Water Hardness Determination by EDTA Titration Lab Report
advertisement

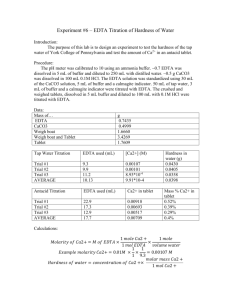
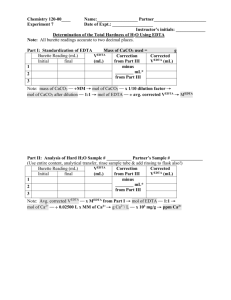
Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 EXPERIMENT NO. 8 DETERMINATION OF WATER HARDNESS BY EDTA TITRATION Introduction: To a child or even a lesser educated person, hardness of water may sound silly. But in this lesson, we are able to grasp the definition of water hardness. As we all know, water is a colorless, transparent, and odorless liquid that makes up the seas, lakes, rivers, and rain, as well as the fluids that keep living beings alive. It is important that our world does not run out of water, or we will all die. In chemistry, there are terms for water describing it as “hard” or “soft”, and as it runs through rocks and soil, natural water dissolves various organic salts. Hard water is water that contains significant levels of calcium, magnesium, and iron ions, while soft water is the opposite of that, meaning they contain low amounts of the aforementioned. In this experiment, we will try to determine the total hardness in a water sample in parts per million by titrating with EDTA solution. Objectives: The goal is to prepare and use an EDTA solution to titrate a water sample to measure the total water hardness, or total calcium and magnesium ion concentration. Materials and Reagents: ✓ Burette ✓ Erlenmeyer flask ✓ Pipette ✓ Wash bottle ✓ Volumetric pipette ✓ Clamp and stand ✓ Beaker ✓ Volumetric flask Procedure: A Buffer solution was prepared by dissolving 16.9 g of NH4C in a 143 ml NH4OH. Then 1.25 g magnesium salt of EDTA was added until obtainment of a sharp change in color of indicator before it was diluted to 250 ml. After that, 1.179 g disodium salt of EDTA (AR grade) and 780 mg MgSO4.7H20 or644 mg MGCl2.6H20 was dissolved in a 50 ml distilled water since magnesium salt of EDTA was not available. NH4Cl was then added to NH4OH as the solution and was diluted to 250 ml. For the preparation of a standard EDTA solution, the primary standard calcium carbonate was prepared by weighing almost 1.0 g of calcium carbonate standard and was dried at 110°C for an hour, and then cooled in a desiccator. After that a dried CaCO3 weighing 0.3 to 0.4 g was transferred into a 250 ml beaker, dissolved with enough water, transferred into a 500 mL beaker, and added 2 mL of concentrated before swirling the flask until all the CaCO3 was dissolved and diluted to the mark with distilled water. For the preparation and standardization of a 0.005 M EDTA solution, 0.4560 g of EDTA was weighed and put into a 250 mL beaker before the solution was transferred into a 250 mL volumetric flask to be filled halfway with distilled water. 3-4 mL of the 3 M NaOH solution was then added and swirled until it dissolved and diluted to the mark indicating it was mixed thoroughly. Then it was stored in a 250 mL polyethylene container. Next, the burette was washed and rinsed with a small amount of EDTA solution before it was filled and recorded for the initial volume. 25.00 mL of CaCO3 standard solution was pipetted into each of three 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. 5 mL of buffer solution was added then until the pH was equal to 10. 2-3 drops of EBT indicator were added to the solution before it was titrated until the color changed from red wine to blue. Then the final volume of the EDTA was recorded. This procedure of titration was done with the two other Erlenmeyer flasks separately following the last two steps. Finally, the molar concentration of EDTA solution was calculated. For the determination of water hardness, 50.00 mL of the water sample in each of three 250-mL Erlenmeyer flasks was measured before 5 mL of 10 buffer solution was added to it and then 2-3 drops of EBT indicator were put into each flask. After that, a 50-mL burette was filled with the standardized EDTA solution which was used to titrate each water sample to the endpoint and at the Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 endpoint, it was observed that the titrated solution changed from red to blue. Lastly, the hardness of water in terms of ppm CaCO3 was calculated and recorded. Data and Results Mass of CaCO3= 0.3234 g Trial 1 2 3 VCaCO3 25.00 mL 25.00 mL 25.00 mL Vi (mL) 0.00 0.50 1.50 V EDTA Vf (mL) V used 32.55 32.55 32.35 32.85 32.60 34.10 Average M EDTA Vi (mL) 0.00 10.45 21.00 V EDTA Vf (mL) V used 10.45 10.45 10.55 21.00 10.43 31.43 Average ppm CaCO3 MEDTA 4.964 x 10-3 mol/L 4.995 x 10-3 mol/L 4.956 x 10-3 mol/L 4.972 x 10-3 mol/L Hardness of Water Sample Trial 1 2 3 Vsample 50.00 mL 50.00 mL 50.00 mL Calculations: ppm CaCO3 104.0 ppm 105.0 ppm 103.8 ppm 104.3 ppm Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Table 2 Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 Discussion Using one value for the mass and volume of calcium carbonate, and the initial and final volume of EDTA to get the total volume used and moles of EDTA, we have successfully calculated both. Then for obtaining the necessary values needed to gain the final volume used and ppm of calcium carbonate, we can infer that the average water hardness level of our water sample is moderately hard since it is within the moderate level of 60 – 120 ppm. This is an indication that the water can be softened by using a water softener to remove the iron while carefully following the rule of thumb in measuring. Also, upon further reading by my group, we have known that it is important that pH 10 buffer is used in EDTA titration, because Y4- is prevalent in EDTA, and we want Y4- to react with the metal ions present in the titration solution, in other words, EDTA is insoluble in water at low pH. Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 Conclusion After careful study, calculation, and prior hypothesis formulation of this experiment, we can conclude that the most prevalent sources of hardness in water are Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions or mainly compounds of calcium and magnesium, or a variety of other metals, which could make water cause problems in both the household and the workplace. Furthermore, we have known that CaCO3 was used as a unit to calculate the level and severity of hardness effects to tell whether the hardness is calcium, magnesium, carbonate, or non-carbonate. For the possible sources of errors for this experiment, it mirrors with the previous ones which were about titration. These errors could be caused by a variety of factors including misreading volumes, incorrect concentration values, faulty technique, or improper use and application of instructions such as misinterpreting the color of the indicator near the end point, transferring different solutions with the same pipette without washing pipette with distilled water between each one, using solutions of incorrect concentration, unwashed equipment, rinsing burette and/or pipette with incorrect solution, transferring too much volume of liquid, leaking burette, titrating at incorrect temperature and pH value, and so on are all possible sources of error. Application Applications of titration in life, as mentioned beforehand in the previous experiments (3-5), can be seen in the food, wine, and pharmaceutical industries, especially in the water treatment industries since our world runs entirely, literally, with water. So, knowing the total hardness of water is necessary because it is used to assess the number of metal ions in it, and the higher the concentration, the greater the risk to aquatic life and other species. This in turn means a riskier life for humans since high levels of calcium and magnesium could affect several of our organs which could lead to health problems, one of such is cardiovascular diseases, according to one study. Name: Isabelle M. Escamis CYS: BSES-2B Group: 5 (De Peralta, Donadillo, Escamis) Date: Crs. Proff. Lab. Rep.: May 31, 2022 Ma’am Corazon D. Sacdalan 8 References: 06 Determine the total hardness of a water sample using EDTA https://youtu.be/r97t1HegA94 16. Hardness in a Water Sample https://youtu.be/-aAYjOmhkhg The Negative Impact of Hard Water on Your Home and Body https://serviceprosplumbers.com/the-negative-impact-of-hard-water-on-your-home-and-body/