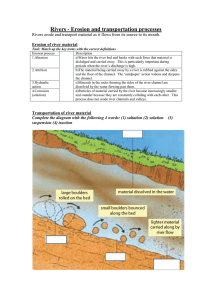
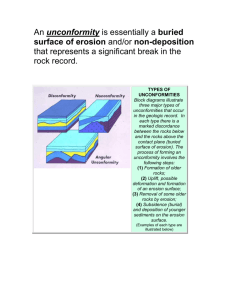
RIVERS Rivers are large natural flowing streams of water over land from the source to the mouth. Source: This is the point where the river Starts ,usually in the highlands Mouth: This is the point where the river ends , usually at the Lake, oceans, seas and swamps Diagram : RIVER River Basins A river basin is an area of land drained by a river and its tributaries. River basins have typical features, these include: Tributaries - smaller rivers flowing into a larger river. A Watershed - an area of highland surrounding the river basin. A confluence - where a river joins another river. Source - the start of a river. Mouth - Where a river meets a lake, the sea or an ocean. A drainage basin is an example of an open system because it is open to inputs from outside, such as precipitation, and is responsible for outputs out of the system, such as output of water into the sea and evaporation of water into the atmosphere. RIVER PROFILE A long profile is a line representing the river from its source (where it starts) to its mouth (where it meets the sea). It shows how the river changes over its course. The three phases of the river’s course The chart above shows the river isolated into three phases – upper (near the source), center, and lower (close to the mouth). The vitality of the river fluctuates inside each phase of the river. Upper stage/young – in the upper course, where the river starts, there is often an upland area. The river's load is large in the upper course, as it hasn't been broken down by erosion yet. Center stage/youthful – the angle of the river diminishes as you approach the center stages, potential vitality is changed over into dynamic vitality (development), and the rivers speed increments. Lower stage/old – in the lower course, the land is a lot flatter. The river's load is fine sediment, as erosion has broken down the rocks.. This are all process that takes place along the river , which helps in shaping up the land.The main river process are as follows ((The wearing away of the land) (The movement of eroded material) (The laying down of eroded material) RIVER EROSION is the process by which soil and rock are removed from the Earth's surface by exogenic processes such as wind or water flow, and then transported and deposited in other locations. River Erosion :is the process that which a river wears away the river bed and banks. River erosion can either be Lateral or Vertical erosion There are four main process of river erosion. These are- ): There are four types of erosion: Hydraulic action - This is the sheer power of the water as it smashes against the river banks. Air becomes trapped in the cracks of the river bank and bed, and causes the rock to break apart. Abrasion - When pebbles grind along the river bank and bed in a sand-papering effect. Attrition - When rocks that the river is carrying knock against each other. They break apart to become smaller and more rounded. Solution - When the water dissolves certain types of rocks, eg limestone. River Transportation The process by which the materials are moved from one place to another . This depends on the size of the material as well as the energy of the river. A river uses its energy to transport the eroded material down the river channel. The river transport its load in the following four ways: . There are four types of river transportation: • Traction - large, heavy pebbles are rolled along the river bed. This is most common near the source of a river, as here the load is larger. • Saltation - pebbles are bounced along the river bed, most commonly near the source. • Suspension - lighter sediment is suspended (carried) within the water, most commonly near the mouth of the river. • Solution - the transport of dissolved chemicals. This varies along the river depending on the presence of soluble rocks. Diagram :2 This is the process where by a river puts down or unload its load. When velocity begins to fall, it has less energy and no longer had competence and capacity to carry all its load so largest particles, materials begins to be deposited. Deposition occurs when-- Low discharge during period of low precipitation Less velocity when river enter sea or lake. Shallow water occurs on inside of a meander. The load suddenly increase (debris from landslide) River overflow its bank so velocity outside channel is reduced. (resulting in floodplain) ASSIGNMENT