_____/ 22 Botany ... Intro to structure WS Date________________________
advertisement

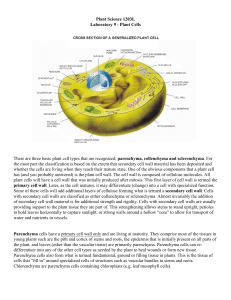
_____/ 22 Botany Intro to structure WS (see Chapter 5 in text) Name___________________________ Date________________________ Period________ 1. 2. 3. 4. (3) What three parts does the body of an herb plant contain? (1) Why would it be a disadvantage for a cactus to have leaves? (1) Flowering plants are informally known as ____. (2) Angiosperms are divided into the ______ or broadleaf plants, such as roses, asters, and maple trees and the _____ such as grasses, lilies, cattails, palms, philodendrons and bromeliads. 5. (1) Three classes of plant cells are based on the nature of their _____ _______. 6. (3) The three classes of plant cells are: 7. (1) Parenchyma cell walls are ___. 8. (1) Parenchyma cells remain ________ while they function. 9. (1) Parenchyma cells have _________ functions. 10. (1) Collenchyma cells are ___ thickened. 11. (1) Collenchyma cells are typically at maturity. 12. (1) Collenchyma cells stretch, so they can provide plastic _______. 13. (2) Sclerenchyma cells have ____ walls and ____ walls . 14. (1) Sclerenchyma are ______ at maturity. 15. (1) Sclerenchyma cells provide ______ support. 16. (1) Some sclerenchyma cells are involved in transport of ______. _____/ 22 Botany Intro to structure WS (see Chapter 5 in text) Name___________________________ Date________________________ Period________ 1. (3) What three parts does the body of an herb plant contain? 2. (1) Why would it be a disadvantage for a cactus to have leaves? 3. (1) Flowering plants are informally known as ____. 4. (2) Angiosperms are divided into the ______ or broadleaf plants, such as roses, asters, and maple trees and the _____ such as grasses, lilies, cattails, palms, philodendrons and bromeliads. 5. (1) Three classes of plant cells are based on the nature of their _____ _______. 6. (3) The three classes of plant cells are: 7. (1) Parenchyma cell walls are ___. 8. (1) Parenchyma cells remain ________ while they function. 9. (1) Parenchyma cells have _________ functions. 10. (1) Collenchyma cells are ___ thickened. 11. (1) Collenchyma cells are typically at maturity. 12. (1) Collenchyma cells stretch, so they can provide plastic _______. 13. (2) Sclerenchyma cells have ____ walls and ____ walls . 14. (1) Sclerenchyma are ______ at maturity. 15. (1) Sclerenchyma cells provide ______ support. 16. (1) Some sclerenchyma cells are involved in transport of ______.