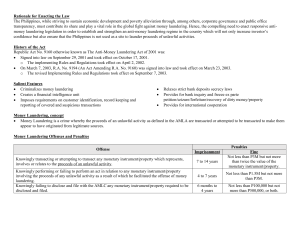
Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2001 (R.A 9160 as amended by R.A 9194, R.A 10167, R.A 10365) - Money Laundering has been criminalized Purposes: a. To protect b. To ensure c. To extend Money Laundering. A crime whereby the proceeds of unlawful activity have been transacted, thereby making them appear to have originated from legitimate sources Money Launderer. Any person that any monetary instrument or property represents involves, or relates to, the proceeds of any unlawful activity. 3 Basic Steps in Money Laundering 1. Placement. The launderer inserts the dirty money into a legitimate financial institution usually in the form of cash bank deposits 2. Layering. Involves sending money through the various financial transaction to change its form and make it more difficult to follow. It consists of bank-to-bank transfers, changing currency, or purchasing high-value items. This is the most complex step. 3. Integration. The money re-enters the mainstream economy in a legitimate-looking form appearing to have come from some legitimate transaction. Ways to Prevent Money Laundering 1. Customer identification. Anonymous accounts, those under fictitious names, and similar accounts are prohibited. 2. Record Keeping. All records of all transactions of covered institutions must be safely stored for 5 years. In closed accounts, records on customer identification and correspondence shall be preserved for 5 years from the date of closing. 3. Reporting of Covered and Suspicious Transactions. Covered institutions shall report to AMLC all covered and suspicious transactions within 5 days from the occurrence, therefore. The extension can only be up to 15 working days Covered Entities/Persons. Under Se.3(a) of the AMLA, the following are covered entities or persons who are obligated to report covered ad suspicious transactions: 1. Persons supervised or regulated by the BSP – Banks, non-banks, etc. 2. Persons supervised or regulated by the Insurance Commissions – Insurance companies, insurance agents, etc. 3. Persons supervised or regulated by SEC – Securities dealers, mutual funds, etc. 4. Designated Non-Financial and Professions – Jewelry dealers, company services providers, persons who are subject to the exception under Sec 3 (a) par 2 5. The Land Registration Authority and all its Registries of Deeds with respect to covered real estate transactions Professionals Excluded from “Covered Persons” - “Covered persons” shall exclude lawyers and accountants acting as independent legal professionals in relation to information concerning their clients or where disclosure of the information would compromise client confidences or attorney-client relationship Covered Transaction - Is a single series, or combination of transactions of more than P4 000 000 r an equivalent amount in foreign currency based on the prevailing exchange rate within 5 consecutive banking days Refers to a single, series or combination, or pattern of unusually large and complex transactions of more than P4 000 000 especially cash deposits and investments having no credible purpose or origin, underlying trade obligations or contract Covered Transactions Transaction in cash or other equivalent monetary instruments Transactions by dealers of jewelry precious materials and precious stones Real estate transactions Amount Exceeding P500 000 Term Within 1 banking day Excess of P1 000 000 Excess of P500 000 Within 15 days from the date of registration of the transaction Suspicious Transactions - A transaction, regardless of the amount involved where any of the following circumstances exists 1. There is no underlying legal or trade obligation, purpose, or economic justification. 2. Client is not properly identified. 3. Amount involved is not commensurate with the business or financial capacity of the client 4. Taking into account all known circumstances, it may be perceived that all client’s transaction is structured in order to avoid being subject to reporting requirements under AMLA 5. Any circumstance relating to the transaction which is observed to deviate from the profile of the client and/or the client’s past transactions with the covered person 6. The transaction is anyway related to an unlawful activity or any money laundering activity or offense that is about to be committed, is being, or has been committed. 