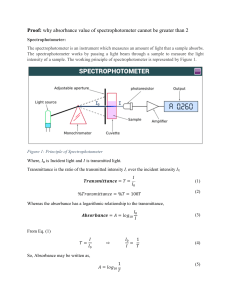
THE VISIBLE SPECTRA OF SOFT DRINKS Pre-laboratory Questions 1. Define spectroscopy. Spectroscopy is the study of interaction between radiation and matter. 2. What type of electromagnetic radiation will be used in this experiment? Visible light 3. i. Define: transmittance and absorbance. Transmittance is the fraction of incident light which is transmitted and absorbance is the quantity of light that absorbed. ii. Give the equation which shows how you mathematically convert between terms. A= -log T 4. State Beer’s Law mathematically and define each term. Beer’s Law states that the concentration of the chemical solution is directly proportional to absorption of light. A=ɛxbxc A = absorbance ɛ = molar absorptivity b = optical path length c = concentration 5. Define λmax. The wavelength of a substance has a strongest photon absorption. Questions 1. Based on Beer’s Law, when the concentration of an analyte increases, how will the following be affected? i. Absorbance Increased ii. Transmittance Decreased 2. Why is it important to first obtain the absorption spectrum of the soft drink before make a calibration curve? To obtain lambda max/wavelength of the maximum absorption. 3. What is the purpose of using the ‘blank’ solution? To identify any contamination artifically. 4. What colour(s) is/are being absorbed in you soft drinks? Blue and green