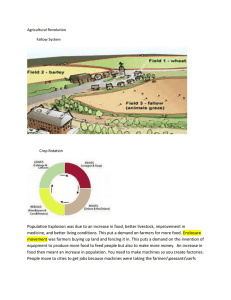
Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ Europe in the 18th Century Questions • Who held the power in Europe in the 18th century? • What economic changes were happening in Europe in the 1700’s? • What types of political systems were present? The Old Regime • Ancient Régime: France’s social, ______________, and economic order before the Revolution of 1789 • Hierarchical class system: o Aristocracy and nobility had inherited legal privileges; o Established churches held power and land o Urban labor force were usually organized into guilds o Rural peasantry were subject to high taxes and feudal dues • Little concept of “individual rights” among the people, collective consciousness • The monarchs of France, like ______________, kept the Ancient Regime in place while other countries like Great Britain were evolving politically The Aristocracy • __________of population • Their wealth was based on ______________ • Nobility were paid by the government for simply being nobility • They held the most social, political, economic power • Interested in economic growth, innovation (like commercial classes) British Aristocracy • The British nobility were the ______________, wealthiest, & most socially responsible o Around 400 families • Represented the House of Lords in Parliament o They owned around ¼ of land good for farming or grazing Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ o Due to British law, they did not have many legal privileges, but they did hold great political power French Aristocracy • French nobility had undergone changes due to the monarch’s wish to have a weaker noble class after the French Wars of Religion • Around 400,000 nobles – Two ______________ o “Nobles of the sword” derived from military service back to the Middle Ages o “Nobles of the ______________” attained their title from service in bureaucracy or they simply purchased it o Due to the sheer number, some were wealthy and some poor, but they all shared certain hereditary privileges like a government paycheck • Different than Eastern European nobles where military traditions were important and they held extensive power over their serfs Aristocratic Resurgence • Aristocrats around Europe tried to maintain their power and rights as monarchs consolidated power during the Age of Absolutism • They attempted to keep their privileges by making it harder to gain a noble title • They wanted to reserve high-ranking appointments in the church, government, or military for ______________ o Sought to gain more power with noble-controlled institutions (British Parliament, French parlements, German diets, etc.) o Tried to build up additional wealth through new ______________ exemptions and raising rents • Remember this when we cover the French Revolution Peasants & Serfs • Living day-to-day while being ______________ dependent on landowners and frequently exploited by the aristocracy and/or government • Power of European landlords increased from west to east • French peasants still had feudal dues and ______________ service o Corveé service was annual forced labor, like building a bridge, that peasants had to do • Serfs under the Hapsburgs: nearly slavery o compulsory service to lord • Russian serfs were the worst off Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ • o Noble wealth was measured by number of serfs, not by acres of land o Russian Tzars historically gave nobles more and more power over serfs so they could attain more power Ottoman Empire (SE Europe) allowed peasants to be nominally free o They had some marginal powered due to a scarcity of labor Enlightened Despots • Usually worked at reducing ______________ of aristocracy o Sometimes not on purpose, but their reforms naturally did it o Spanish Carlos III • Some monarchs tried to either free their ______________ or make life better for them o Frederick the Great opened up more farmland in Prussia • The floodplains of the Oder River were opened to farmers after the river was restructured to cause less flooding • Joseph II of Austria: "Everything for the people, nothing by the people" Peasant Rebellions • Pugachev’s Rebellion (1773–1775) happened under the reign of Catherine the Great in Russia o Anger over continued war with the __________________ o Some still loyal to Peter III o Pugachev called for the abolition of serfdom o Occurred in southern Russia o Crushed after the Imperial government saw how much of a threat the rebellion was o Pugachev was captured and executed in ______________ Families • In northwestern Europe, people tended to get married between the ages of 23 and 26 years old • People lived in a nuclear family structure with usually ______ family members o Some had live-in ______________ • Young servants could gain experience as to how to run their future household • Each family produced and consumed items, this is known as the Family Economy Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ • o Think of the Cottage Industry, farmers, artisans, etc... Families in Eastern Europe tended to live with extended family and people married before they