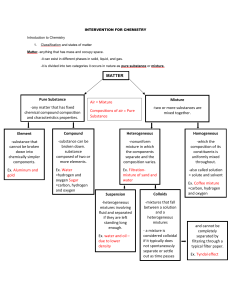
WHY MATTER MATTERS WHAT’S THE MATTER? • Anything that takes up space and has mass • Mass – amount of matter in an object • Matter vs. Weight • Volume – Amount of space an object takes up • Extensive Properties • Depends on the amount of matter • Intensive Properties • Depends on type of matter THE SIMPLEST FORM OF MATTER: • Element • Unique set of properties • Ex. Oxygen, Hydrogen, Carbon • 2+ element = Compound • Chemically combined • Ex. Sugar, salt, water • Substance • Matter that has a uniform and definite composition • Physical Property – quality of substance that can be observed/measured without changing substances composition • Used to identify substances • Color • Melting/boiling point • State at room temp • Lets look at air STATES OF MATTER • Solid • Liquid • Gas Physical Change: alters properties of material without changing composition Chemical Change: Produces matter with a different composition • Versus Vapor Solid Fixed Shape? Fixed Volume? Space between particles: Particle movement Compressible? Expands when heated? Liquid Gas MIXTURES • A blend of two or more components Homogeneous mixture -Solution Distillation Heterogeneous mixture Filtration EXAMPLES • Table Salt: • Compound! • Hydrogen Peroxide: • Compound • Mercury • Element • Sweetened Ice tea • Mixture • Chicken noodle soup • Mixture GROUP THE PERIODIC TABLE PERIOD CHEMICAL REACTIONS • One or more substances change into a new substance • Reactant Product • Every chemical reaction involves ENERGY LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS • Mass is neither created nor destroyed • …What about burning wood?