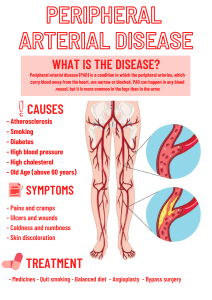
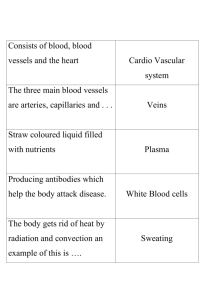
Vascular - Capillary refill < 3s - Poor arterial circulation if is delayed - Hypotension, sepsis, peripheral arterial disease - Circulation in the legs - Valves push the blood back up to the ivc - Prevents backflow - If valves aren't working well → varicose veins - Assessing vascular system - Assess pulses - Arms & legs are the same amount of hair, are they the same size? - Allen's test: assessing the arterial blood supply to the hand - Radial artery & ulnar artery - Recommended before blood pressure ** should know ** - Hand in fist. Occlude both arteries, let color come out of the wrist, then remove the hand. Color should come back quickly. - This is done so that you can: - A. Arterial catheter in artery - B. Take blood pressure - C. Take blood from ulnar artery - Swollen feet and legs: - Venous obstruction / is inadequate. Not enough going back up - Arterial insufficiency - Clinical findings: pain, cool and pale, decreased pulses, claudication - Peripheral arterial disease: - Management: gentle exercise such as walking (helps form collateral vessels), smoking cessation, socks, - Collateral vessels: vessels that occur parallel to existing vessels - Happens when there is inadequate circulation - Venous ulcers: - Wound is shallow, irregular edges, base is red (veins are more shallow) → blood is pooling - Arterial ulcers: - Smooth edges, deeper, base will be pale (arteries are more deep) - Femoral pulse: - Should be in supine position, bent at knee, and spread out. Frog like position - Surgical procedures put a person at risk for development of dvt - Knee & hip procedures (replacements) - Clotting usually happens in the lower extremities - Prevention: sequential device, do not massage the legs, raise legs slightly, ambulate asap. - Raynaud's syndrome - Fingers will look pale - Tell pt. to wear gloves, movement, smoking cessation, avoid stress - Difference between carotid pulse vs jugular vein - Carotid should be easily palpable - Should not be able to feel jugular vein at all because there is more muscle within the wall - Peripheral artery disease: - Prevent arterial ulcer- break in the skin - Apply moisturizer to the feet. - Feet kept dry - Socks that breathe - Shoes are fitted appropriately with lots of padding - Make sure they are seeing a podiatrist regularly - Avoid pedicures - Pulse deficit - Apical - radial Abdomen - Inspection: contour & symmetry, scars looking at umbilicus for hernias / discharge. - Percussion if filled with air: tympanic - Filled with fluid: dull - Auscultation: High pitched gurgling → use diaphragm - If no bowel sounds, listen for 5 min - Palpating: light palpation → rub in circular motion - Right lower is liver, gallbladder - Left upper is spleen kidney, pancreas - Left lower is sigmoid colon, Ascites - Assessing: measure abdominal circumference - compare it day to day - Fluid collects in spaces within abdomen Diverticulitis - Eat foods high in fiber - Whole grains, sweet potatoes, berries, beans, broccoli Thrombo stockings: not too tight or too loose → no wrinkles GERD: avoid eating spicy, drinking caffeine, alcohol Post op client - belly surgery. You expect to not hear bowel sounds. Continual assessments every so hours - Going to be listening for bowel sounds - Signs of peristalsis: expect gas, did they pass a stool? - Ileus: temporary lack of contractions in intestines. Bloated, nausea, vomiting Gerd: - What position do you want them in at night - Left side → reduce nighttime heartburn Hepatitis C: - Watch for people who use injectable drugs - Trade sex for drugs - Multiple tattoos - Blood borne pathogen Client reports pain in the flank- Kidney infection, stone, nephrolithiasis There will be no questions on lymphatics on the exam - Need to know what's in each quadrant