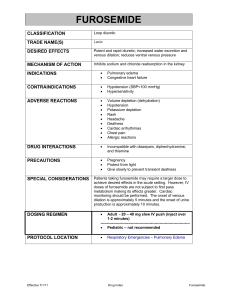
Furosemide Generic name: Furosemide (oral/injection) Brand name: Lasix Drug class: loop diuretic (water pill) Indication: High blood pressure (hypertension) and edema Route: Furosemide is taken by mouth and the injection is injected into the muscle or given as an infusion into the vein Adverse Effects: Taking more than recommended can cause irreversible hearing loss Furosemide causes urination more often, so you can possibly get dehydrated easily Avoid getting up too fast from a sitting or lying position, avoid becoming dehydrated, drinking alcohol with this medicine can cause side effects Nursing implications/patient teaching: recheck blood pressure, lung sounds, and monitor weight, amount/location of edema, skin turgor, and mucous membranes. Place patient on fall risk precautions, avoid prolonged exposure to sun (furosemide make skin sensitive to sunlight). IV Administration: Inject 20 to 40 mg of furosemide slowly over 1 to 2 minutes; in pediatric patients inject no faster than 0.5 mg/kg/minute IV compatibility: furosemide is compatible with bicarbonate solution, heparin, insulin, morphine, and nitroglycerin. Furosemide is incompatible with amiodarone, cisatracurium, haloperidol, midazolam, and urapidil. IV dilution: dilute the dose with 50-250 mL of a compatible solution and infuse at a maximum rate of 4mg/minute Diltiazem Generic name: Diltiazem Brand name: Cardizem, Cartia XT, Dilacor XR, Dilt-CD, Diltia XT, Matzim LA, Tiazac Drug class: Calcium channel blocking agent, Group IV antiarrhythmics Indication: hypertension (high blood pressure), angina (chest pain) and certain heart rhythm disorders Route/Frequency: Take PO; do not crush, chew, break or open an extended-release diltiazem tablet or capsule. The tablets is usually taken 3 to 4 times a day. The extended – release capsule and tablet are taking 1 or 2 times a day. Take the medicine around the same time daily. Adverse effects: Overdose symptoms include slow heartbeat, weakness, chest pain, shortness of breath or fainting Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice as it may interact with diltiazem and lead to side effects. Diltiazem may impair your thinking or reactions, avoiding drinking alcohol, avoid taking herbal supplements containing St. John’s wort Nursing implications/patient teaching: check blood pressure, heart rate and cardiac monitor, assess BUN/Creatine, liver function (AST, ALT) labs. Make position changes slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension, patient should be listed as a fall risk, may cause drowsiness or dizziness. Administer before meals and at bedtime. Direct patient to take medicine at the same time daily. Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice. IV administration: 0.25 mg/kg; may repeat in 15 mins with a dose of 0.35 mg/kg. may follow with continuous infusion beginning at 10mg/hr. continuous IV infusion immediately following the IV bolus IV compatibility: Compatible with albumin, alemtuzumab, alfentanil IV dilution: the common dilution is 125 mg of diltiazem injection added to 100mL of an appropriate diluent which would give a final concentration of 125 mg/125mL (1mg/mL). Digoxin Generic name: Digoxin Brand name (Trade name): Lanoxin, Toloxin Drug class: Antidysrhythmics, cardiac glycosides Dose: 0.05 mg/mL Route: Can be given PO, IM, IV Indication: heart failure, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter (slows ventricular rate), paroxysmal atrial tachycardia Action (what does the drug do): increases cardiac output (positive inotropic effect) and slows the heart rate (negative chronotropic effect) Side effects: CNS: fatigue, headache CV: arrhythmias (life threatening), bradycardia, AV block, SA block EENT: blurred vision GI: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea HEMAT: thrombocytopenia Nursing implication/patient teaching: check patient pulse and contact healthcare professional if rate is less than 60 or greater than 100. Instruct patient to take medicine as directed. Do not share medications. Inform health care professionals of any OTC medications they take. Instruct patient to keep medicine if it’s original container and not to mix in pill boxes with other medications. Review fall precautions with elderly patients and families. Notify health care professionals if patient is pregnant or is planning pregnancy. IV administration: 0.5-1mg given as 50% of the dose initially and ¼ of the initial dose in each of 2 subsequent doses at 6-12 hr. intervals IV compatibility: acyclovir, alemtuzumab, alfentanil IV dilution: may be administered undiluted; may also dilute with 1mL of digoxin in 4 mL of sterile water for injection, D5W, or 0.9% NaCl (sodium chloride). Use diluted solution immediately. Potassium Chloride Generic name: Potassium Chloride Brand name: Klor-Con, Kal Potassium, K-Tab Drug class: Minerals and electrolytes Route: PO Dosage: 40 to 100 mEq per day, orally, in 2 to 5 divided doses. Maximum single dose 20 mEq per dose. Maximum daily dose 200 mEq. Indication: hypokalemia Action (what does the drug do): used to prevent or to treat low blood levels of potassium (hypokalemia). A normal level of potassium help your cells, kidneys, heart, muscles and nerves work properly. Side effects: upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, gas, diarrhea Adverse effects: vomit that resemble coffee grounds, stomach/abdominal pain, black/tarry stools, arrhythmias, bleeding, hyperkalemia Nursing implications/patient teaching: note any allergies, history of heart or kidney problems or high levels of potassium in the blood. Note if patient is take a diuretic (water pill) or on heart/blood pressure medication. IV administration: administration should be via a volumetric infusion pump. Iv administration via a peripheral line should not exceed 40mEq/L IV compatibility: aminophylline, amiodarone, Ca gluconate, cimetidine, clindamycin, dobutamine, erythromycin, furosemide IV dilution: always dilute KCI never give a bolus or IV push.