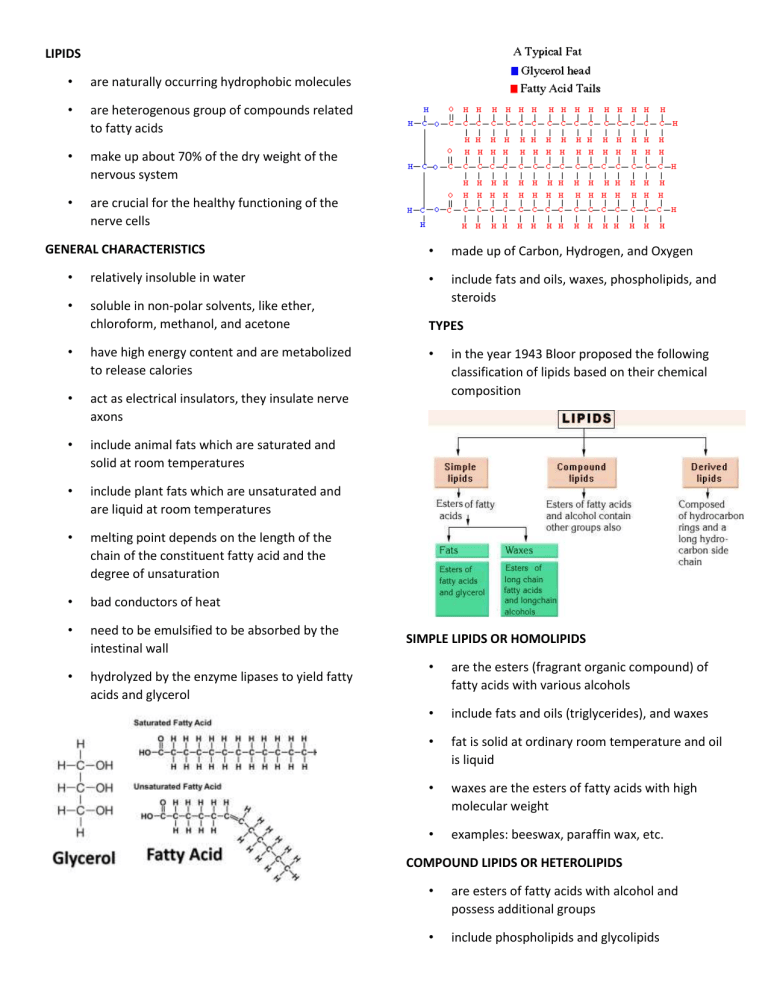
LIPIDS • are naturally occurring hydrophobic molecules • are heterogenous group of compounds related to fatty acids • make up about 70% of the dry weight of the nervous system • are crucial for the healthy functioning of the nerve cells GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS • made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids • relatively insoluble in water • • soluble in non-polar solvents, like ether, chloroform, methanol, and acetone TYPES • have high energy content and are metabolized to release calories • act as electrical insulators, they insulate nerve axons • include animal fats which are saturated and solid at room temperatures • include plant fats which are unsaturated and are liquid at room temperatures • melting point depends on the length of the chain of the constituent fatty acid and the degree of unsaturation • bad conductors of heat • need to be emulsified to be absorbed by the intestinal wall • hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipases to yield fatty acids and glycerol • in the year 1943 Bloor proposed the following classification of lipids based on their chemical composition SIMPLE LIPIDS OR HOMOLIPIDS • are the esters (fragrant organic compound) of fatty acids with various alcohols • include fats and oils (triglycerides), and waxes • fat is solid at ordinary room temperature and oil is liquid • waxes are the esters of fatty acids with high molecular weight • examples: beeswax, paraffin wax, etc. COMPOUND LIPIDS OR HETEROLIPIDS • are esters of fatty acids with alcohol and possess additional groups • include phospholipids and glycolipids • phospholipids are compound containing fatty acids and glycerol in addition to a phosphoric acid and other substituent • phospholipids can be phosphoglycerides, phosphoinositides and phosphosphingosides • phosphoglycerides are major phospholipids, they are found in membranes • example: lecithin and cephalins • phosphoinositides play important roles in lipid signaling, cell signaling and membrane trafficking • phosphosphingosides are commonly found in nerve tissue • example: sphingomyelins • glycolipids are the compounds of fatty acids with carbohydrates and contain nitrogen but no phosphoric acid • terpenes are produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers and by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies • carotenoids are organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria and fungi • are carboxylic acids consisting of a hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxyl group, especially any of those occurring as esters in fats and oils FUNCTIONS • storage compounds • important component of cell membranes structure • regulate membrane permeability • serve as source for fat soluble vitamins like A, D, E, K • act as an electrical insulators to the nerve fibers • act as cellular metabolic regulators such as prostaglandins and steroid hormones • act as signaling molecules DERIVED LIPIDS • • are the substances derived from simple and compound lipids by hydrolysis includes fatty acids, alcohols, monoglycerides and diglycerides, steroids, terpenes and carotenoids • steroids do not contain fatty acids, they are nonsaponifiable and are not hydrolyzed on heating • are widely distributed in animals, where they are associated with physiological processes