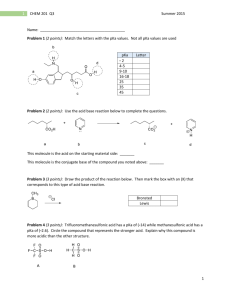
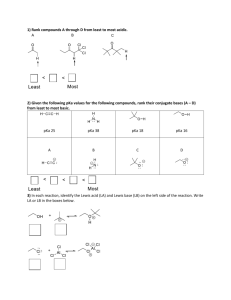
Chemistry 101 Bronsted Acid and Bases Bronsted acid: proton donor Bronsted base: proton acceptor Bronsted Acid/Base Practice Bronsted Acid/Base Practice Conjugate Acids and Bases What are conjugate acids and bases? Conjugate base: Bronsted acid that has lost a proton Conjugate acid: Bronsted base that has gained a proton Conjugate Acid/Base Practice How to identify conjugate acids/bases: compare your reactants to products and track the movement of hydrogens Conjugate Acid/Base Practice Compare Lewis A/B and Bronsted A/B Considering only the forward direction, classify each reaction as a Brønsted acid–base reaction or a Lewis acid–base association/dissociation. Classify each labeled species (or a group within each species) with one of the following terms: Brønsted base, Brønsted acid, nucleophile, nucleophilic center, electrophile, electrophilic center, and/or leaving group. For Brønsted acid–base reactions, show the conjugate acid–base pairs. pKa What is pKa? ● pKa is the number that shows how strong or weak an acid is. ● The smaller the pKa, the stronger the acid! Acid-Base Equilibrium ● The equilibrium in the reaction of an acid and a base always favors the side with the weaker acid and the weaker base! Acid-Base Equilibrium Practice More Acid-Base Equilibrium Practice Acid Strength ● The strength of a bronsted acid is determined by how well it transfers a proton ● The strength of a bronsted base is determined by the pKa of its conjugate acid ● Acid strength increases when the Hydrogen is attached to a more EN or very large atom -- can you explain why? 1. Which is the stronger acid of the two? pKa= 4.31 pKa= 4.76 Free Energy What is free energy? Energy that is able to do work (deltaG) How does free energy impact equilibrium? 1. Chemical equilibrium favors the species of lower standard free energy. 2. The more two compounds differ in standard free energy, the greater the difference in their concentrations at equilibrium. Free Energy Practice Free Energy Practice Alkene Physical Properties Physical Properties of Alkenes ● ● Alkenes are less dense than water and insoluble in water. The dipole moments of some alkenes, though small, are greater than those of the corresponding alkanes. ○ Sp2-hybridized carbons are somewhat more electronegative than sp3-hybridized carbons. As a result, any sp2–sp3 carbon–carbon bond has a small bond dipole (Sec. 1.2D) in which the sp3 carbon is the positive end of the dipole and the sp2 carbon is the negative end. Alkene Physical Property Practice Alkene Physical Properties Alkene Stability When we ask which of two compounds is more stable, we are asking which compound has lower energy. The standard heat of formation of a compound, abbreviated deltaH°f, is the heat change that occurs when the compound is formed from its elements in their natural state at 1 atm pressure and 25 °C. -deltaH: exothermic rxn (favored) +deltaH: endothermic rxn Alkene Stability the alkene with the greatest number of alkyl substituents on the double bond is usually the most stable one. Trans tends to be more stable than cis Cis vs Trans Alkene Stability Practice