7. Any transaction that is similar, analog, or identical to any of the foregoing Revised IRR of R.A 9160) Prohibited Acts During Reporting of Covered or Suspicious Transactions 1. Communicating to any person or media about such fact 2. Publish or air such report by the mass media, e-mail, or another device Immunity from Other laws 1. R.A No. 1405 – Act Prohibiting Disclosure of Deposits 2. R.A No. 6426 – Foreign Currency Deposits 3. R.A No. 8791 – General Banking Law Predicate Crimes to Money Laundering (“Unlawful Activities”) - Kidnapping for Ransom Robbery and Extortion Piracy on High Seas Qualified Theft Swindling Under Article 315 and Other Forms of Swindling Exception - Safe Harbor Provision – No administrative, criminal, or civil proceedings shall lie against any person for having made a covered transaction report in the regular performance of his duties and in good faith Prosecution of Money Laundering Cases - The prosecution shall proceed independently. Rationale: The elements of money laundering are separate and distinct from the elements of unlawful activity. The latter need not be established by proof beyond a reasonable doubt in the cause for money laundering. Policy Against Political Harassment - The AMLA shall not be used for political prosecution or harassment or as an instrument to hamper competition in trade and commerce No case for money laundering may be filed against and no assets shall be frozen, attached, or forfeited to the prejudice of a candidate for an electoral office during an election period. Jurisdiction of Money Laundering Cases - All cases on money laundering RTC Those committed by public officers and private persons who are in conspiracy with such public officers shall be under Jurisdiction of the Sandiganbayan Anti-Money Laundering Council - Tasked to implement AMLA Composed of: 1. Governor of BSP as Chairperson 2. Commissioner of the Insurance Commission and the Chairperson of SEC, as members *The AMLC shall act unanimously in the discharge of its functions Power to Freeze Accounts - The power of AMLC to freeze accounts has been deleted under R.A No. 9164 However, the CA may issue a Freeze order under the following conditions: 1. Petition from the AMLC 2. Court of Appeals must determine the probable cause that is related to any unlawful activity in accordance with the AMLA 3. The FO shall be effective immediately 4. The FO shall be for a period not exceeding 6 months *The Court of Appeals should act on the petition to freeze w/in 24 hours from filing. If the application is filed a day before a non-working day, the computation of the 24-hour period shall exclude such a day Nature of Freeze Order - - A FO is an extraordinary and interim relief issued by the Court of Appeals to prevent the dissipation, removal, or disposal of properties that are suspected to be the proceeds od, or related to unlawful activities Its objective of a freeze is to temporarily preserve monetary instruments or property that are in any way related to unlawful activity Remedy Against Freeze Order - A person whose account has been frozen may file a motion to lift the freeze order and the court must resolve this motion before the expiration of the order No court shall issue a temporary restraining order or a writ of injunction against any freeze order except the Supreme Court Authority of AMLC to Inquire into and Examine Bank Deposits - The AMLC may inquire about or examine particular deposit or investment, including related accounts, with any banking institution or non-bank financial institution When Court Order Required - In cases of violations of AML, when it has been established upon ex parle application that there is probable cause that the deposits or investments including related accounts involved are related to: 1. An Unlawful Activity 2. A Money-Laundering offense When No Court Order Required 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Kidnapping Violation of the Comprehensive Dangerous Act High Jacking Destructive Arson and Murder Terrorism Pre-Existing Case Not Required - Inquiry into deposits under Sec. 11 does not require a pre-existing criminal case Who Shall Report Suspicious Transactions? - - Suspicious transactions shall be reported by covered persons, natural or judicial: a. Acting as a formation agent or juridical persons b. Acting as a director or corporate secretary of a company Persons who provide any of the following services a. Managing client money, securities, or other assets b. Management of bank, savings, or securities c. Organization of contributions for the creation, operation, or management of companies d. Creation, operation management of juridical persons or arrangements, and buying and selling business entities When should covered persons report suspicious transactions? - - Per Republic Act No. 9160 Within 5 working days from the occurrence thereof, unless the Supervising Authority concerned prescribes a longer period not exceeding 10 working days Per Republic Act No. 10365 Within 5 working days from the occurrence thereof, unless the AMLC prescribes a different period not exceeding 15 working days