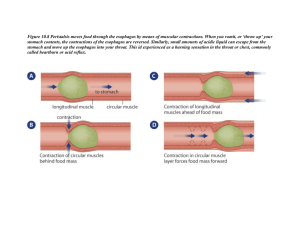
GI Embryology + Physiology ORAL CAVITY Function: sensory analysis, mechanical processing (teeth, tongue + palatal surface), lubrication (mucus + salivary gland secretions), Slight digestion via salivary amylase Cephalic Phase (Initial): Involves ingestion, mechanical/chemical digestion in mouth ESOPHAGUS hollow muscular tube behind the trachea (begins posterior to cricoid cartilage), innervated by fibers of esophageal plexus. Has longitudinal (lateral) + circular (medial) m. fibers Location of swallowing: Voluntary (oropharyngeal) phase and Involuntary phase (UES relaxes peristalsis LES relaxes) Function: Move food to stomach via peristalsis circular m. behind bolus will contract while longitudinal m. in front of bolus contracts pushes/pulls bolus down esoph. – also occurs in stomach and intestine. GASTRIC Bolus enters the gastroesophageal junction. Stomach made up of tissue that allows stretch when full and contraction when empty. Note: different areas have different cell types secretion of different hormones when triggered by bolus’ arrival. Gastric Phase: Begins when food enters distended stomach stim. Stretch receptors + peptide sensitive chemoreceptors o VAGAL reflexes turned ON: ParaNS is most important for digestion. Vagovasal reflex: afferent and efferent fibers of the vagal nerve (CN X) via dorsal vagal complex in brain coordination of gastric, intestinal, and pancreatic secretions req for digestion. Allows contraction of muscle and accomodation for large amounts of food Clinically vagotomy (thanksgiving is NOT fun) o Some digestion of proteins, lipids, and carbs but NO ABSORPTION! Gastric Secretions: 1. Hydrochloric Acid: secretion from parietal cell d/t distention of stomach; l/t [H+] = pH~2; kills microbes from bolus, denatures protein/ inactivates enzymes, aids digestion of plant walls and meats, activates pepsin from pepsinogen a. Parietal cells: Stimulated by Ach, Gastrin + Histamine b. Beware mechs and OTCs that decr. Acid production = impaired digestion i. Atropine = Blocks Ach; Omeprazole = blocks H/K-ATPase 2. Gastrin: Peptide hormone secreted by G cells binds to parietal + ECL (via Cholecystokinin B receptors) cells a. ECL cells release Histamine + nearby parietal cells to take up CO2/ H2O (carbonic acid HCl) pump out HCl via K/H ATPase pump. i. Histamine release regulated by low pH of stomach ie) H2 blockers (Zantac, Cimetidine) work to decr. acid production b. Clinically: Patient’s on PPI’s have gastrin levels b/c of no (-) feedback to turn off gastrin secretion parietal cells increase in sz despite acid production. i. Stop medications = crazy amounts of acid released 2/2 increased parietal cell sz 3. Somatostatin: Decreases acid production and slows down digestion via inhibition of gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, etc. 4. Pepsin: Released from chief cells as pepsinogen pepsin via HCl; Aids in protein break down SMALL INTESTINE: 90% of absorption thus is required for living (along with liver); main function is absorption of nutrients, salt, electrolytes, and water. High SA via valvulae, conniventes, villi and microvilli. Intestinal Phase: Involves secretions and movements Intestinal Enzymes: Localized to the brush border sucrose, maltose, lactose, peptidases, nucleases Duodenum: Absorption of Iron and Folate; Pts with gastric bypass or ulcers will require supplements. Folic Acid (B9): Pteroylmonoglutamic acid (absorbable form) post-conversion via jejunal enzymes o Deficiency: D/t decreased intake (tea + toast in elderly; alcoholics), Jejunal disorders (celicac dz, tropical sprue, drug effects), requirement in pregnancy Ileum: Vitamin B12 and Bile salts are absorbed; Patients with Chron’s are deficient + have trouble digesting fats d/t surgical resection of the ileum. Cobalamin Absorption: Bound to proteins in food pepsin + low pH releases cobalamin Parietal cells secrete IF which eventually binds to B12 absorbed by ileal hepatocyte and cleaved from IF storage in liver (3-5 years) o Cobalamin Deficiency: Susceptible to megaloblastic anemia, myelopathies d/t damage to the posterior column of spinal cord problems with vibration + proprioception (can feel numbness and tingling in extremities) Megaloblastic Anemia Pernicious 2/2 no IF for b12 absorption. PANCREAS Lies posterior to stomach + bound to the posterior wall of cavity. Endocrine: a and b cells secrete glucagon and insulin respectively. Exocrine: Acinar and ductal epi cells secrete pancreatic juices includes pancreatic amylase, protease, lipase and nucleases to produce intestinal enzymes. Flows from pancreatic duct to duodenum. o Secretes Bicarb to buffer the gastric acid traveling to SI o 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Secretes trypsin, chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase for protein digestion ABSORPTION Water and Electrolytes: 90% water reabsorbed by SI; Na/Cl reabsorbed via transporters l/t passive water movement No watery poo! a. SI also secretes electrolytes + water. Simultaneously absorption > secretion net absorption of water and electrolytes. i. Response to bacterial toxins, bile salts, hormones secretory diarrhea Amino Acids: Via proteolytic degradation with serine proteases from pancreas (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase) and carboxyl proteases from stomach (pepsin) Dietary Fats: TGs digested in jejunum via pancreatic lipase FFAs + B-monoglycerol a. 2/2 Emulsification via bile salts regenerated into chylomicrons lymphatics. b. MCT: Don’t need emulsification; Useful for patients with bile salt deficiency. Vitamins: a. Water Soluble: Thiamine, Niacin, Riboflavin, Biotin, Vit C b. Fat Soluble: A, D, E, K Calcium: Occurs in SI with Vit D to increase serum levels; Iron: Occur in duodenum MUCOSAL IMMUNE SYSTEM: 70% in the digestive tract GALT: Peyers patches (SI), Mesenteric LN, Appendix, Solitary LN (Ileum) o Peyer’s patches: mucosa submucosa; follicles responsible for monitoring bacteria population in intestines + prevention of overgrowth o Mesenteric LN: Next in line of defense + attaches intestine to abd wall Trap and attack bacteria o Appendix: Maintains microbiome to extent; composed of B cell mediated immune responses and T cells coming from outside of the thymus