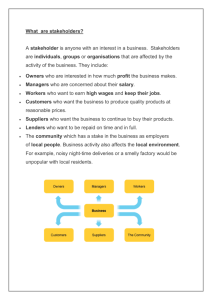
Introduction to Business Definition of Business • “Business is the exchange of goods, services, or money for mutual benefit or profit.” – Skinner and Ivancevich • “Business may be defined as any form of commercial activity to satisfy the economic wants of people at a profit.” – Keith Davis • “Business is any enterprise engaged in production and distribution of goods for sale in a market or rendering services for a price.”Professor Owen. Peter Drucker's Definition of a Business In the early 1970s, Peter Drucker published this definition of business in his book, Management: Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices. • "A business is a social group that differs from other social groups in only one way: Businesses must have customers." • "There is only one valid definition of business purpose: To create a customer." • "Because its purpose is to create a customer, the business enterprise has two, and only these two, basic functions; marketing and innovation. Marketing and innovation produce the results; the rest are costs." • "It is the customer who determines what a business is...The customer is the foundation of a business and keeps it in existence. He alone gives employment." Basic Differences Between Business and Companies • Businesses and companies serve completely conflicting classes of people to achieve different purposes by executing different functions. These basic characteristics of a business and a company are polar opposites. • A business is defined by its customers; a company is defined by its owners/investors, its directors, its executives, and by law. • The ONLY purpose of a business is to create customers; the purpose of a company is to protect its owners and executives from liabilities and deliver a good return on the investments of its owners. • The functions of a business are marketing and innovation. The functions of a company are organizational management and administration. Definition of Organization • Organization - The framework within which people act; it involves the arrangement of staffing and allocation of duties. To organize is to arrange the parts so that the whole works as an integrated body. (Denyer) • Organization - the process of identifying and grouping the work to be performed, defining and delegating responsibility and establishing relationships for the purpose of enabling people to work most effectively together in accomplishing objectives. (Louis Allen) Definition of Organization • An organization, or organisation, is an entity – such as a company, an institution, or an association – comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. • The word is derived from the Greek word organon, which means tool or instrument, musical instrument, and organ. What is the purpose of business? Generally speaking, the purpose of business is: • to create / make profits? • To be one’s own boss? • To support an advocacy? • To provide a community a livelihood? What is the ideal purpose of a business? • The ideal purpose of a business is NOT to create profits. Because a business cannot exist outside of society and must satisfy a specific need in order to stay in business, it has to create or add additional value to the community or individuals. That’s why the ideal purpose of a business is to create customers. • Peter Drucker, perhaps one of the best management thinkers of all time, said that businesses exist to fulfill a specific social purpose and to satisfy a specific need of a society. • However, a lot of business owners think of organizations only from a capitalist mindset. Now, that isn’t bad nor wrong by itself. It’s just another way to look at it. But if that’s the only thing that enters your mind — to make money — you are looking at businesses in the wrong way. Business enterprises … are organs of society. They do not exist for their own sake, but to fulfill a specific social purpose and to satisfy a specific need of a society, a community, or individuals.” Peter Drucker Stakeholders in Business • A stakeholder is any group, individual, or community that is impacted by the operations of the business, and therefore must be granted a voice in how the business functions. • Stakeholders can affect or be affected by the business organization's actions, objectives and policies. • There are two types of business stakeholders: a) b) Internal stakeholders, include primarily employees, owners and managers, who are directly involved in the operations and strategy of the organization. External stakeholders have no financial stake in the organization, but are indirectly influenced by the organization’s operations. • Some examples of key stakeholders are creditors, directors, employees, government (and its agencies), owners (shareholders), suppliers, unions, and the community from which the business draws its resources. • The primary stakeholders in a typical corporation are its investors, employees, customers, and suppliers.