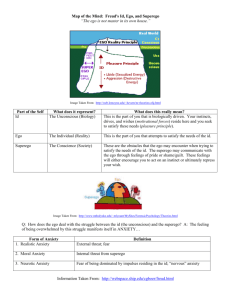
Module 4 SIGMUND FREUD Father of Psychoanalaysis and Psychosexual (1856 to 1939) was the founding father of psychoanalysis, a method for treating mental illness and also a theory which explains human behavior. 1) ID – the Pleasure Principle 1st develop, basic instinct (seeking pleasure, avoiding pain and SUFFERING) Pleasure Principle In our unconscious the past of our mind that we are not aware of is the source of all psychic energy, making it the primary component of personality is the only component of personality that is present from birth is entirely unconscious and includes instinctive and primitive behavior is driven by the pleasure principle 2) EGO – the Reality Principle Connected to reality Reality Principle Mostly in the conscious (we are aware of it) partly unconscious develops from the id and ensures that the impulses of the id can be expressed in a manner acceptable in the real world is responsible for dealing with reality operates based on the reality principle 3) SUPEREGO Moral Principle Conscience (what is right from wrong)begins to emerge at around age five holds the internalized moral standards and ideals that we acquire from our parents and society provides guidelines for making judgments Psychoanalysis - Freudian psychology which stresses importance of sex, childhood determinism and unconscious thinking The Unconscious - thoughts and wishes you are not aware of which influence conscious thoughts and behavior Repression - unconsciously pushing thoughts and wishes into the unconscious and keeping them there Sublimation - redirecting sexual and aggressive energy into social approved activity Libido - sexual energy/sexual drive Psychosexual growth stages - stages of sexual development that a human being normally goes through Anxiety - a vague fear of what might happen next Castration Anxiety - the child’s vague fear that his penis could be cut off Types of Anxiety Id – Neurotic Anxiety Unconscious traumatic experience anxiety that originates in unconscious conflict and is maladaptive in nature: It has a disturbing effect on emotion and behavior and also intensifies resistance to treatment. Neurotic anxiety contrasts with realistic anxiety about an external danger or threat and with moral anxiety, which is guilt posited to originate in the superego. Superego – Moral Anxiety anxiety contrasts with realistic anxiety about an external danger or threat and with moral anxiety, which is guilt posited to originate in the superego. Ego – Realistic Anxiety (e.g. unfamiliar places) This type of anxiety is considered a normal response to danger in the real world and serves to mobilize resources to protect the individual from harm. Also called objective anxiety. This types of anxieties is not clear-cuts Only the Ego can feel the anxiety Id – innate animal nature with sexual and aggressive drives Ego – conscious, rational problem solving part of the personality Superego – moral part of personality that condemns some behavior as sinful STAGES: Anal (1 to 3 years) All babies have to grow up some time, and when they do they graduate to the erogenous focus of the anal stage. The libido now becomes focused on the anus, and the child derives great pleasure from defecating. The child is now fully aware that they are a person in their own right and that their wishes can bring them into conflict with the demands of the outside world (i.e., their ego has developed) Phallic (3 to 6 years) The child in this stage is focused on the stimulation of the genitals. In the Phallic stage, gratification begins with autoeroticism. That means masturbation. But our need for satisfaction soon turns to our parents, typically the parent of the opposite sex. As this happens we find ourselves in one of Freud’s most controversial and strange contributions to the study of personality, the Oedipus complex. As adults, most of us would cringe at the thought of marrying someone like our mothers or fathers, least of all having sex with them, but we’ve all known a little boy who wants to grow up and marry his or her parent. Freud observed that children in the phallic stage of personality shifted from self-gratification to seeking gratification from their opposite sex parent. There is one problem the parent of the same sex. And a resentment or childhood hate sometimes grows towards that parent of the same sex. Latent Approx 7-11 yrs old Freud says we are genrally ‘happy’ and pretty ‘normal’ at this stage Genital Approx 11+yrs When we go through puberty we reach the genital stage of development and are obsessed with our genitals He said “we stay in this phase for the rest of our lives!” Module 5 ERIK-ERIKSON (Post Freudian) Psychosocial Development Identity crisis Post-Freudian