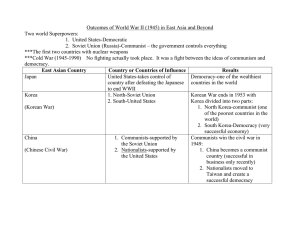
Name: ______________________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ The Cold War Begins Guided Notes The Cold War • After WWII the __________________________ and the ________________________ became rivals • They never confronted each other in open warfare, but tensions were high between the two ________________ • They often would________________ groups within countries that were having civil wars like Korea and Vietnam • Since there was no direct combat between the US and the Soviet Union it is called a “cold” or a war without ___________________________________________ • Since both sides had ____________________________________ it kept each other from attacking one another • For the US the Cold War was about _______________________________ Soviet Communism • There was only _______ political party in the Soviet Union • The __________________________ Party controlled all labor groups and associations • The ________________owned all farms and industries • The government determined the nation’s _________________ needs • _______________________property was limited • Healthcare and education were provided by the____________________ • The Soviet government discouraged _________________________and even destroyed religious buildings • The ______________________________ would arrest those who spoke out against communism • There was ________________________________ and no free exercise of beliefs American Democracy • The United States had a_________________________________ democracy • ____________________________negotiated with unions and other labor organizations • The U.S. had a free enterprise system where __________________ citizens owned property and businesses • ______________ and_________________ determined the price of goods • The government had limited involvement in the ______________________ • People met their own ____________________ • There was freedom of ________________________ • There was also freedom of the_________________ Joseph Stalin • He was the leader of the _____________________________ during WWII and the beginning at the Cold War • He was communist and a brutal ________________ • Anyone who spoke out against him would either disappear or be sent to the gulag work ___________ Yalta Conference • _____________________, Stalin, and Churchill met in February 1945 • They planned how to reorganize ______________________ after WWII • They also agreed to form the ______________________________ • In addition they decided to divide _________________________into four occupied zones • All parties agreed to allow _______________________ in the countries that they had liberated from Nazi control Division of Germany • After WWII Germany was divided into four ____________________-__zones • Each zone was controlled by one of the major ___________________________ (United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union) • The capital city of __________________was also divided into four occupied zones • Eventually the zones that were controlled by the United States, Great Britain, and France joined together to form ____________________________ Potsdam Conference • Truman, Churchill, and Stalin met in ________________________, Germany in July 1945 • The purpose of the conference was to negotiate the terms to end __________________ • Tensions between ___________________ and ___________________ were very apparent Soviet Union and the Cold War • The Soviet Union wanted to insure their _________________________ • They also distrusted the West, especially the __________________ • Stalin created a ring of ____________________________________________________ to act as a buffer from any future invasions • Stalin denied free elections in ________________________ • The Soviet Union was also suspicious because the US refused to share how they built the __________________ • Eastern Europe was still occupied by ___________________________________ • The Soviets helped to place local _____________________________ in power in the countries of Eastern Europe • The __________________________suppressed anti-Communists The US and the Cold War • The United States was concerned about containing the spread of ______________________________ • The U.S. decided that it would not interfere in countries that were already ___________________________, but they would provide aid to countries that might fall to communism • The US refused to share how they built the _______________________________ with the Soviets • The US condemned Soviet force in ______________________________________ • The US never directly did anything to stop what was happening behind the ______________________________ The Iron Curtain • After the Soviets helped to place communist leaders in control of_____________________ Europe contact between Western and Eastern Europe was cut off • During the next 40 years there would be very__________ communication between Eastern and Western Europe • The Eastern countries of Europe became known as satellite nations of the ________________________ • _____________________________________ is noted for calling the division of Europe, The Iron Curtain Truman Doctrine • President Truman didn’t want to make the same mistakes that had been made at the ______________________ • He said that the U.S. would provide military aid to any country that was fighting ______________________ • Truman believed that those who were_______________________ were often attracted to communism Marshall Plan • After WWII much of_________________________ infrastructure had been destroyed • __________________________ included roads, bridges, tunnels, electricity lines, water lines, buildings etc… • Their __________________________ were also in shambles, people were not spending or earning much money • ____________________________________________________ was Secretary of State for Truman • He proposed that they U.S. should provide aid to countries that had been war-torn by WWII in Europe to help them rebuild their _________________________________ • Marshall felt that by giving the aid to these countries that they would become allies and _____________________________________________________ of the U.S. • The U.S. also wanted to prevent a repeat of post-WWI Europe, where the continent remained devastated for ____________________________ • The Marshall Plan was a____________________________ West Germany • Germany was divided into four occupied zones after ________________________ • The zones that were controlled by Great Britain, France, and the United States were joined together to form _____________________________________________ • They also combined their sections of Berlin to form _____________________________ • The Eastern part of Germany and Berlin remained under _________________________ control • Berlin was located in___________________________ Germany Berlin Airlift • The Soviets blocked off roads and railroads that went into ___________________________ • The United States along with other allies ___________ over West Berlin to drop food and supplies to the people • The _________________________________of Berlin and the Berlin Airlift lasted for 11 months • The US had successfully bypassed a Soviet blockade without provoking a ________________________________ North Atlantic Treaty Organization • The North Atlantic Treaty Organization is also called _____________________ • It was created in _________________________ • NATO was based on ________________________________________ • Each member nation pledged to defend one another in the event of an_________________ on a member nation • The __________________ was a member of NATO • Thanks to NATO, members also had the protection of ___________________________ that belonged to the U.S. Fear of an Atomic Bomb Spreads • During the Cold War the US government created videos to teach students how to “________________________________________” under their desks to protect them from a nuclear bomb • They also produced films that showed what the government was doing to learn more about the effects of ______________________________________ on housing, infrastructure, food, and clothing. • Many people built ______________________________________________ to protect themselves and their families from a nuclear blast and the radiation fallout afterwards Warsaw Pact • The Warsaw Pact was created in response to the creation of _____________________ • It consisted of the ______________________________ and its Eastern European satellite nations • The Warsaw Pact was created in ____________________________ Berlin Wall • The Berlin Wall was constructed in _________________ • It ____________________________ East and West Berlin • People who were in _______ Germany or East Berlin were not allowed to travel to West Germany or West Berlin China Falls to Communism • China was one the most ________________________ nations in the world • Chinese __________________________ had been trying to overthrow the Nationalists in China since the 1920s • The _________________________ began aiding them in 1945 • Chinese communists were led by ___________________________ • They were successful in overthrowing the _______________________________in 1949 • Many Nationalists fled to the island of ___________________________ • Under the leadership of Mao, China became the world’s largest ______________________ state • ¼ of the world’s population came under _________________________________ control • Under communist rule China became known as “________________________” Korea After WWII • After WWII ____________________ had been divided into South and North Korea • The Soviets helped North Korea to rebuild and they adopted _____________________ as their economic system • The U.S. helped South Korea to rebuild and they adopted _______________________ as their economic system Korean War • The U.S. government faced criticism for the fall of ________________ to communism • Many Americans wanted the US to intervene in ___________________ • North Korea invaded South Korea in 1950 in an attempt to unify the ___________________________________ • Stalin believed that the U.S. would not get involved in the _______________________________ • As the North Koreans advanced the _____________________________________ and ______________________________________South Korean army retreated further south Korean War Continued • The _________ sent troops to aid the South Koreans • The ______ also sent troops, the Soviet Union could not veto it because they were at the time protesting the UN • The Korean War was the first time that a peace keeping organization was successful in using its military to ___________________________________________ Korean War and MacArthur • ________________________________________________________ was sent to Korea by Truman to help the South Koreans during the Korean War • He was successful in pushing the _________________________________ back north • The North Koreans retreated towards their border that they shared with ______________________ • China was concerned about a large _______________________________ near their border • The _____________________________ became involved Korean War and MacArthur Continued • McArthur wanted to liberate China from ________________________ control • He wanted to stage an __________________________ of China • He also wanted to use _____________________________ if needed • Truman _________________________________ • MacArthur openly criticized ____________________________ • Truman removed MacArthur from his __________________________ • The American public was ___________________________________ with MacArthur’s removal Korean War Ends • North Korea and the US signed an armistice in 1953 to end to _______________________________ • Both sides agreed to create a _______________________________________________________ along the border between North and South Korea • They also agreed to exchange _______________________________________________ with each other • Korea remained divided at the _____________parallel, exactly where the border previously was The Arms Race • After WWII tensions between the US and Soviet Union ______________________ • The _________wouldn’t share information on how they built the atomic bomb in 1945 • The __________________developed their own in 1949 • After the development of the Soviet atomic bomb an ___________________________initiated • Each country sought to have more _________________________ and military personnel than the other • The US developed the ______________________________________________ in 1952 • The __________________________ developed their hydrogen bomb in 1953 Massive Retaliation • In the 1950s the United States government relied on having a large stock pile of ______________________________________ as opposed to having a very large military • Nuclear weapons acted as a deterrent to discourage an ___________________________________ • If nuclear weapons were used on the __________then they would also be used on the _____________________ • The possibility of ________________________________ was cheaper than keeping a very large standing army • Many leaders realized that the use of nuclear weapons was impractical as they could really only be used if it meant the _____________________________of the nation • Many people were concerned about President Eisenhower’s willingness to ___________________________ nuclear war to maintain peace • Critics called Eisenhower’s willingness to go to war _________________________________ Sputnik I • In 1957 the Soviets launched ____________________________ • It was the first man-made __________________________________ to be sent into space to orbit the earth • It was about the size of a ______________________ and weighed 184 pounds • It was _____________________ to do very much • It emitted a beep, which allowed it to be______________________ Space Race • After the Soviets launched Sputnik I a __________________________ ignited • Many were afraid that the Soviets might be capable of using _______________ to send nuclear bombs to the US • Americans were concerned that they were falling behind the ______________________ • In response the US government created________________________ • In _______________ the US launched its own satellite into space Loyalty Review Boards • President _______________________ created Loyalty Review Boards to investigate people who might be participating “un-American” activities • For example people who were members of the American_________________________ Party were questioned • The majority of those questioned were done so with very little ______________________ against them • Victims were usually unable to __________________________ themselves • They were also not allowed to know __________ accused them • Under the constitution you have a right to know your accuser and confront them, this did not happen so their constitutional rights were ___________________________________ House Un-American Activities Committee • ____________________ conducted its own loyalty checks through the House Un-American Activities Committee • They question directors, writers, actors, and anyone else whom they thought might sympathize with _________ • People who were either former or current ______________________ of the American Communist Party were often “blacklisted” • People who were “__________________________” lost their jobs • Many of the people who cooperated with the committee were asked to ________________ on others Joseph McCarthy • He was a US Senator who claimed to know 205 __________________________________ who were working in the US Department of State in addition to several other government agencies • His allegations stirred up fears over Communism, much like the _______________________ had in the 1920s • ______________________________ worked with the House Un-American Activities Committee and the FBI during their investigations of accused communists • The hearings lasted for three years and no _________________________ was ever provided for his charges • Despite being unable to prove his claims, his ________________________________ scared many Americans • McCarthyism became associated with making harsh accusations ____________________________________ The Rosenberg Trials • Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were American citizens who ____________ for the Soviet Union during the Cold War • They gave the Soviets secrets about the _________________________ • They were both tried, convicted, and _____________________ for spying • Many people believed that they were_______________________ • In 1997 the ________________________________________ were declassified and proved that the Rosenbergs had played a role in a Soviet Spy Ring in the US Eisenhower Doctrine • John Foster Dulles was Eisenhower’s _______________________________________________ • He was very anti-Communist and wanted to stop the spread of ________________________ • He believed that it was important to prevent the Soviets from gaining anymore influence in order to contain the spread of ______________________________ • Under the Eisenhower Doctrine, Eisenhower promised to aid any ____________________________________ country that was trying to fight off Communism • The Eisenhower Doctrine was an extension of ________________________________ Conformity • The __________________ became a period that emphasized conformity • Any ______________________ activity was regarded with suspicion • The fear of communism also increased the dislike of non-conformists Southeast Treaty Organization • The United States helped to form the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization also known as ______________in 1954 • It was created for the ________________________________________________ of Southeast Asian countries • The US began to send aid to French forces who were fighting ____________________________ in Vietnam Khrushchev • After ____________________ died in 1953 there was a power struggle in the Soviet Union • Khrushchev became the _____________________________ in 1956 • He spoke out against ___________________________________ and Stalin • He was willing to conduct ___________________________ with the US, up until the U-2 Spy plane incident U-2 Spy Plane • In 1960 the Soviets shot down a US spy plane called the ________________________________ • The plane was trying to gather______________________________ • The incident ___________________________ an important summit that was supposed to occur between President Eisenhower and the Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev