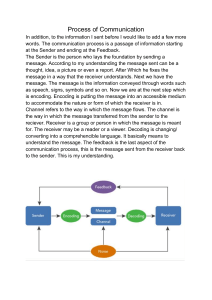
In what aspects of your life do you need communication? How do you communicate ? Why is it important to communicate well? When does communication happen? Communication Module 1 Language and communication Learning Objectives : At the end of the lesson , the students will be able to : • identify the role of language in communication ; • demonstrate an understanding of the key ideas in language as well as the nature , elements and process of communication; • Relate your personal experience with the input presented. What is language ? the method of human communication, either spoken or written, consisting of the use of words in a structured and conventional way. According to Linguists , language can only be called language if it has a system of rules (grammar),a sound system (phonology), and a vocabulary (lexicon) Speech community a group of people sharing a common language or dialect. Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language (in other words, gain the ability to be aware of language and to understand it), as well as to produce and use words and sentences to communicate. Mother tongue The languages acquired while growing up. Second Language is any language that a person uses other than a first or native language. Second-language acquisition is the process by which people learn a second language. Situation : What happens if you as a Filipino who speaks a mother tongue and English go to work in China where the residents speak in Mandarin and a little bit of English ? Will you be able to communicate with the Chinese residents? Language Contact Language contact occurs when speakers of two or more languages or varieties interact and influence each other. is the social and linguistic phenomenon by which speakers of different languages (or different dialects of the same language) interact with one another, leading to a transfer of linguistic features. Q U E S T I O N S 1. What is the importance of knowing the nature of language in relation to communication? 2. How can you describe an effective Communication ? 3. Is effective Communication important ? Why or why not? Communication Process Communication process refers to a series of actions or steps taken in order to successfully communicate. It involves several components such as the sender of the communication, the actual message being sent, the encoding of the message, the receiver and the decoding of the message. Elements of Communication Process 1. Speaker or Sender 2. Message 3. Encoding 4. Channel 5. Decoding 6. Receiver 7. Feedback 8. Context 9. Barrier 1. Speaker or sender The source of information or message 2. Message The information ideas or thoughts conveyed by the speaker in words and in actions. 3. Encoding The process of converting the message into words, actions or other forms that the speaker understands. 4. Channel The medium or the medium, mean, manner or method through which a message is sent to its intended receiver. 5. Decoding The process of interpreting the encoded message of the speaker by the receiver. 6. Receiver The recipient of the message. 7. Feedback The reactions , responses or information provided by the receiver. 2 kinds of feedback Positive feedback confirms the source that the intended effect of the message was achieved and tells the source that everything is going in the desired way. Negative feedback informs the source that the intended effect of the message was not realized. 8. Context It refers to the interrelated conditions of communicat ion which affect how people understand the message . 5 TYPES OF CONTEXT Physical context – includes the setting where the communication takes place, time of the day, the environmental condition, distance between or among the communicator. Meeting places must be well-chosen to avoid ay physical interferences. Social context – refers to the nature of relationships existing between or among the communicators and it also sets the formality of the interaction. Psychological context – involves the communicators’ mood and feeling. Cultural context – is comprised of the beliefs, values and norms shared by a large group of people. Historical context – involves the background provided by previous interactions between or among communicators which affect understanding of the current exchange. 9. Barrier The factors that affect the flow of communication. NOISE - is any barrier to communication which results to loss of meaning during the transmission. Kinds of noise a. Physical noise or channel noise such as loud music, irritating engine of a motorcycle, a seatmate who talks to you while you listen to your teacher. b. Physiological noise happens when the body becomes a hindrance to good communication. c. For example, because of a headache or toothache you may not be able to effectively listen to a friend. c. Psychological Noise occurs when one is thinking deeply for something or is suffering from an emotional condition (sadness, depression, confusion), which discourages participation in a communication. d. Semantic Noise happens when words have multiple meanings which could have different interpretations, and subject is too tough for the receiver to comprehend. This results in the wrong interpretation of message. ALWAYS REMEMBER ! Communication is both oral and written . Nature of Communication 1.Communication is systematic System is an organization interdependent element or component parts that form a complex whole and achieve certain purpose. • In the same way , society is comprised of systems. Each system has its own patterns of communication, language and vocabulary use and rules that depend on elements such as the behavior and shared experiences of its members. • A change in any part or element of a system affects the system of communication as a whole. Example : In a family reunion, Mark overheard his aunt utter the statement, “we’ll talk later,” to her son. She said this in a firm but gentle manner, though in the presence of other guest. Mark understood this as his aunt’s way of reprimanding her son for being too noisy and disruptive. Mark’s own mother used to say this to him as a warning before scolding. 2. Communication is irreversible Since communication is a continuous process, it is impossible for one to actually take back what was said. Thoughts when put into words become significant representation of experience; and words said in haste or anger may influence possible communication in the future or even destroy relationships. 3. Communication is proactive. When people receive information, they actively evaluate the content and purpose of the message and the credibility of the speaker, even when they seem to be listening passively. Meaning rest not only in the person who conveys the message. The receiver is also involved in the active construction of meaning. 4. Communication is symbolic. Symbols are representation used to communicate and interpret one’s thoughts and feelings. Symbols are arbitrary, which means that any symbol can be used to represent a concept, that is, as long as the meaning is shared by a group of people. Question: Can two people who do not speak the same language communicate with each other? 5. Meaning in communication is individually construed. Individuals involved in communication play a significant role in meaning construction, which means that they actively create meaning taken from experiences or phenomena through symbolic representation. References • https://www.coursehero.com/file/36064107/Lesson-1Communicationpdf/ • https://www.quora.com/What-is-purposivecommunication • https://ched.gov.ph/wpcontent/uploads/2017/10/PurposiveCommunication.pdf • https://www.scribd.com/document/381227914/Pur posive-Communication • https://www.slideshare.net/gilremoral/nature-andelements-of-communication