Plant Structure and Types of Cells Notes
advertisement

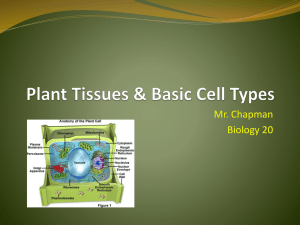
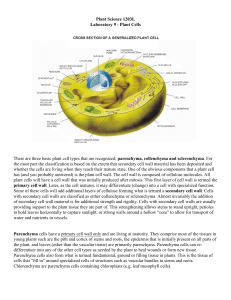
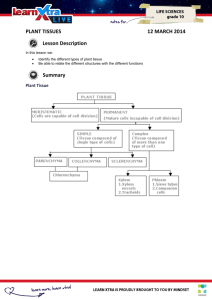
Plants Characteristics: •Multicellular • Eukaryotic •Photosynthetic •Cells have cell walls made of cellulose 2 Categories of Plants: Non-vascular: •Does not have true stems, roots and leaves. •Does not have xylem and phloem Vascular: •Have true stems, roots and leaves. •Have xylem and phloem (Vascular tissue) Cell Types in Plants Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma Parenchyma: Functions: Conduct photosynthesis Stores starch, oils, and water for the plant. Also important for healing wounds of the plant Parenchyma Details: Thin cell walls and large water-filled vacuoles in the middle. Most common type of cell in plants Collenchyma Functions: Provide support for the plant, while still allowing it to grow. They are flexible. EX: As a young leaf grows, collenchyma cells can elongate, giving the leaf structure. Do not conduct photosynthesis. Collenchyma Details: Most common in the younger tissues of leaves and shoots Cell walls range from thick to thin. Often form into strands. EX: celery strings Cells walls do not contain lignin, so they are stretchy and can change size. Comparing Parenchyma and Collenchyma Sclerenchyma Functions: Found in parts of the plant that are no longer growing. Skeletal support for water-conducting tissues and the plant itself. These cell fibers are used to make linen and rope. Form a major part of fruit pits and hard outer shells of nuts. Sclerenchyma Details: This is the strongest cell type of the three Have a second cell wall that is hardened by lignin. Makes the cells very tough, durable, and rigid. These cells are not able to grow with the plant. Comparing all three Vocabulary enchyma: cellular tissue Ex: parenchyma para: beside coll: glue scler: hard Identify: