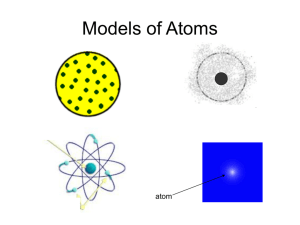
Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Bell Task What is the definition of the word: Theory ? General Definition: an untested hunch, or a guess without supporting evidence. But for scientists, a theory has nearly the opposite meaning… Science Definition: A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of an aspect of the natural world that can incorporate laws, hypotheses and facts. It is robustly tested and is the consensus best explanation. Examples include: • Astronomy: Big Bang Theory. • Biology: Cell Theory; Theory of Evolution; Germ Theory of Disease. • Chemistry: Atomic Theory; Kinetic Theory of Gases. • Physics: General Relativity; Special Relativity; Quantum Field Theory. Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Lesson Objectives Knowledge • Name some of the scientists involved in the stages of atomic structure evolution, and state what they found. Skills • Read and interpret a timeline. Understanding • Explain how the alpha particle scattering experiment led to a change in the model of the atom from the plum pudding model. • Describe the differences between the Plum Pudding and the Nuclear models Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Early Theories (pre 1890) Early investigations were limited due to technology however some philosophers and scientists came up with some theories Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Atomic Theory Timeline 450BC Democritus – a Greek natural philosopher 1. 2. 3. 4. Atoms are indestructible. Atoms are solid but invisible. Atoms are homogenous. Atoms differ in size, shape, mass, position, and arrangement. 1803 Dalton – English chemist, physicist and meteorologist 1. 2. All matter is made up of atoms . All atoms of the same element are identical. All atoms of different elements are different. In Summary: Before the discovery of the electron, atoms were thought to be tiny spheres that could not be divided. Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Post 1890 discoveries 1890 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1897 – Electrons discovered 1897 – JJ Thompson developed the Plum Pudding model 1. The discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model Wednesday, 08 June 2022 The Plum Pudding model In 1897, whilst studying cathode rays, JJ Thomson discovered tiny particles with a negative charge (electrons). These negative particles were given out by atoms and were much smaller than atoms. Thomson had discovered the existence of electrons. Wednesday, 08 June 2022 The Plum Pudding model Based on his discovery, Thomson adapted Dalton’s model of the atom. He suggested that an atom is a positivelycharged sphere with negative electrons distributed throughout it. Thomson’s model became known as the plum pudding model, because the electrons in the atom were thought to be like raisins in a plum pudding. Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Post 1890 discoveries 1890 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1897 – Electrons discovered 1. The discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model 1897 – JJ Thompson 1909 – E Rutherford 2. the Nuclear model using alpha developed the Plum developed the particle scattering Pudding model Nuclear model using the alpha particle scattering experiment Wednesday, 08 June 2022 The Nuclear model In 1909 Ernest Rutherford designed an experiment to test the plum pudding model. Positively charged alpha particles were fired at thin gold foil. Copy and complete the following: Observation Conclusion most alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil the mass of the atom is in the nucleus or most of the atom is empty space some alpha particles were deflected / reflected the atom has a positively charged nucleus Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Comparing Models 1. Create a table that compares the Plum Pudding and Nuclear models (Level (4), 3) Ball of positive charge spread throughout Atom solid sphere with no empty space mass concentrated at the centre Mass spread throughout Atom mostly empty space Electrons outside the nucleus Positive charge concentrated at the centre Electrons embedded in the ball of positive charge 2. What similarities do the models have? (Level (5), 3) 3. Evidence from the alpha particle scattering experiment led to a change in the model of the atom from the plum pudding model. Explain how. (Level (7), 4) Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Comparing Models 1. Create a table that compares the Plum Pudding and Nuclear models (Level (4), 3) Plum Pudding Ball of positive charge spread throughout Nuclear Model Positive charge concentrated at the centre Atom solid sphere with no empty space Atom mostly empty space Electrons embedded in the ball of positive charge Electrons outside the nucleus Mass spread throughout Mass concentrated at the centre 2. Both have positive charges (1), both have (negative) electrons (1), neither has neutrons (1) – Don’t like Q as Protons and Neutrons are not discovered yet 3. most alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil (1), the mass of the atom is in the nucleus or most of the atom is empty space (1). Some alpha particles were deflected / reflected (1), the atom has a positively charged nucleus (1) Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Post 1890 discoveries 1890 1900 1897 – Electrons discovered 1910 1920 1930 1940 1913 – Bohr Model 1. The discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model 1897 – JJ Thompson 1909 – E Rutherford 2. the Nuclear model using alpha developed the Plum developed the particle scattering Pudding model Nuclear model 3. Bohr’s revision of the nuclear using the alpha particle scattering model experiment Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Bohr’s Changes Ernest Rutherford’s back-scattering experiment resulted in the acceptance of his Nuclear Model Nuclear Model + Revised Nuclear (Bohr) Model In 1913, Niels Bohr revised Rutherford's model + Electrons are randomly distributed What 2 changes did Bohr make to the Nuclear Model? (Level (5), 2) 1. Electrons orbit the nucleus 2. Electrons are at specific distances from the nucleus Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Post 1890 discoveries 1890 1900 1910 1920 1918 – Protons discovered 1897 – Electrons discovered 1930 1940 1932 – Neutrons discovered (James Chadwick) 1913 – Bohr Model 1. The discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model 1897 – JJ Thompson 1909 – E Rutherford 2. the Nuclear model using alpha developed the Plum developed the particle scattering Pudding model Nuclear model 3. Bohr’s revision of the nuclear using the alpha particle scattering model experiment 4. Protons and Neutrons Wednesday, 08 June 2022 Post 1890 discoveries The Plum Pudding Model 1890 1900 The Nuclear model 1910 1920 1918 – Protons discovered 1897 – Electrons discovered 1930 1940 1932 – Neutrons discovered (James Chadwick) 1913 – Bohr Model 1. The discovery of electrons and the plum pudding model 1897 – JJ Thompson 1909 – E Rutherford 2. the Nuclear model using alpha developed the Plum developed the particle scattering Pudding model Nuclear model 3. Bohr’s revision of the nuclear using the alpha particle scattering model experiment 4. Protons and Neutrons Timeline Review Wednesday, 08 June 2022 1803 1897 1907 1913 John Dalton JJ Thompson Ernest Rutherford Niels Bohr XX − − − X XX atoms are positivelycharged spheres with negative electrons embedded throughout. Date Particle 1897 Electron 1918 Proton 1932 Neutron + XX atoms are tiny spheres that could not be divided + + XX − X − the atom has a positively charged nucleus, most of the atom is empty space electrons orbit at specific distances from the nucleus Additional Notes Discovered by James Chadwick Wednesday, 08 June 2022 On mini whiteboards: Plenary B 1. Which diagram shows the plum pudding model of the atom? 2. Which diagram shows the model of the atom developed from the alpha particle scattering experiment? 3. Which diagram shows the model of the atom resulting from Bohr’s work? Extension In your book Chadwick’s experimental work on the atom led to a better understanding of isotopes. Explain how his work led to this understanding (Level (6), 3). Chadwick discovered neutrons (1) isotopes have the same number of protons (atomic number) (1) but with different numbers of neutrons (or different mass numbers) (1) C A