were 20. Family Economy • Living alone was almost impossible economically and was viewed as _______________________ • All household members worked in some capacity, even young children helping with the family economy o Money earned or items produced belonged to the family, not to the individual • Most people were still farming, but families usually had someone working in a different field, like being a servant, sending money home, to ensure the family’s survival o The death of a father could be disastrous for a ______________ Women in the 1700’s • Women were in ______________ of the household and had to maintain it • Marriage was an economic necessity, being a single woman outside of the household would be quite difficult to impossible • Women had to help make sure the family had enough food to eat o They also had to figure out how many children the family could maintain and think of ways to control it. • Childbirth was dangerous for the mother and child o 1 in 10 pregnancies ended in the death of the mother o Wet nurses were needed – but also used by the wealthy so the mother did not need to breastfeed but could focus on giving birth to more children. o 25% of births were out of ______________ Children & the Family Economy • Children helped as much as they could to make ______________ or products for the family • Some babies were left out to the elements to die or be found by others as families could not afford them • “Foundling hospitals” were established for abandoned children o Babies and children were victims of poverty or illegitimacy Agricultural Revolution • The peasants wanted improvements to have a stable ______________ supply Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ • • • • o Bad summer, famine There was resistance to changes that could endanger food supply o Can slow the process of positive change The Dutch started the innovations with better ways to gain more land by draining low areas. They had clovers or turnips planted on fields that would have been bare for a year to rebuild minerals and still provide a product. Jethro Tull invented the ______________ __________which helped improve planting of crops and increased yields. Robert Bakewell helped improve animal breeding methods The Start of the Industrial Revolution • More to come with the Industrial Revolution PowerPoint 2nd semester • The major part of the revolution occurred during the 2nd half of 1800s o Started in Great Britain o Textile industry was ______________ o 1769 – Steam Engine – James Watt o Improvements in ______________ production • Commercial revolution also occurred as people wanted and could afford more material items • Cities boomed during the Industrial Revolution Urban Centers • Cities grew throughout the ______________, but the rich and the poor were in separate areas of the cities • Cities were dirty and unsanitary, which is why cholera and other diseases became more and more common • The Middle Class (bourgeoisie) were a growing class of merchants, bankers, lower level lawyers, business professionals, etc… They sought change politically and economically. • Urban Riots usually occurred because the price of bread was too high • Near the end of the century, riots became more politically focused o French Revolution 1789 – Bread and ______________ The Jewish Population • The highest concentration of Jews was in ______________ Europe • Commonly regarded as a kind of nonresident alien o They were usually denied citizenship unless specifically granted o Every year the head of the Jewish community had to ask Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ • • • the mayor of Rome if they could continue to live there in a public “ceremony” Some lived in separate communities known as ghettos “The age of the ghetto”—did not mix with mainstream societies A few became famous or wealthy but most lived in poverty Politics of the 1700s • The 1700s saw some major ______________, especially in the 2nd half of the century o Austria vs. Prussia over dominance of central Europe o Great Britain vs. France for commercial & colonial supremacy • Prussia emerges as great power and Great Britain was becoming a world ______________ • American Revolution • Continental enlightened ___________________ • Continued French financial crisis • Reform of Spanish South American empire European Overseas Empires • Four phases of European contact with the New World: o Discovery, exploration, conquest, & __________________ o Mercantile empires with power trade rivalries • Some Caribbean Islands experienced on and off again warfare between rival European powers trying to own the ______________ o Slavery o 1700’s Independence Movement in the Americas began • Source of European world domination: Guns, Germs, and Steel • Mercantilism Economic Theory of Europe in the 1700s • Think of it as a contest, you want your ______________ to get the most gold and make international trade laws to make sure you get the most. o European imperial powers wanted their colonies to only trade with the home country, only in rare situations can they trade with other colonies under the same flag • For