Heart, Neck Vessels, and Peripheral Vascular defintions
advertisement
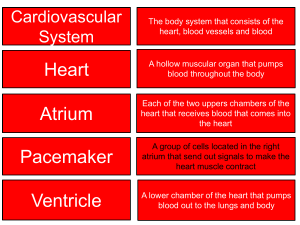
HEART, NECK VESSELS, AND PERIPHERAL VASCULAR SYSTEM DEFINITIONS Kim and Stephanie NSG 173 Aneurysm localized, blood-filled dilation of a blood vessel caused by disease or weakening of the vessel wall Angina spasmodic, choking, or suffocating pain Apical Relating to the apex of a pyramidal or pointed structure Arrhythmia An irregularity in the force or rhythm of the heartbeat Arteriosclerosis Any of a group of chronic diseases in which thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the arterial walls result in impaired blood circulation. Also called arterial sclerosis Bradycardia A slowness of the heartbeat, usually under 60 beats per minute in adults Bruits an abnormal sound or murmur heard in auscultation Diastole the rhythmic period of relaxation and dilation of a chamber of the heart during which it fills with blood Edema an abnormal accumulation of fluid in intercellular spaces of the body Embolism the sudden blocking of an artery by a clot or foreign material which has been brought to its site of lodgment by the blood current. Fibrillation a small, local, involuntary, muscular contraction, due to spontaneous activation of single muscle cells or muscle fibers whose nerve supply has been damaged or cut off. Myocardial infarction Necrosis of a region of the myocardium caused by an interruption in the supply of blood to the heart, usually as a result of occlusion of a coronary artery. Also called cardiac infarction. Orthostatic hypotension A form of low blood pressure precipitated by moving from a lying or sitting position to standing up straight Palpitation a subjective sensation of an unduly rapid or irregular heartbeat Pericardial pertaining to the pericardium that surrounds the heart. Phlebitis Inflammation of a vein Precordium the region of the anterior surface of the body covering the heart and lower thorax Stroke volume The volume of blood pumped out of one ventricle of the heart in a single beat Systole the contraction, or period of contraction, of the heart, especially of the ventricles, during which blood is forced into the aorta and pulmonary artery Tachycardia abnormally rapid heart rate Thrombophlebitis Inflammation of a vein caused by or associated with the formation of a blood clot.