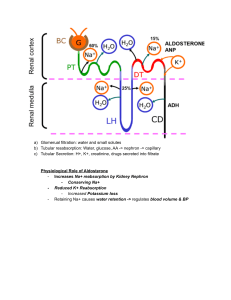
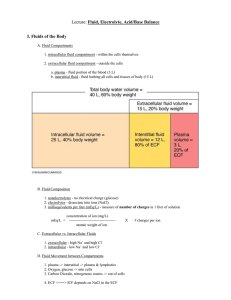
FLUID & ELECTROLYTES I. FLUID AND ELECTROLYTES Please note that all normal ranges for blood tests will depend on the lab performing the test. The normal values listed in this book are to be used as reference only. A. Fluid Volume Excess/Hypervolemia: • VASCULAR SPACE Define: Too much fluid in the ___________________ ________________. 1. Causes: a. Heart Failure (HF): Heart is __________, Cardiac Output _______, Kidney perfusion _____________, Urinary Output __________. *The volume stays in the ____________________ ________________. b. Renal Failure (RF): Kidneys aren’t ____________________________. c. Three things with a lot of sodium: Rx 1) Effervescent soluble medications 2) Canned/processed foods Rx 3) IVF with sodium 2. Hormonal Regulation of Fluid Volume: Rx a. Aldosterone (steroid, mineralocorticoid): • Where is aldosterone found? ______________ ___________ • Normal action: When blood volume gets low (vomiting, hemorrhage, etc.) Aldosterone secretion increases retain sodium/water blood volume goes _________. **Diseases with too much aldosterone: __________________________________________ __________________________________________ **Disease with too little aldosterone: __________________________________________ b. Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH): • Normally makes you retain or diurese? ____________________ • Retain __________________________ A CLINICAL JUDGMENT APPROACH | STUDENT MANUAL 1 FLUID & ELECTROLYTES TWO ADH PROBLEMS Too Much ADH Not Enough ADH Retain _________________________ Lose (diurese) _______________ Fluid Volume ___________________ Fluid Volume ________________ SIADH DI _________________________ Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion Diabetes Insipidus (TOO MANY ________________, TOO MUCH _________________) Urine ______________________ Urine _______________________ Blood ______________________ Blood ______________________ *Concentrated makes the #s go up Urine specific gravity, sodium, and hematocrit *Dilute makes the #s go down • ADH is found in the ______________. • Key words to make you think potential ADH problem: craniotomy, head injury, sinus surgery, transsphenoidal hypophysectomy, or any condition that can lead to an increased ICP can lead to an ADH problem. • Trans-______________________________, sphenoid _______________, hypophysis ______________, ectomy _____________________________ Rx *Another name for anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is vasopressin (Pitressin®). The drug vasopressin (Pitressin®) or desmopressin acetate (DDAVP®) may be utilized as an ADH replacement in diabetes insipidus. 2 Copyright protected. Reproduction prohibited without authorization and release by Hurst Review Services.