example, trade items from New England going to Barbados as that island solely produced sugar Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ Colonies as of the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht • Spain: South America except for Brazil; ______________ & California & the North American Southwest; Central America; Caribbean Islands • Britain: 13 American colonies, Nova Scotia & Newfoundland, 13 Caribbean Islands & trading posts on Indian subcontinent • France: Canada (Quebec), Ohio, & Mississippi River; Caribbean Islands; trading posts in India & West ______________ • Netherlands: Surinam in South America; Cape Colony (S. Africa); Caribbean Islands, trading posts in West Africa, Sri Lanka, & India; also controlled trade with Java in SE Pacific The British and their Colonies • Due to the diverse British __________________ and the start of the Industrial Revolution in Britain, wealth was increasing • The British colonies had to buy British goods due to mercantilism • Navigation Acts – all goods into England had to be on British ships o Monopoly on trade with their ______________! o This built up some resentment in some of their colonies • During the American Revolutionary War, the 13 British Caribbean Islands feared what would happen if the Americans won and they were unable to trade with them anymore • Trade was cut off for some time, but after awhile, new trade networks were created and the islands prospered again French-British Rivalry • The French and the British ______________ over the St. Lawrence River, Caribbean Colonies, the Ohio River valley, fishing territories in the Atlantic, fur trade areas, and both tried to gain American Indian or First Nation alliances that would help them with the fur trade. • Biggest area of rivalry with the most fighting (not large scale war, but fighting for specific islands or commandeering other ships was the West Indies or Caribbean Islands due to tobacco, cotton, indigo, coffee, & most importantly ______________ • India became a battle ground area as the century progressed Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ The Spanish • The Spanish were also involved in the feuds in the West Indies • The Spanish also instigated the ______________ Rebellion, slave revolt, in Colonial South Carolina when it stated that slaves that escaped and made it to Spanish controlled Florida would be granted their freedom • Colonial Government o ______________________ administration, almost no selfgovernment o The Spanish Colonies did not have the manufacturing or artisan areas develop like the British 26 colonies o Casa de Contracion was Spain’s form of a Navigation Act Spain after Utrecht • A new ruling power came on the throne in Spain after the War of Spanish Succession o Bye bye Habsburgs, Hello House of ______________ o France lost some colonial possessions to the British o British won more trading rights with Spain • Philip V (r. 1700–1714) tried to stimulate their trade monopoly and recover losses o They also wanted to suppress ______________ • Charles III (r. 1759–1788) was known as being a reformer during the time of enlightened monarchs • More imperial control of colonies versus local councils. o This caused tension between Spanish from Spain and creoles (Spanish born in America) African Slaves in the Americas • Slavery existed in Europe, but the Spanish, Portuguese, and British began to rely on it in their ______________ • The push for slaves was driven by labor shortages and the desire for higher profits among landowners o British Caribbean Colonies and South Carolina had issues with landowners making money in their colony and then moving back to Britain to have others run their estate or plantation, called absenteeism • Slave markets on the West Coast of ______________ existed before the European came. Europeans though wanted an unthinkable number of slaves • Internal African warfare and a drive for profits pushed forward the slave trade in Africa • Slavery began in 16th century in Spanish America, 17th century in Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ • • British America Slave trade grew in 18th century because of low fertility rate and high mortality rate of established slaves It was difficult to create stable self-reproducing population Slavery and the Transatlantic Economy • The slave trade was dominated by Portuguese & ______________ in 16th century, the Dutch in 17th century, and the English in 18th century • “Triangular ______________” Slavery • Around 9 million Africans or ______________ were brought to the Americas over 4 centuries o Slaves faced horrible and unthinkable conditions in Middle Passage • “Seasoned” slaves worth more than those newly arrived o South Carolina and other colonies over time made laws against accepting new slaves as they were more likely to rebel. • It is accepted that all the slaves in _________________ societies led difficult lives with little variation • Some slaves mixed Christianity with African religions • Slavery was a maintained due to a racist ideology Mid-Eighteenth Century Wars • War of Jenkins’ Ear (1739) o English-Spanish competition in __________ ____________ o Member of the Spanish Coast Guard cut off the ear of Captain Jenkins • The ear was then brought to Parliament • What wasn’t told was that the British were trying to commandeer the Spanish vessel o British declared war on Spain in 1739 with the war ending in 1742 o Minor war but showed that colonial issues could lead to a major European ______________ Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748) • Central & Eastern Europe • Prussia invades Habsburg controlled Silesia in ______________ • France & Spain back Prussia while England backed Austria • Maria Theresa was able to maintain the Hapsburg empire as a major political power even though their army looked weak • Ended with Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in ______________ o Prussia gained Silesia, Spain renewed Treaty of Utrecht with Britain so they could import slaves from Spanish colonies The Seven Years’ War (1756–1763) • England backed Prussia but only by sea. It would not land troops in Europe to help Prussia • France and Russia backed ______________ o Prussia was virtually surrounded. Frederick the Great had a great feat to accomplish o Prussia was saved by the death of Czarina Elizabeth dying and Peter III taking the throne and pulling Russia out of the war, even though they were on the doorstep to Berlin. • Fighting occurred in the colonies as Britain beat France in North America o French-Indian War • Treaty of Paris made ______________ into a world power with its colonies Europe and the American Revolution • Britain was in debt after the ______________ Years War and desired for the colonists to help pay for the war o Up to this point, taxation was a local issue, not an issue from London o British tried to tax colonies to ______________ for war o The 13 North American colonies stated that they wouldn’t be taxed without representation o Many of the 13 Caribbean Colonies agreed, but they needed British military protection as the foreign threats were large and the islands had a majority slave population and the colonists feared revolts Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ The American Independence • There were riots on some Caribbean colonies when the ______________ Act was introduced o William Pitt and King George III asked Parliament to reverse the act • The 13 American Colonies broke away and went to war for their independence o Thomas Paine • The United States won the war with the assistance of the French o French navy was able to make it to the U.S. because a British sea captain was fighting to take a Dutch Caribbean Island instead of finding the ______________fleet John Wilkes affair o Arrested after criticizing the ______________ with France in print o Elected several times to Parliament but the king would not allow him to take his seat o Pushed the movements that rejected the monarchy and social hierarchies o Yorkshire movement demanded progressive changes in parliamentary elections Impact of American Revolution • Demonstrated the possibility of government without ______________ • Idea of preserving traditional liberties • Reject social status and the European class system • France more in debt Vocabulary • Old Regime o Term applied to the pattern of social, political, and economic relationships & institutions that existed in Europe before the French Revolution • Vingtieme o Meaning “one twentieth” A tax on income in France before the Revolution • Corvees o A French labor tax requiring peasants to work on roads, bridges, and canals • Aristocratic Resurgence o Term applied to the 18th century aristocratic efforts to resist Summary Name:____________________________________________ Period:________ • • • • • • • • • • • the expanding power of European monarchies Seigneur (sane-your) o A noble French landlord Robot o The amount of labor landowners demanded from peasants in the Habsburg Monarchy before 1848 Family Economy o The basic structure of production & consumption in preindustrial Europe Agricultural Revolution o The innovations in farm production that began in the 18th century & led to a scientific & mechanized agriculture Enclosures o The fencing in of common lands Industrial Revolution o Mechanization of the European economy that began in Britain in the 2nd half of the 18th century Consumer Revolution o The vast increase in both the desire & the possibility of consuming goods & services that began in the early 18th century & created the demand for sustaining the Industrial Revolution Domestic system of textile production (putting-out) o Method of producing textiles in which agents furnished raw materials to households whose members spun them into thread & then wove cloth, which the agents then sold as finished products Spinning Jenny o A machine invented in England by James Hargreaves around 1765 to mass-produce thread Water Frame o A water-powered device invented by Richard Arkwright to produce a more durable cotton fabric. It led to the shift in the production of cotton textiles from household to factories Ghettos o Separate communities in which Jews were required by law to live Summary