Earth Structures Study Guide: Rock Cycle & Plate Tectonics
advertisement

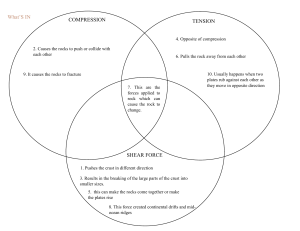
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: __________ Period: _____ Earth Structures Study Guide - Comp Sci 2 DUE ON: ____________________ 1. Review all vocabulary terms. You may use Quizlet to study the vocabulary terms for this unit. There are 3 study sets: ● ● ● Dating Relative-Age & Absolute Age Earth's Interior & The Rock Cycle Plate Tectonics 2. Name and describe the 4 layers of Earth (list from outermost layer to innermost layer). ● _____________________________________________________________________________________________ ● _____________________________________________________________________________________________ ● _____________________________________________________________________________________________ ● _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the lithosphere. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What are the 3 types of rocks? ___________________________ ___________________________ 5. Which crust is more dense? Underline one: ___________________________ continental crust oceanic crust 6. Explain how each rock is formed in the rock cycle. Using the word bank provided, place each word in its correct location on the diagram. Some terms may be used more than once. cementation compaction cooling erosion melting pressure weathering heat 7. How is sediment formed? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Which events of the rock cycle occur on Earth’s surface? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Which events of the rock cycle occur under Earth’s surface? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Using the word bank provided, place each word in its correct location on the diagram of Earth’s layers. asthenosphere continental crust crust inner core lithosphere lower mantle mantle oceanic crust outer core upper mantle 11. Draw a line to match the plate boundary with the type of stress that occurs at the boundary? Convergent boundary Shear Divergent boundary Tension Transform boundary Compression 12. Explain the Theory of Continental Drift. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. At what plate boundaries can volcanoes form? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Describe the plate boundaries that form mountains. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Identify and describe the movement of each plate boundary shown above. A. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ B. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ C. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. Explain how a mid-ocean rift is formed. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Explain convection currents in Earth’s mantle and how they move the tectonic plates. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. Define deforestation. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 19. Define Urbanization. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 20. Define desertification. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 21. What is erosion? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 22. What are the two ways that scientists determine the age of the earth? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Explain how scientists determine the relative ages of rocks. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the law of superposition? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 25. Explain how scientists find the absolute age of the earth? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ This study guide is a grade! When is this study guide due? _________________________ 26. Using the word bank provided, place each answer in its correct location on the concept map. absolute age correlation half-life inclusion index fossils isotopes radioactive decay relative age superposition unconformity uniformitarianism 27. Which layer(s) experienced erosion? _____________________________________________ 28. Which layers are folded? _____________________________________________ 29. Where is the fault line? _____________________________________________ Additional Notes: __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Dating Relative-Age & Absolute Age geologic time scale a chart representing all of the individual time periods in Earth’s history divided into units called eons, eras, periods, and epochs Law of Superposition the principle that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are on the bottom fault a fracture line between two blocks of rock intrusion igneous rock, formed from magma that cools and solidifies under Earth's surface extrusion extrusive rock, formed above the surface of the crust relative age the age of rocks and geologic features compared with other rocks and features nearby radioactive dating scientists measure the ratio of radioactive isotopes in a mineral to determine how much time has passed since the mineral formed uniformitarianism processes we see acting today acted in the past, and explain what we see in the geologic record deforestation the purposeful clearing of forested land urbanization the redistribution of populations from rural (farming or country life) to urban (town and city) life desertification the spread or encroachment of a desert environment into a non desert region weathering a natural process that slowly breaks apart or changes rock correlation matching rocks and fossils from separate locations inclusion a piece of an older rock that becomes part of a new rock fossil the preserved remains or evidence of ancient living things index fossil a fossil that represents a species that existed on Earth for a short length of time, was abundant, and inhabited many locations unconformity a surface where rock has eroded away, producing a break, or gap, in the rock record Earth's Interior & The Rock Cycle sediment rock and mineral fragments that are loose or suspended in water magma molten rock when it is inside Earth rock a naturally occurring solid mixture of minerals or grains erosion break down exposed rocks by water, wind, or ice rock cycle the series of processes that continually change one rock type into another sedimentary rock type of rock made of layers that are pressed or cemented together metamorphic rock type of rock that forms when a parent rock is squeezed, heated, or exposed to hot fluids igneous rock type of rock that forms when magma or lava cools and hardens Earth's layers crust, mantle, outer core, inner core core the dense metallic center of Earth crust rocky, outermost layer of Earth mantle thick middle layer in the solid part of Earth inner core a dense ball of solid iron crystals outer core the liquid metallic center of Earth lithosphere rigid layer that includes the crust and uppermost mantle asthenosphere the plastic layer within the mantle convection currents the cycle of heating, rising, cooling, and sinking of fluids oceanic crust crust under oceans, more dense than continental crust continental crust crust on land, less dense than oceanic crust plastic capable of being molded Plate Tectonics tectonic plate rigid plates that make up Earth's crust convergent boundary where two plates move toward each other divergent boundary where two plates move apart from each other transform boundary where plates slide horizontally past each other subduction where one plate slides under another sea floor spreading new oceanic crust forms along a mid-ocean ridge and older oceanic crust moves away from the ridge Theory of Plate Tectonics states that Earth’s crust is broken into rigid plates that move slowly over Earth’s surface Pangaea a former “supercontinent” that included all the present continents in one large landmass compression stress resulting from squeezing shear stress resulting from parallel forces acting in opposite directions tension stress that pulls something apart continental drift the hypothesis that continents are in constant motion on the surface of Earth subduction zone the area where one plate slides under another