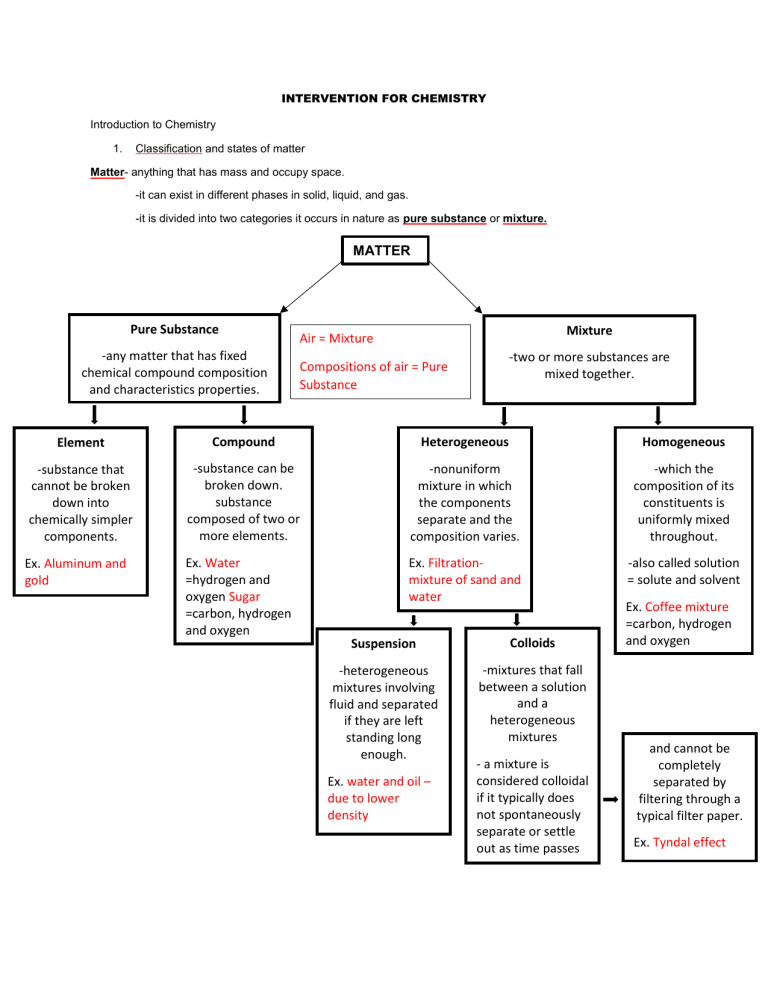
INTERVENTION FOR CHEMISTRY Introduction to Chemistry 1. Classification and states of matter Matter- anything that has mass and occupy space. -it can exist in different phases in solid, liquid, and gas. -it is divided into two categories it occurs in nature as pure substance or mixture. MATTER Pure Substance -any matter that has fixed chemical compound composition and characteristics properties. Mixture Air = Mixture -two or more substances are mixed together. Compositions of air = Pure Substance Element Compound Heterogeneous Homogeneous -substance that cannot be broken down into chemically simpler components. -substance can be broken down. substance composed of two or more elements. -nonuniform mixture in which the components separate and the composition varies. -which the composition of its constituents is uniformly mixed throughout. Ex. Aluminum and gold Ex. Water =hydrogen and oxygen Sugar =carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Ex. Filtrationmixture of sand and water -also called solution = solute and solvent Suspension Colloids -heterogeneous mixtures involving fluid and separated if they are left standing long enough. -mixtures that fall between a solution and a heterogeneous mixtures Ex. water and oil – due to lower density - a mixture is considered colloidal if it typically does not spontaneously separate or settle out as time passes Ex. Coffee mixture =carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and cannot be completely separated by filtering through a typical filter paper. Ex. Tyndal effect Introduction to Chemistry 1. Classification and states of matter Matter- composed of individual tiny parts known as atoms. Solids Liquids Gas -definite shape -no definite shape -no definite shape -definite volume -definite volume -no definite volume -high density -mid to high density -low density -slightly compressible -slightly compressible -highly compressible Ex. Aluminum and gold Viscous Liquids- honey and other syrup Density= mass/volume d(solid) > d(liquid) *Solids have the higher density than liquids and gasses has lower density *The lower the density the highly it is compressible Phase Change Heat Solid Heat Liquid Heat Gas ice Endothermic process Solid to Liquid Melting Liquid to Gas Vaporization Solid to Gas Sublimation Exothermic process Liquid to Solid Freezing Gas to Liquid Condensation Gas to Solid Deposition steam Plasma -ionized gas Gas + heat = Plasma (ionization) Reverse (recombination)