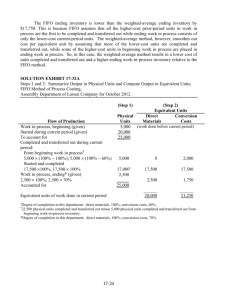
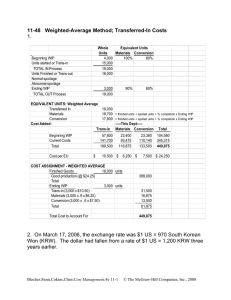
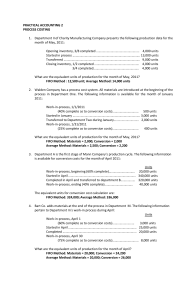
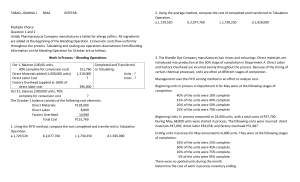
Problem 8 – Process Costing with Spoilage Kristina Company, which manufactures quality paint sold at premium prices, uses a single production department. Production begins with the blending of various chemicals, which are added at the beginning of the process, and ends with the canning of the paint. Canning occurs when the mixture reaches the 90% stage of completion. The gallon cans are then transferred to the Shipping Department for crating and shipment. Labor and overhead are added continuously throughout the process. Prior to May, when a change in the process was implemented, WIP inventories were insignificant. The change in the process enables greater production but results in material amounts of WIP for the first time. The company has always used the WA method to determine equivalent production and unit costs. Now, production management is considering changing from the WA method to the FIFO method. Spoilage is detected when the mixture reaches the 60% stage of completion. Normal spoilage is equal to 2% of units transferred out. The following data relate to actual production during the month of May: COSTS FOR MAY Work-in-process inventory, May 1 (4,000 litres 25% complete): Direct materials-chemicals Direct labor Factory overhead May costs added: Direct materials-chemicals Direct materials-cans Direct labor Factory overhead UNITS FOR MAY - Litres Work-in-process inventory, May 1 (25% complete) Sent to Shipping Department Started in May Work-in-process inventory, May 31 (80% complete) $ 45,600 6,250 18,750 228,400 7,000 35,000 105,000 4,000 19,350 21,000 5,000 Required – Calculate the cost of units transferred out and the cost of abnormal spoilage using (a) FIFO and (b) weighted average. © CMA Ontario 2011