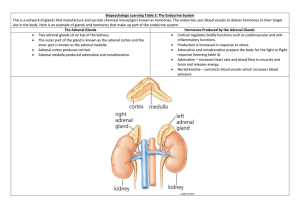
ADRENAL FUNCTION Embryology and Anatomy 2 Embryologically distinct but conjoined glands Outer: Adrenal Cortex Inner: Adrenal Medulla G-Zone - Refers to the zona glomerulosa (Outermost layer which is 10%) - Synthesizes mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) - Functions: Sodium Homeostasis Potassium Homeostasis Acid-Base Balance Cell: Distinct in a way that they have small cytoplasmic: Nuclear Ratio. With dense chromatin with intermediate lipid inclusions F-Zone - Zone Fasciculata (75%) - Synthesizes glucocorticoids (cortisol) - Function: Glucose homeostasis - Cells has a high cytoplasmic to nuclear ratio - It Generates DHEA (Dehydroxyepiandrosterone) which plays a role in zona reticularis R-Zone - Zona Reticularis - Innermost layer (10%) - Sulfates DHEA to DHEAS - Cells: Sharply demarcated with lipid-deficient cords of irregular, dense cells with lipofuscin deposits. DHEA - Serves a raw material Cortex - Cortisol, Sex Hormones Medulla - Epinephrine and norepinephrine CORTISOL - Principal glucocorticoid. - 90% is inactive (requires hypoglycemia). - Increases blood glucose level. - The only adrenal hormone that inhibits the secretion of ACTH. - With anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions. - Secretion is diurnal (6am-8am). - Sample that can be used in analysis: Serum, plasma, saliva, and urine. Urinary Metabolites: 17-Hydroxycorticosteroid - Measure by Porter-Siber Method - Reagent: Phyenyl hydrazine in 17-Ketogenic Steroids All hormones produced by the adrenal cortex are steroids (hormones that are synthesized by cholesterol making them appear with fatty characteristics). Clinical Disorders Hypercortisolism “Cushings Syndrome” - Excessive production of ACTH or Cortisol - Overuse of corticosteroids. Signs: Weight gain but with thin extremities. Hyperglycemia Thinning of the skin Lymphocytopenia Diagnosis: Appearance of the Clinical Symptoms Laboratory Findings: Cortisol excess Loss of Diurnal Rhythm Suppression Resistance Urine Free Cortisol (and/or metabolites) Screening Test: 24hr urinary free cortisol test Overnight dexametha HYPOCORTISOLISM Primary Hypocortisolism (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency) - Also called Addison’s disease - It is caused by 90% destruction of the adrenal cortex - Screening test: ACTH Stimulation Test - Associated with Koilonychia or spooning of the nails with bronze pigmentation. Secondary Hypocortisolism (SAI) - It is due to hypothalamic-pituitary insufficiency - Screening test: ACTH Stimulation Test CORTEX STEROIDOGENESIS - Controlled by 3 factors: Substrate Availability Enzyme activities Inhibitory Feedback loops - All adrenal steroids are derived by sequential enzymatic conversion of a common substrate, CHOLESTEROL (made by “pregnenolone” which is the precursor or generally bad cholesterol). - Adrenal Parenchymal cells: Functions in “Storage”. Disorders Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) - Inherited family of enzyme disorders causing decreased cortisol production. - 5 enzymes: P450 (StAR deficiency) – most fatal (Deficiency in aldosterone and DHEA) - Symptoms: Shock (hypovolemic/hypoglycemic) Salt-washing Anomalous sexual development (Boy but with female characteristics). Hirsutism Infertility Impotence – Sexual drive issues Infertility – Sex cell issues Enzyme Deficiency 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency