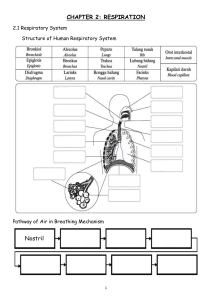
Notes Breathing is the process of taking in and pushing out air. Taking in air is called inhalation. Pressure in the chest decreases and lungs volume increases. Pushing out air is called exhalation. Pressure in the chest increases and the lung volume decreases. Air enters the respiratory system through the nose and mouth. It passes the voice box into the trachea and two bronchi. The bronchi goes into the lungs where they divide into small bronchioles. Then these lead into many alveoli’s where gas exchange takes place. The lungs are enclosed at the front back and sides within the ribcage at the base of the chest cavity the diaphragm. Inhalation. Inhalation results from the negative pressure in the lungs caused by contraction of the diaphragm, which causes it to move downwards and to expand the chest cavity. Exhalation. Exhalation is the flow of the breath out of an organism. It is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing. This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, as well as the internal intercostal muscles, which lower the rib cage and decrease thoracic volume. As the thoracic diaphragm relaxes during exhalation it causes the tissue it has depressed to rise superiorly and put pressure on the lungs to expel the air. Difference between inhaled and exhaled air. Oxygen- There is more oxygen inhaled than exhaled air. Carbon dioxide- there is more carbon dioxide inhaled in the air. Nitrogen and other gasses- These gasses stay the same, as they are not involved in respiration. Heat- Exhaled air is usually warmer than inhale air. Water vaporexhaled air usually has more water vapor than inhaled air as water is released in respiration and some is breathed out. Characteristics of respiratory surface Large and thin- they are large for diffusion and thin to diffuse. Moist- The surfaces are moist gasses have to dissolve in moisture before they diffuse. Supplied with gasses- Gasses are brought to and from the respiratory surface by breathing. Supplied with blood- respiratory surfaces are well supplied with blood vessels to transport to and from the surface. Gaseous exchange in mammals In mammals, gas exchange occurs in the lungs in the alveolus region. In the nasal cavity, the warming of air takes place and then the air is humidified and moves into the lungs through the track called trachea. In the lungs, air travels through bronchi and reaches the bronchioles, which have the alveoli where gas exchange occurs. Gaseous exchange in fish Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment. Gaseous exchange in amphibians Amphibians live in two environments air and water and are therefore adapted to gaseous exchange in land and in water. They also show change of respiratory surfaces and organs as they develop from gills in tadpoles to lungs, skin and mouth in adults. Gaseous exchange in plants Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment. What is respiration? Respiration is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within tissues, and the removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. The physiological definition of respiration differs from the biochemical definition, which refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) by oxidizing nutrients and releasing waste products. Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thus life in animals, the processes are distinct: cellular respiration takes place in individual cells of the organism, while physiologic respiration concerns the diffusion and transport of metabolites between the organism and the external environment. What happens when living things respire? Respiration is the process that all living things go through to create the energy they need to live. This happens in the cells so it is also called cellular respiration. It usually involves exchanging two gases oxygen and carbon dioxide. The cells take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide.