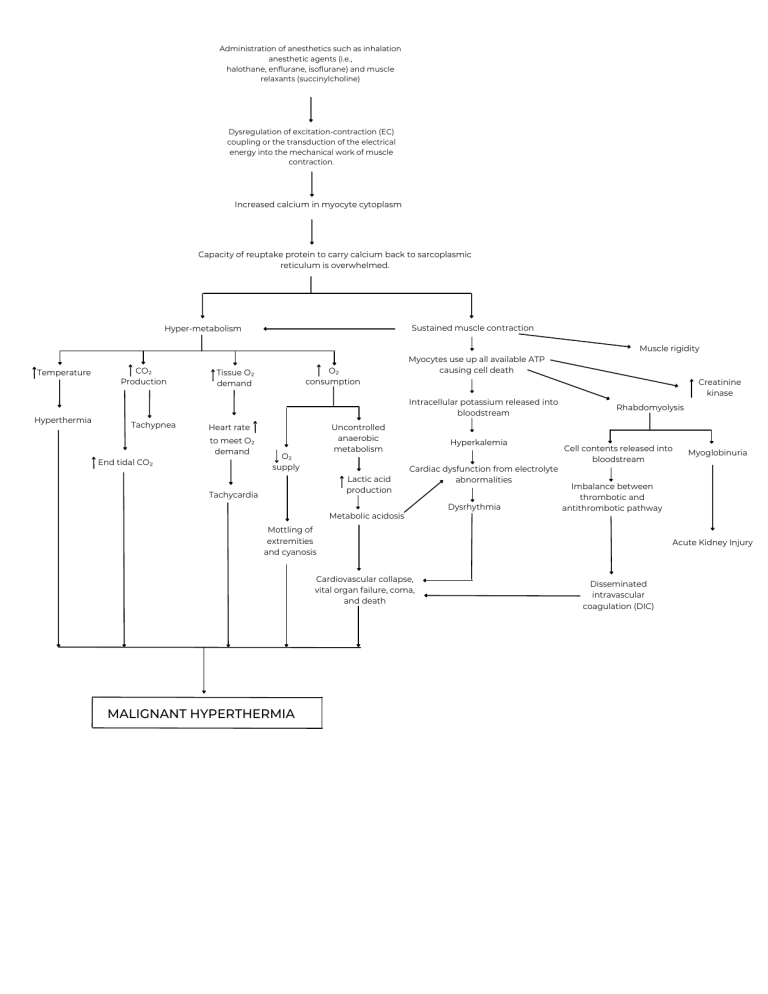
Administration of anesthetics such as inhalation anesthetic agents (i.e., halothane, enflurane, isoflurane) and muscle relaxants (succinylcholine) Dysregulation of excitation-contraction (EC) coupling or the transduction of the electrical energy into the mechanical work of muscle contraction. Increased calcium in myocyte cytoplasm Capacity of reuptake protein to carry calcium back to sarcoplasmic reticulum is overwhelmed. Sustained muscle contraction Hyper-metabolism Muscle rigidity Temperature Hyperthermia CO₂ Production O₂ consumption Tissue O₂ demand Myocytes use up all available ATP causing cell death Intracellular potassium released into bloodstream Tachypnea Uncontrolled anaerobic metabolism Heart rate to meet O₂ demand End tidal CO₂ O₂ supply Lactic acid production Tachycardia Hyperkalemia Cardiac dysfunction from electrolyte abnormalities Metabolic acidosis Dysrhythmia Creatinine kinase Rhabdomyolysis Cell contents released into bloodstream Imbalance between thrombotic and antithrombotic pathway Mottling of extremities and cyanosis Cardiovascular collapse, vital organ failure, coma, and death MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA Myoglobinuria Acute Kidney Injury Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)