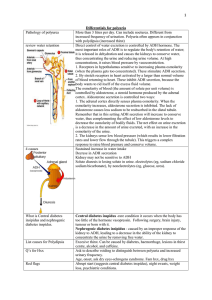
a) Glomerual filtration: water and small solutes b) Tubular resabsorption: Water, glucose, AA -> nephron -> capillary c) Tubular Secretion: H+, K+, creatinine, drugs secreted into filtrate Physiological Role of Aldosterone - Increases Na+ reabsorption by Kidney Nephron - Conserving Na+ - Reduced K+ Reabsorption - Increased Potassium loss - Retaining Na+ causes water retention -> regulates blood volume & BP Renin-Angiotensinogen System - - Each nephron has Juxtaglomerular apparatus associated with Distal tube and glomerulus JGA comprises sensory cells (macula densa) in the wall of distal tubule of nephron - Associated secretory cells that release RENIN enzyme into the glomerulal blood vessels Sensory cells continously monitor Na+ concentration in glomerular filtrate in distal tubule, and the BP in Kidney If Na+ or BP Falls -> the macula densa stimulates RENIN release from secretory cells into the blood 1) Renin enzyme acts on Angiotensinogen (ATG) and CATALYZES formation of Angiotensin I 2) ACE (Angiotensin Convertin Enzyme) converts Ang I into Angiotensin II in capillary endothelial cells in the LUNGS 3) Ang II causes vasoConstriction of peripheral BV and acts to INCREASE BP a) Also Directly stimulates the secretion of ALDOSTERONE by the Zona Glomerulosa of the Adrenal cortex 4) Aldosterone acts to Retain Na+ (DISTAL TUBULES) a) Recruits ATPase for active Na+/K+ transport, and Na+/K+ channels b) Na+ retention causes Water Retention -> Increases BP ADH - ARG vasopressin in most species; Vasotocin in birds reptiles, Lys vaso in pigs Long neurosecretory cells of Supraoptic nuclei produce ADH and Paraventricular produce oxytocin 2 Receptor Types for ADH/Vasopressin 1) V1a - vasoconstriction (increase BP) 2) V1b - causes ACTH secretion a) IP3 pathways 3) V2 - decreased urine production a) Increased salt & water reabsorption b) cAMP dependent Increased Insertion fo Water Channels Osmoreceptor (Atrial Rc) - Signal to brain center detect 1% change in osmolality (mainly Na+) & BV/BP Diabetes Insipidus - Central - Lack of ADH secretion - Nephrogenic - Renal Tubule Insensitivity to ADH Symtpoms: - Polyuria - Watery urine - Polydipsia - Increased Thirst Diagnosis & Treatment - Pitressin (purified ADH; 3-h effect) - Desmopressin intranasal 8hr Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) - Peptide produced by cardiomyocytes of the right atrium - Functionally antagonizes the RAS- aldosterone system - Defends against Corticoid & diet-related salt retention (Hypertensive Protective) - Inhibits RENIN secretion from JGA - Inhibits ALDOSTERONE DIRECTLY - Decreases salt appetite Stress - Organisms total response to external or internal factors that destablize homeostasis - Stressors may be physical, hpysiological (Starving), emotional (fear) - Short tearm (acute) stress does not exert any deleterious effects; some stimmulatory effects - Chronic Stress with protracted levels of adrenal hormones may be detrimental Fight or Flight - Increased HR & Force of ebat - Constriction of BV in skin & viscera - Dilation of BV in heart, lungs, brain, skeletal muscle - Conversion of glycogen -> glucose in liber - Sweating - Water retention in Kidneys -> Increase BP - Decreased Digestive function