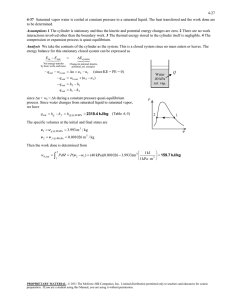
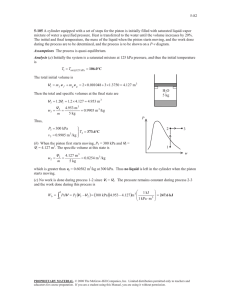
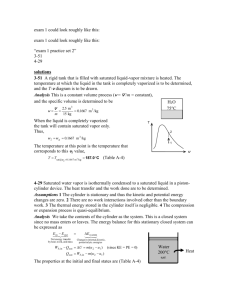
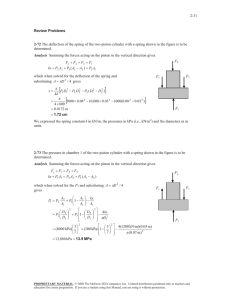
Thermodynamics I. Consider a system whose temperature is 18°C. 1. Temperature in K is ……………… a) 255 b) 291 c) 318 d) 354 c) 572.4 d) 637.2 c) 168.8 d) 177.8 2. Temperature in R is ………………. a) 459 b) 523.8 3. Temperature in °F. is ……………… a) 55.4 II. b) 64.4 The temperature of a system drops by 45°F during a cooling process. 4. The drop in temperature in K is …………….. a) 25 b) 45 c) 48 d) 57 C) 48 d) 57 5. The drop in temperature in R is …………….. a) 25 b) 45 6. The drop in temperature in °C is …………….. a) 25 III. b) 45 C) 48 d) 57 A gas is contained in a vertical, frictionless piston–cylinder device. The piston has a mass of 4 kg and a cross-sectional area of 35 cm2. A compressed spring above the piston exerts a force of 60 N on the piston. The atmospheric pressure is 95 kPa. 7. The pressure inside the cylinder is ................. kPa. a) 28.35 IV. b) 66.65 C) 95.28 d)123.35 A 2000-kg car climbs a 100-m-long uphill road with a slope of 30° (from horizontal) in 10 s. Disregard friction, air drag, and rolling resistance. 8. The power required for this climbing, at constant velocity, is .............. kW. a) 98.1 b) 170 C) 981 d) 1700 9. The power required for this climbing, from rest to a final velocity of 30 m/s, is ....................... kW. a) 101.1 b) 188.1 C) 173 d) 260 10. The power required for this climbing, from 35 m/s to a final velocity of 5 m/s, is kW. a) -290 V. b) -21.9 C) 50 d) 218.1 A frictionless piston–cylinder device contains 2 kg of nitrogen at 100 kPa and 300 K. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly according to the relation PV1.4 = constant until it reaches a final temperature of 360 K. (Molecular weight of N2 is 28 g/mol) 11. The N2 Gas Constant is .................. J/kg.k. a) 0.297 b) 297 C) 0.594 d) 594 12. The work input during this process is .................... kJ. a) -178.2 b) -89.1 C) 89.1 d) 178.2 Nitrogen at an initial state of 300 K, 150 kPa, and 0.2 m3 is compressed slowly in an isothermal process to a final pressure of 800 kPa. VI. 13. The mass of N2 is .............. g. a) 297 b) 337 C) 373 d) 733 14. The work done during this process is .......................... kJ. a) -44 VII. b) -50 C) 44 d) 50 0.1m3 of air is contained in a piston cylinder assembly at 1.5 bar and 27oC. It is first heated at constant volume until the pressure has doubled, then it's expanded at constant pressure until the volume has tripled. 15. The total work is .......................... kJ. a) 0.06 b) 0.6 C) 6 d) 60 VIII. A piston-cylinder device contains 0.5 m3 helium gas at 150 kPa and 20oC. The helium is now compressed in a polytropic process to 400 kPa and 140oC. (Molecular weight of helium is 4 g/mol) 16. The helium gas constant is ..................... J/kg.k. a) 2078.5 b) 2.0785 C) 4.1572 d) 4157.2 C) 61.57 d) 0.06157 17. The mass of helium is ....................... g. a) 0.12315 b) 123.15 18. The volume of helium is ............................... m3. a) 0.192 b) 0.264 C) 0.528 d) 0.705 19. The index n for this polytropic process is ………… a) 1.025 b) 1.536 C) -1.025 d) -1.536 20. The work done during this process is .......................... kJ. a) -1228.6 b) -114.61 C) -57.306 d) 57.306 C) 24 d) 38 IX. 21. For state (a), Q equals …………… a) 2 b) 12 22. For state (a), E2 equals …………… a) 14 b) 26 C) 24 d) 28 C) 15 d) 30 C) 25 d) 55 C) 30 d) 65 C) 35 d) 65 C) 3 d) 6 C) 21 d) 27 23. For state (b), W equals ………… a) -30 b) -15 24. For state (b), E2 equals ………….. a) -15 b) 15 25. For state (c), E1 equals …………… a) 5 b) 15 26. For state (c), ΔE equals …………… a) 15 b) 30 27. For state (d), W equals …………….. a) -6 b) -3 28. For state (d), E1 equals ………………. a) -27 b) -21 X. An insulated piston-cylinder device contains 100 L of air at 400 kPa and 25oC. A paddle wheel within the cylinder is rotated until 15 kJ of work is done on the air while the pressure is held constant. 29. The mass of the air is ....................... g. a) 429.2 b) 446.8 C) 467.7 d) 5575 30. The difference between the final and initial temperature is ....................... oC. a) 25 b) 31.9 C) 56.9 d) 65.9 31. The pressure value of saturated liquid water at T=190 oC is .............. bar. a) 12.27 b) 12.54 C) 12.82 d) 13.1 32. The specific enthalpy (h) value of saturated liquid water at T=190 oC is ……………… kJ/kg. a) 806.2 b) 807.6 C) 810.6 d) 812.1 33. The specific internal energy (u) value of saturated liquid water at T=190 oC is ……………… kJ/kg. a) 806.2 b) 807.6 C) 810.6 d) 812.1 34. The specific entropy (s) value of saturated liquid water at T=190 oC is ……………… kJ/kg.k. a) 2.226 b) 2.236 C) 2.245 d) 2.255 35. The specific volume (υ) value of saturated liquid water at T=190 oC is ……………… m3/kg. a) 0.001138 b) 0.001141 C) 0.001143 d) 0.001144 36. The dryness factor (x) value of saturated liquid water at T=190 oC is ………… a) 0 b) 0.5 C) 0.9 d) 1 37. The temperature value of saturated vapor water at P=3bar is .............. oC. a) 130.5 b) 131.5 C) 132.5 d) 133.5 38. The specific enthalpy (h) value of saturated vapor water at P=3bar is ……..………. kJ/kg. a) 2542.19 b) 2543.37 C) 2723.68 d) 2725.25 39. The specific internal energy (u) value of saturated vapor water at P=3bar is ……..………. kJ/kg. a) 2542.19 b) 2543.37 C) 2723.68 d) 2725.25 40. The specific entropy (s) value of saturated vapor water at P=3bar …….kJ/kg.k. a) 7.015 b) 7.004 C) 6.992 d) 6.981 41. The specific volume (υ) value of saturated vapor water at P=3bar ……. m3/kg. a) 0.6063 b) 0.6258 C) 0.6468 d) 0.6692 42. The dryness factor (x) value of saturated vapor water at P=3bar is ………….. a) 0 b) 0.5 C) 0.9 d) 1 43. The specific enthalpy (h) value of water at P=20bar, T=150oC is …………kJ/kg. a) 631.1 b) 633.3 C) 676.5 d) 2798.71 44. The specific internal energy (u) value of water at P=20bar, T=150oC is.…kJ/kg. a) 631.1 b) 633.3 C) 676.5 d) 2583.23 45. The specific entropy (s) value of water at P=20bar, T=150oC is ….……kJ/kg.k. a) 1.633 b) 1.738 C) 1.840 d) 1.941 46. The specific volume (υ) value of water at P=20bar, T=150oC is ………… m3/kg. a) 0.001079 b) 0.00189 C) 0.001101 d) 0.001113 47. The phase of water at P=20bar, T=150oC is ……………… a) sub-cooled XI. b) liq.-vap. mix. C) superheated d) none A closed, rigid tank contains 2 kg of water initially at 80°C and a quality of 0.6. Heat transfer occurs until the tank contains only saturated vapor. Kinetic and potential energy effects are negligible. 48. The specific internal energy of water before heating (u1) is ..................... kJ/kg. a) 1623 b) 1719 C) 2147 d) 2482 49. The specific internal energy of water after heating (u2) is ..................... kJ/kg. a)393.7 b) 2105 C) 2272 d) 2498 50. The amount of energy transfer by heat, in kJ, equals ……………… a) 784 b) 875 C) 1106 d) 1750