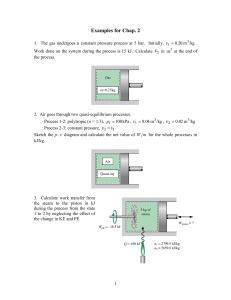
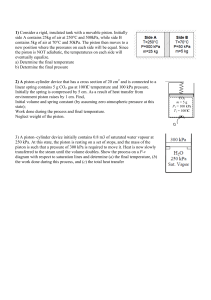
5-82 mixture of water a specified pressure. Heat is transferred to... 5-105
advertisement

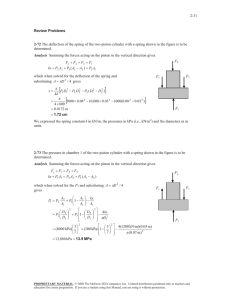
5-82 5-105 A cylinder equipped with a set of stops for the piston is initially filled with saturated liquid-vapor mixture of water a specified pressure. Heat is transferred to the water until the volume increases by 20%. The initial and final temperature, the mass of the liquid when the piston starts moving, and the work done during the process are to be determined, and the process is to be shown on a P-v diagram. Assumptions The process is quasi-equilibrium. Analysis (a) Initially the system is a saturated mixture at 125 kPa pressure, and thus the initial temperature is T1 Tsat @125 kPa 106.0qC The total initial volume is V1 m f v f mgv g 2 u 0.001048 3 u 1.3750 4.127 m 3 H2O 5 kg Then the total and specific volumes at the final state are V3 v3 1.2V1 V3 m 1.2 u 4.127 4.953 m 3 5 kg 4.953 m 3 0.9905 m 3 /kg P Thus, P3 v3 ½° ¾ T3 0.9905 m /kg °¿ 300 kPa 3 2 373.6qC (b) When the piston first starts moving, P2 = 300 kPa and V2 = V1 = 4.127 m3. The specific volume at this state is v2 V2 m 4.127 m 3 5 kg 3 1 v 0.8254 m 3 /kg which is greater than vg = 0.60582 m3/kg at 300 kPa. Thus no liquid is left in the cylinder when the piston starts moving. (c) No work is done during process 1-2 since V1 = V2. The pressure remains constant during process 2-3 and the work done during this process is Wb ³ 3 2 P dV P2 V 3 V 2 · ¸ ¸ © 1 kPa m ¹ § 300 kPa 4.953 4.127 m 3 ¨¨ 1 kJ 3 247.6 kJ PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.