PPT7 - University of North Florida
advertisement

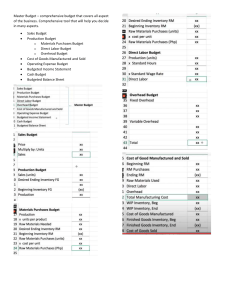
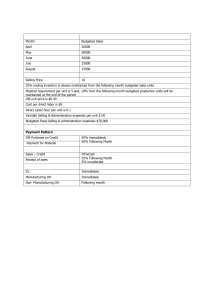
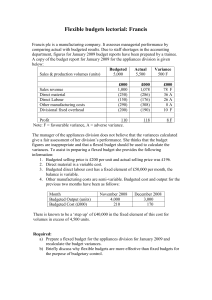
1 Chapter 7 Standard Costs Prepared by Diane Tanner University of North Florida Standard Costs What is a standard cost? The unit ‘cost’ that management believes should be incurred to produce a good or service under anticipated conditions Primary benefit Allows for comparison of standard versus actual costs Functions as a benchmark Differences are flagged for investigation if significant Standard Costs and Budgets Terminology Standard cost Standard cost of a single unit Budgeted cost Cost, at standard, of a single unit or the total number of budgeted units How are Standard Costs Developed? Formulas or recipes Price lists provided by suppliers Time and motion studies conducted by industrial engineers Union contracts Analyses of past data Insight from management Expected economic changes Ideal Versus Attainable Standards Two views when developing standard costs: Ideal standards Assumption that no obstacles to the production process will be encountered Called ‘perfection’ standards Attainable Standards Assumption that there will be occasional problems in the production process Such as equipment failure, labor turnover, and materials defects Standard Costs Standard Price is the budgeted price of the material (per RM unit), labor (per hour), and overhead for each unit of product Standard Quantity is the budgeted quantity of material (in RM quantities), labor (in hours), and overhead in a product Investigation of Standard Cost Variances Variances are not a clear sign of good or bad performance Indicate a potential problem Must be investigated if material in amount Management by exception Many reasonable explanations The End 8