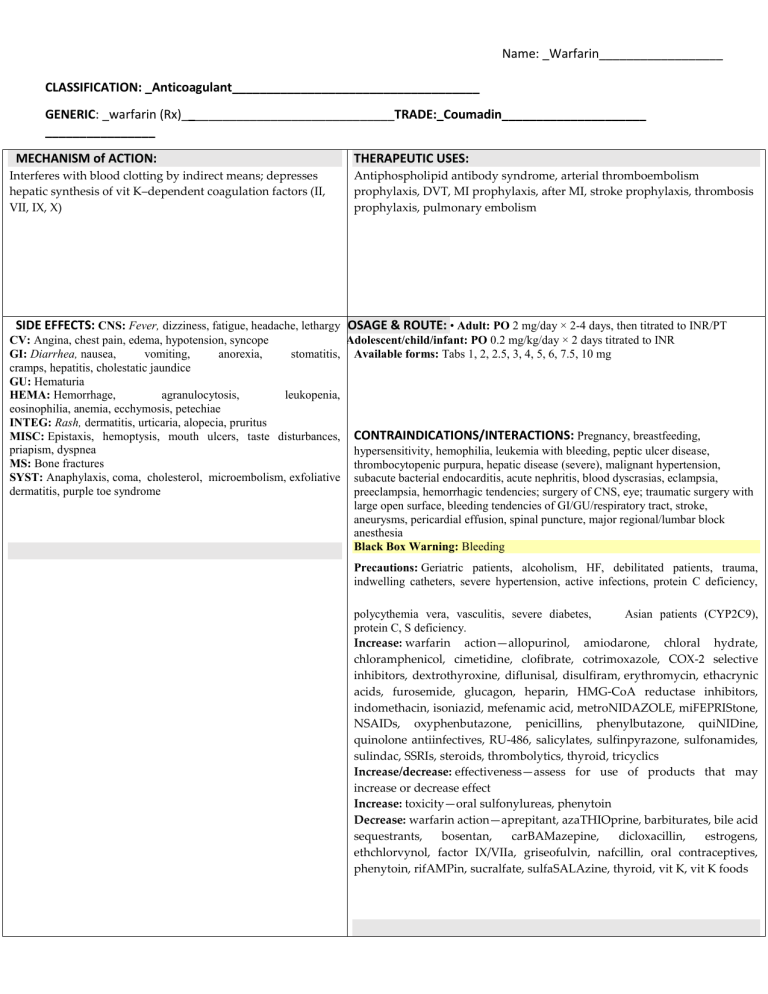
Name: _Warfarin__________________ CLASSIFICATION: _Anticoagulant____________________________________ GENERIC: _warfarin (Rx)_______________________________TRADE:_Coumadin_____________________ ________________ MECHANISM of ACTION: Interferes with blood clotting by indirect means; depresses hepatic synthesis of vit K–dependent coagulation factors (II, VII, IX, X) THERAPEUTIC USES: Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, arterial thromboembolism prophylaxis, DVT, MI prophylaxis, after MI, stroke prophylaxis, thrombosis prophylaxis, pulmonary embolism SIDE EFFECTS: CNS: Fever, dizziness, fatigue, headache, lethargyDOSAGE & ROUTE: • Adult: PO 2 mg/day × 2-4 days, then titrated to INR/PT CV: Angina, chest pain, edema, hypotension, syncope • Adolescent/child/infant: PO 0.2 mg/kg/day × 2 days titrated to INR GI: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, stomatitis, Available forms: Tabs 1, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.5, 10 mg cramps, hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice GU: Hematuria HEMA: Hemorrhage, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, eosinophilia, anemia, ecchymosis, petechiae INTEG: Rash, dermatitis, urticaria, alopecia, pruritus MISC: Epistaxis, hemoptysis, mouth ulcers, taste disturbances, CONTRAINDICATIONS/INTERACTIONS: Pregnancy, breastfeeding, priapism, dyspnea hypersensitivity, hemophilia, leukemia with bleeding, peptic ulcer disease, MS: Bone fractures thrombocytopenic purpura, hepatic disease (severe), malignant hypertension, SYST: Anaphylaxis, coma, cholesterol, microembolism, exfoliative subacute bacterial endocarditis, acute nephritis, blood dyscrasias, eclampsia, dermatitis, purple toe syndrome preeclampsia, hemorrhagic tendencies; surgery of CNS, eye; traumatic surgery with large open surface, bleeding tendencies of GI/GU/respiratory tract, stroke, aneurysms, pericardial effusion, spinal puncture, major regional/lumbar block anesthesia Black Box Warning: Bleeding Precautions: Geriatric patients, alcoholism, HF, debilitated patients, trauma, indwelling catheters, severe hypertension, active infections, protein C deficiency, polycythemia vera, vasculitis, severe diabetes, Asian patients (CYP2C9), protein C, S deficiency. Increase: warfarin action—allopurinol, amiodarone, chloral hydrate, chloramphenicol, cimetidine, clofibrate, cotrimoxazole, COX-2 selective inhibitors, dextrothyroxine, diflunisal, disulfiram, erythromycin, ethacrynic acids, furosemide, glucagon, heparin, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, indomethacin, isoniazid, mefenamic