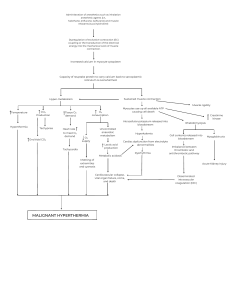
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 1. Neurotransmitter must stimulate muscle. This happens at the neuromuscular junction. Axon of neuron, ‘Synaptic bulb’ AcH Muscle Formed by Muscle fiber membrane Contain AcH The space = synapse, synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter = Acethylcholine. Stored in vesicles on the distal end of the axon. 1. A nerve impulse/action potential reaches the synaptic bulb 2. Calcium ions diffuse into the terminal. 3. This causes the vesicles to move to the cell membrane, fuse with it and release AcH into the synaptic cleft. 4. AcH binds to receptor proteins on the muscle side of the junction. 5. This causes an impulse in the muscle that travels along and around the muscle. Motor end plate = membrane of muscle fiber. Receptor proteins Depolarizes = becomes less negative 6. This muscle impulse/action potential moves along the sarcolemma, into transverse tubules and into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Action potential = A spike of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell 7. Calcium ions are released into sarcoplasmic reticulum 8. Calcium ions expose binding sites on actin. 9. Myosin heads bind to the binding sites and form cross bridges. 10. Myosin heads lose ADP and P, change shape and pull actin to the center of the sarcomere… this results in the contraction of the muscle. 11. ATP forms, binds to myosin head, cross bridges break and muscle relaxes Muscle relaxes Muscle contracts http://www.wiley.com/college/pratt/0471393878/student/animations/actin_ myosin/actin_myosin.swf http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter10/animation__breakdown_of_atp_and_crossbridge_movement_during_muscle_contraction.html http://www.dnatube.com/video/5034/Contraction-of-muscle-function-ofneuromuscular-junction http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter10/a nimation__action_potentials_and_muscle_contraction.html http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/muscle.html