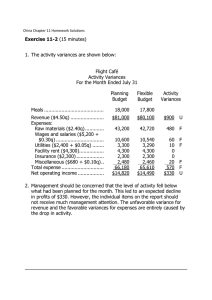
Financial Statements Forms of Business Organisations Sole proprietors: They are not only involved in trade activities but provision of services as well. Example: Individual tradesperson, such as self-employed painter or decorator. Partnerships: Here, two or more people operate a business. Example: A legal or accountancy practice. Limited Liability Company: The name usually ends with "limited" or ltd. It is a completely separate identity to the person or people who own it. Example: Aspire2 International Ltd. Budgeting Budgeting is an estimation of revenue and expenses over a specified future period of time; it is compiled and re-evaluated on a periodic basis. In business, the budgeting for operations will include the following: Preparing estimates of future sales, future expenses, future cash collections and disbursements Summarising these estimates into an income statement, balance sheet and cash flow Functions of Budgeting: Control resources - how best use limited resources effectively Communicate plans, goals, and responsibilities to various departments and stakeholders. Motivate managers and staff to strive to achieve budget goals by rewarding them with incentives allowance and bonuses. Evaluate the performance of managers for future promotion Provide visibility into the company's performance and usage of resources Ensure accountability of responsible managers Balance Sheet A Balance Sheet is a snapshot of a business's financial condition at a specific moment in time, usually at the close of an accounting period. Example : Financial Year 01 April 2019 – 31 March 2020. A balance sheet comprises assets, liabilities, and owners' or stockholders' equity. Asset is anything the business owns that has monetary value. Liabilities are the claims of creditors against the assets of the business. At any given time, assets must equal liabilities plus owners' equity. Assets Assets are subdivided into current and non – current (long-term) assets to reflect the ease of liquidating each asset. Current assets are any assets that can be easily converted into cash within one calendar year. Non – current Assets are used in connection with the business. Assets : Key Words Cash Money available immediately and is the most liquid of all short-term assets. Accounts receivables This is money owed to the business for purchases made by customers, suppliers, and other vendors. Notes receivables Notes receivables that are due within one year are current assets. Notes that cannot be collected on within one year should be considered long-term assets. Liabilities These includes all debts, loans and obligations owed by the business to outside creditors, vendors, or banks that are payable within one year, plus the owners' equity. Owners' equity is made up of the initial investment in the business as well as any retained earnings that are reinvested in the business. Liabilities : Key Words Accounts payable This includes all short-term obligations owed by your business to creditors, suppliers, and other vendors. Notes payable This represents money owed on a short-term collection cycle of one year or less. It may include bank notes, mortgage obligations, or vehicle payments. Accrued payroll and withholding This includes any earned wages or withholdings that are owed to or for employees but have not yet been paid. Example of Balance Sheet Example of Balance Sheet Budgeted Income Statement Each department, area of business, or project, will normally have its own budget. All these individual budgets will need to be gathered into a Master Budget. In order to construct a budgeted income statement, First, need to work out expected sales ie. Sales Budget. Second, need to work out production required ie. Production Budget. Third, need to work out estimated expenses ie. Operating Expenses Budget. Example of Budgeted Income Statement Sales Budget Shows the expected number of sales units during a period and the expected price per unit. Total sales = Expected sales units X Expected price per unit. Total Revenue = $41760 Production Budget Contains the amount of inventory or stock that a company must produce or purchase during a period so that sufficient inventory is available to meet customer demands. Operating Expenses Budget This includes most expenditures for operating the firm's normal line of business. Balance Sheet VS Income Statement Balance sheet and income statement are both important financial statements that detail the financial accounting of a company. The balance sheet details a company's assets and liabilities at a certain period of time, while the income statement details income and expenses over a period of time (usually one year). Flexible Budget A flexible budget adjusts or flexes with changes in volume or activity. For costs that vary with volume or activity, the flexible budget will change as it includes a variable rate per unit of activity instead of one fixed total amount. Variance Report Budgeting process involves comparing actual figures to budgeted figures. Any significant differences (or variances) needs to be investigated and explained by the manager responsible and corrective action taken. Good reasons for variances could be things like an unexpected increase in demand for the product. Bad reasons for variances could be a loss of a major order to a competitor. Controllable reasons for variances are ones that the manager has authority and responsibility for. Uncontrollable reasons for variances are ones that are outside the authority and responsibility of the manager Calculation of Variance Report Variances are either favourable or unfavourable. Favourable variances are when Actual costs are less than budgeted or Actual revenue is more than budgeted. Unfavourable variances are when Actual costs are more than budgeted or Actual revenue is less than budgeted.