water is the solvent, and sugar is the solute. 7 Explain why water molecules can move from one side of the membrane to the other, but sugar molecules cannot. ANS: The water molecules are small enough to get through the holes in the membrane, but the sugar molecules are too big. 8 In which direction is the net movement of water molecules? ANS : From the dilute solution to the concentrated solution. 9 Where does the energy come from, to cause this movement? ANS: The kinetic energy of the water molecules. 10 In Figure 3.4, which solution has the higher water potential? Explain your answer. ANS: The dilute solution has the higher water potential because it contains more water molecules 11 Copy and complete this sentence: When an animal cell is placed in pure water, water __________________ the cell by ____________________ through the partially permeable cell ____________________. ANS: When an animal cell is placed in pure water, water enters the cell by osmosis through the partially permeable cell membrane. 12 Animal cells burst if they are placed in pure water, but plant cells do not. Explain why? ANS: Plant cells have a strong cell wall surrounding the cell membrane, which stops the cell bursting. 13 Here are some descriptions of what happens to a plant cell when it is placed in a concentrated solution. They are in the wrong order. Write the descriptions in the correct order. • The cytoplasm and vacuole shrink. • The cell membrane is pulled away from the cell wall. • Water moves out of the cell through the partially permeable cell membrane. ANS: • Water moves out of the cell through the partially permeable cell membrane. • The cytoplasm and vacuole shrink. • The cell membrane is pulled away from the cell wall. 14 Look at Figure 3.9. What fills space X? Explain your answer. ANS: The same solution that the cell is immersed in. The only thing between the external solution and space X is the cell wall, which is fully permeable. 15 A group of plant cells has been placed in a concentrated solution, and the cells are plasmolysed. Predict what will happen if the cells are now placed in pure water. Explain your answer, using the term water potential. ANS: The cells will take up water by osmosis because the water potential of the water outside the cell is greater than the water potential of the solution inside the cell. The vacuole and cytoplasm will increase in volume, so the cell membrane will be pushed back against the cell wall, into its normal position. EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS 1 Diffusion is a result of the movement of particles. How does each particle move? A down a concentration gradient B in one direction only C randomly D up a concentration gradient [1] 2 Where does the energy for diffusion come from? A glucose B kinetic energy of molecules and ions C respiration in mitochondria D sunlight [1] 3 Which change would increase the rate at which a substance diffuses across a membrane? A a decrease in concentration gradient B a decrease in the surface area of the membrane C an increase in distance across the membrane D an increase in temperature [1] 5 Which process involves active transport? A the uptake of carbon dioxide by a cell in a plant leaf B the uptake of magnesium ions by a root hair cell C the uptake of oxygen by an animal cell D the uptake of water by a root hair cell [1] 6 A learner investigated how temperature affected the rate at which a dye moved through a piece of agar jelly. She filled seven test-tubes with a solution of red dye. She placed each tube into a water-bath at a different temperature and left them for ten minutes. She cut seven cubes of jelly. She placed each cube into one of the tubes containing the red dye. She measured the time taken for the cubes to change colour. This graph shows her results. a Name and describe the process by which the dye moved through the jelly. b Suggest why the learner left the tubes of red dye in the water-baths for ten minutes. c List two variables that the learner should standardise (keep the same) in her experiment. d i One of the learner’s results is anomalous. Identify this result and explain why you think it is anomalous. ii Describe the trend or pattern shown by the results. iii Use your knowledge of diffusion to explain the results. 7 a Describe what is meant by osmosis. b Compare the effect of immersing an animal cell and a plant cell in pure water. Explain the reasons for any differences that you describe. 8 This bar chart shows the concentration of potassium ions and sodium ions in a sample of pond water, and in the cells of a plant growing in the water. a Describe the differences between the concentrations of the ions in the pond water and in the plant cells. [3] b Use the data in the graph to suggest how the ions move between the pond water and the plant cells. Explain your answer. c Describe how the process you have described in your answer to b takes place. [4] ANSWER Exam-style questions 1 C ; [1] 2 B ; [1] 3 D ; [1] 4 B ; [1] 5 B ; [1] 6 a diffusion [1] ; random movement of particles [1] ; down a concentration gradient [1] ; b to allow time for the dye solution to come to same temperature as the water bath ; [1] c Any two from: • the concentration of the dye solution ; • the volume of the dye solution ; • the volume of the jelly cubes ; • the surface area of the jelly cubes ; [Max. 2] d i the value at 20°C, time 4.5 minutes [1] ; because the time is shorter than the time at 30°C [1] ; ii As the temperature increases, the time to change colour decreases. [1] ; iii at higher temperatures, kinetic energy of particles increases [1] ; so, particles move faster / diffusion happens faster [1] ; 7 a • the net movement of water molecules [1] ; • from a higher water potential to a lower water potential / down a water potential gradient [1] ; • through a partially permeable membrane [1] ; b Any six from: • both take up water by osmosis ; • because there is a water potential gradient from outside the cell to inside ; • the volumes of both cells increase ; • the animal cell bursts but the plant cell does not ; • because the plant cell has a cell wall (but the animal cell does not) ; • the plant cell becomes turgid ; • as the contents of the cell push outwards on the cell wall ; • which is called turgor pressure ; [Max. 6] 8 a more potassium in the plant cells than in the water [1] ; more sodium in the water than in the plant cells [1] ; use of comparative figures [1] ; b active transport [1] ; if diffusion then concentrations in the cells and the water would be the same [1] ; c Any four from: • cells are using energy; • from respiration ; • to move potassium ions into the cell / move sodium ions out of the cell ; • against their concentration gradients ; • reference to transport proteins ; [Max. 4]