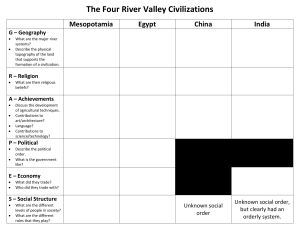
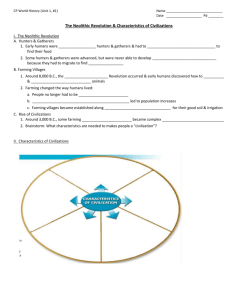
Unit 1: Ancient Civilizations Chapter 1: The Rise of Civilization Lesson 1: Early Humans Bellwork Notes: Prehistory - ________________= the time before writing was developed - ________________= the study of past societies through an analysis of the items people left behind - ________________= the study of human life and culture based on artifacts and human fossils - Dating Artifacts and Fossils - _________________ dating: All living things absorb radioactive carbon (C-14). After death, it slowly loses C-14. Scientists can measure how much C-14 an object has to determine the general age. - DNA has also helped provide information about the lifestyle and region Early Development - ____________= humans and other humanlike creatures that walk upright - ______________________ = a species that appeared in Africa 150,000 to 200,000 years ago. They were the ________ anatomically modern humans The Paleolithic Age aka ______________________ - The early period of human history (2,500,000 B.C. - 10,000 B.C.) when humans used simple stone tools - Hunter and ______________. They had to move to follow the __________ source - The main job of Paleolithic people was to find enough food - This group was the first to discover and use fire - Kept people warm, kept animals away from the campsite, cooked food (taste better, last longer, easier to chew and digest) - The Ice Age (10,000 B.C. - 8,000 B.C.) - Sea levels went down, people ______________ across land they couldn't before - Cave art Lesson 2: The Neolithic Revolution Bellwork Notes: Agricultural Revolution - Shift from hunting and gathering to _______________ animals and ______________food on a regular basis. - Humans began planting crops and domesticated animals for human use - With enough food, humans could then live in settled communities with each other. Neolithic Farming Villages - Found in _______________, _____________, Egypt, China, and ________________ - Jericho was the oldest known civilization by 8,000 B.C. - Catalhüyük the largest, 6700 B.C. - 5700 B.C. - Covered 32 acres with 6,000 people - Simple mud homes with few ________. People would walk on the ______of houses and entered through the rooftops. - They had a steady food supply that led to a ____________of food. - Not all people needed to farm → ___________________of labor Effects of the Neolithic Revolution - ________________ of labor - Systematic agriculture created _____________ positions - Men took over jobs that took them away from the home, like herding and farming - Women stayed behind in the villages and did any jobs the home needed Unit 1: Ancient Civilizations - Men took more and more responsibility for obtaining food and protecting the settlements → play more dominant role in society Civilization Emerges - _____________= the way of life a people follows - __________________= a complex culture in which a large group of people share a number of common elements. - Basic characteristics of civilization: GRAPES 1. Geography 2. Religion 3. Achievements 4. Politics Government 5. Economics 6. Social structure - First civilizations developed in _________ valleys, mass farming was needed - Growing amounts of food and people, lead to a need to protect the food supply and defense → formation of governments - Governments were typically led by ____________, kings or queens, who organized armies to protect their populations and made laws - _____________- first civilizations developed religions to explain the forces of __________. They believed that gods and goddesses were important to the communities’ success - Social structures based on _____________ power - Rulers and upper class of religious leaders, governors, and warriors - Farmers, artisans, and craftspeople - Bottom class was slaves - New technology and trading items as well as jewelry and luxury items for the upper class - ___________ was used to keep records. Some civilizations depended on __________ experts rather than written records Lesson 3: Mesopotamia Bellwork Notes: The Fertile Crescent - Land from the _______________ Sea to the Persian Gulf, between the rivers of the _______ and ______________ rivers. - Mesopotamia had little rain, but rich soil. - Seasonal _________ brought fertile silt for farming. - People couldn't predict the timing and size of the floods → learn to control the flow of them with _____________and drainage _____________→ more regular farming → an abundance of food → civilization emerges - Mesopotamia refers to people from three different regions: __________, ___________, and ____________. City-States of Ancient Mesopotamia - Sumerian cities: Eridu, Ur, and Uruk - City-states were surrounded by walls and defense towers along the walls. - _______________= a state with political and economic control over the surrounding countryside. - Uruk: had about 50,000 people, making it one of the largest cities - Most buildings were built from mud bricks - Religion and Rulers - People looked to religion to answer their questions about _______ - Mesopotamians were polytheistic with about 3,000 gods and goddesses - ______________= believing in many gods Unit 1: Ancient Civilizations - The most prominent building in a city is the temple dedicated to the chief god or goddess of the city. Belief that the god or goddess owned the city. - __________= a massive stepped tower on which was built a temple dedicated to the chief god or goddess of a Sumerian city - Temples were usually the center of the city (physically, economically, and politically) - Temples would serve as the _______________ for any surplus food or supplies for people - Kings ruled for the gods with the help of the priests, army, and government - _______________= a government established by divine authority. (religious government) - Economy and Society - ______________ society based on farming, with emphasis on trade and industry - Woolen textiles, pottery, and metalwork - Sumerians bartered wool, __________, dried fish, _______, and metal good for copper, tin, and timber. - Three major social groups - _________: kings and priests - ____________: workers for the palace and temple as farmers, merchants, and craftspeople. About 90% of the population were farmers or fishers - _________: belonged to the palace officials and were used in building projects. The Creativity of the Sumerians - Writing and Literature - ______________= “wedge-shaped”, a system of writing developed by the Sumerians using a reed stylus to create wedge-shaped impressions on a _______tablet. - Writing was used primarily for record keeping → ___________became one of the most important jobs - The Epic of Gilgamesh, the first written story - Technology - Inventions were created simply to make life easier - _______, sundial, ______, metalwork, __________system based on 60 (think time), charts of the constellations, etc.