acid, metroNIDAZOLE, miFEPRIStone, NSAIDs, oxyphenbutazone, penicillins, phenylbutazone, quiNIDine, quinolone antiinfectives, RU-486, salicylates, sulfinpyrazone, sulfonamides, sulindac, SSRIs, steroids, thrombolytics, thyroid, tricyclics Increase/decrease: effectiveness—assess for use of products that may increase or decrease effect Increase: toxicity—oral sulfonylureas, phenytoin Decrease: warfarin action—aprepitant, azaTHIOprine, barbiturates, bile acid sequestrants, bosentan, carBAMazepine, dicloxacillin, estrogens, ethchlorvynol, factor IX/VIIa, griseofulvin, nafcillin, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, rifAMPin, sucralfate, sulfaSALAzine, thyroid, vit K, vit K foods Name: _Warfarin__________________ NURSING INTERVENTIONS : • Pregnancy/breastfeeding: do CLIENT TEACHING: • To avoid OTC preparations that may cause serious not use in pregnancy; use effective contraception during and product interactions unless directed by prescriber; to avoid alcohol, herbs, for 1 mo after final dose; cautious use in breastfeeding supplements Black Box Warning: Blood studies (Hct, PT, platelets, occult• To carry emergency ID identifying product taken blood in stools) q3mo; INR: in hospital daily after 2nd or 3rd• About the importance of compliance with exams and doses dose; when in therapeutic range (2-3) for 2 consecutive days, Black Box Warning: Bleeding: to report any signs of bleeding: gums, monitor 2-3× wk for 1-2 wk, then less frequently, depending on nosebleed, under skin, urine, stools; to use soft-bristle toothbrush to avoid stability of INR results; Outpatient: monitor every few days bleeding gums; to use electric razor until stable dose, then periodically thereafter, depending on • To avoid hazardous activities (e.g., football, hockey, skiing), dangerous work stability of INR results, usually at least monthly • To inform all health care providers of anticoagulant intake Black Box Warning: Bleeding: Bleeding gums, petechiae,• To take exactly as prescribed; dosage changes are common for desired effect ecchymosis, black tarry stools, hematuria, occult bleeding• To eat a diet that is not varied; several foods contain vitamin K and can alter (cerebral, intraabdominal; fatal hemorrhage can occur, do not warfarin effect use in uncontrolled bleeding • To report to prescriber fever, rash, trouble breathing • Fever, skin rash, urticaria CLASSIFICATION__________________________________________ GENERIC:_______________________________________TRADE:_____________________________________________ MECHANISM of ACTION: THERAPEUTIC USES: SIDE EFFECTS: DOSAGE & ROUTE: CONTRAINDICATIONS/INTERACTIONS: NURSING INTERVENTIONS: CLIENT TEACHING: