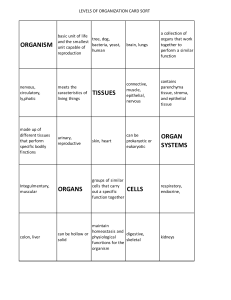
Human Physiology A short introduction to the field of human physiology Introduction Living systems possess a special organization Physiology studies two related aspects of that organization: structure and function For this reason physiology is closely related to Anatomy and Biochemistry Homeostasis This is the name for the processes which keep the condition and environment of the tissues in the proper condition to sustain life. Cells Cells are the basic units of life they make up tissues and organs in the body Cells can only come from other cells (The CELL THEORY) Tissues muscle nervous epithelial connective Glands Epithelial tissue Specialized for secretion Exocrine glands: secrete through ducts to the outside of the body Endocrine glands: ductless glands which produce hormones which are released into the blood Organs Two or more types of primary tissue Organized to perform a particular function Examples of Organs Stomach Heart Liver Kidneys brain many others Homeostasis: The Essence of Life Cells live in a fairly constant environment The cells, in turn, constitute the tissues which provide that environment Homeostasis Body systems Cells Body Systems Nervous Endocrine Immune Circulatory Muscle/skeletal Integument Respiratory Urinary Digestive Reproductive Negative Feedback Fall in temperature - + Thermostat Connecting Circuit Heat Furnace + Negative Feedback Fall in blood pressure - + Pressure sensors Increase in blood pressure Nerves Heart and blood vessels + Failure of Homeostasis Often leads to sickness and eventually death