Theory extended Freuds Psychosexual Development PSYCHOSOCIAL DEVELOPMENT Basic Assumptions Ego – in contrast w Freud’s concept of Ego (being a diplomat with no power of its own), Erikson’s conception of Ego is more powerful. It is a positive force that creates a self- identity or a sense of “I” Ego helps us adapt to the various conflicts and crisis of life and keeps from STAGE 1: Basic Trust vs. Mistrust Birth to age 1 Totally dependent on others Caregiver meets needs: child develops trust Caregiver does not meet needs: child develops mistrust Basic strength: HOPE Belief our desires will be satisfied Feeling of confidence Balance. No to Spoil STAGE 2: Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt Ages 3-5 Child expresses desire to take initiative in activities Parents punish child for initiative: child develops feelings of guilt that will affect self-directed activity throughout life Basic strength: PURPOSE Courage to envision and pursue goals Balance between Autonomy, Shame & Doubt: Basic Strength: WILL Power STAGE 3: Initiative vs. Guilt Oedipal complex – form of roleplaying (gina test kong ano ang mga roles na pwede ga gamapanan sa life nya amo ni nakakaroon ng bahay-bahayan, nanaynanayan or so on) Take ng role na gusto nya and kaya nya Balance: Initaitaive &Gulit Basic Stregnth: PURPOSE STAGE 4: Industriousness vs. Inferiority School Age (7-12 y/o) /Ages 6-11 Child develops cognitive abilities to enable in task completion (school work, play) Parents/teachers do not support child’s efforts: child develops feelings of inferiority and inadequacy Basic strength: COMPETENCE Exertion of skill and intelligence in pursuing and completing task STAGE 5: Identity vs. Role Confusion Ages 12-18 Form ego identity: self-image Strong sense of identity: face adulthood with certainty and confidence Identity crisis: confusion of ego identity (trial and error kong ano ang gusto nya or ayaw nya) Basic strength: FIDELITY- faith in one’s own chosen belief or ideology (mapapanindigan mo ba ID sino ka nang hindi o need ng guidance of other people/ parents / peers) Emerges from cohesive ego identity) Sincerity, genuineness, sense of duty in relationships w/ others STAGE 6: Intimacy vs Isolation Ages 18-35 (approximately) Priority having your own companion/love one/ jowa Undertake productive work and establish intimate relationships Conflict; Intimacy (Syntonic) – abilidad ng tao to fuse sariling identity nya sa iba without fear losing his/her own identity Isolation (Dystonic) – here mo ma discover kong sino ka Inability to establish intimacy leads to social isolation If na balance na the Basic strength: LOVE Mature love; commitment, sexual passion, cooperation, competition and also friendship (according to Erikson dapat bestie kamo sang partner mo lol required?) Mutual devotion in a shared identity Fusing of oneself with another person STAGE 8: Ego Integrity vs. Despair STAGE 7: Generativity vs. Stagnation Ages 35-55 (approximately) Productive in terms of work or having a family, so nagpporoduce na ng something in this stage Basic Conflict: Generativity: Active involvement in teaching/guiding the next generation (concern & naghehelp or build atleast taking care of the next generation ofcourse upod ka generativity is pagegenerate din ng mga new ideas na makakapag contribute pa ikakaganda ng aking society) so, ang tigulang di nag care for the next generation kumbaga lahat nalang ng bagay hinihold nya patunggo for her/himself the outcome is magiging self-absorbed sya. Ang selfabsorption is wht we called stagnation; which leads to “feeling entitled or even feeling nya alam niya lahat) so the tendency is ikokontol nya lahat, in the process imbes na mag produce sya eh nag ddestroy pa sya lalo ng ga other ppl lives. Stagnation involves not seeking outlets for generativity Basic strength: CARE Broad concern for others Need to teach others Ages 55+ (old age) – if ang matanda naging successful sa mga nauna nyang stages mas tumataas ang chance na hindi mag crumble/fall apart ang kanyang identity so therefore, there will be “integrity (strong pa)” if di siya naging successful sa life nya ang tendency is magkakaroon sya ng “despair” lahat ng makikita ng isang matandang tao is nakakapag “triggered” ng mga negative emotions kasi nakikita nila ang family nila ay mga kanya-kanya ng family, hindi na sila pinapansin so therefore, may large tendency na mahulog sa “despair” Evaluation of entire life. Integrity: Look back with satisfaction Despair: Review with anger, frustration Basic strength: WISDOM (situation where someone has already “tanggap” na ang buhay na meron siya dati is “tapos na/nagawa na nya and kailangan nya natong ewan reason dahil sana harap nya na ang “kamatayan” I mean not all people reach that kind of wisdom since mahirap pag old age Detached concern with the whole of life Conclusions It is important na every each maging “successful” each stage Big influence din ang caregivers, teachers, friends, even peers or the society as a whole Module 6 JEAN PIAGET Cognitive Development Theory Jean William Fritz Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called "genetic epistemology". Piaget placed great importance on the education of children. August 9, 1896, Neuchatel, Switzerland Pagbabago na nangyayari sa isang bata Ex. Way niya about processing an information Develop and discover "Cognitive Development"• He found put the children do not think lesser than adult but the think in different ways He believed that these stages are always in sequential order. This means, one satge cannot come first without the prior satges. He also believed that this satges cannot be skippped and that it mark new intellectual abilities upon reaching it. 3 Key Concept Basic Components of Piaget Cognitive Theory 1. Scheme • basic building black of intelligent behavior • Unit of knowledge • Set of linked mental representation of the world, which we use both to understand and to respond to situations • Way of information • refers to the cognitive structures by which individuals intellectually adapt to and organize their environment. It is an individual's way to understand or create meaning about a thing or experience. 2. Assimilation • is the process of fitting a new experience into an existing or previously created cognitive structure or schema. •(new information and knowledge na aadapt ng isang bata sa kanyang surroundings is isinasama doon sa mga unang knowledge na natutunan na nya) 3. Accommodation • is the process of creating a new schema • It is the changing or altering the existing schema in the light of the new information • Means, papalitan ko na ang mga nauna kong natutunan and then angg mga bagong information na naadapt ko sa aking surroundings ko, ayon yon mas ipapasok ko sa isip ko kasi iyon yong mas accurate at katanggap-tangap at mas tama Equilibration • is achieving proper balance between assimilation and accommodation. When our experiences do not match our schemata or cognitive structures, we experience cognitive disequilibrium. This means there is a discrepancy between what is perceived and what is understood 4 Stages of Cognitive Development 3) Concrete Operational Stage • 7-11 years old 1) Sensorimotor Stage • Birth - 2 years old • this stage is characterized by the ability of the child to think logically but only in terms of concrete objects • Sensory Perception - what they, see, smell, hear and touch of the child • Aware of external events • Object Permanence - is the ability if the child to know that an object still exists even hen out of sight. • Less focused on themselves 2) Preoperational Stage • 2-6 or 7 years old • Language Development • Playing & Pretending Symbolic Function – is the ability to represent objects and events Egocentrism – is the tendency of the child to only see his point of view and to assume that everyone also has his same point of view. Centration – refers to the tendency of the child to only focus on one aspect of a thing or event and exclude other aspects. Irreversibility – is the inability to reverse children’s thinking. Animism – is the tendency of children to attribute human traits or characteristics ti inanimate objects. Transductive Reasoning - refers to the pre-operational child’s type of reasoning that is neither inductive nor deductive. • Secrets Decentering – refers to the ability of the child to perceive the different features of objects and situations Reversibility – refers to the ability of the child to follow certain operations. Conservation – is the ability to know that certain properties of objects like number, mass, volume or area do not change even if there is a change in appearance. Seriation – refers to the ability to order or arrange things in a series based on one dimension such as weight, volume or size. 4) Formal Operational Stage • 11-12 onwards • at this stage, adult’s thinking becomes more logical and can solve abstract problems and can hypothesize • Ability to think abstractly and reflectively • Ready to reflect and differentiate what is "right and wrong" Hypothetical Reasoning – is the ability to come up with different hypotheses about a problem and to gather and weigh data in order to make a final decision or judgment. Analogical Reasoning – is the ability to perceive the relationship in one instance and then use that relationship to narrow down possible answers in another similar situation or problem. Deductive Reasoning – is the ability to think logically by applying general rule to a particular instance or situation.