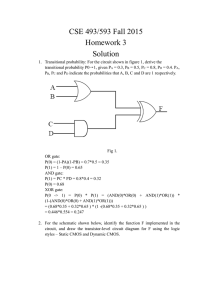
Food Living Outside Play Technology Workshop DIY SRAM - The RAM in your Microcontroller by gigavolt on August 8, 2011 Table of Contents DIY SRAM - The RAM in your Microcontroller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 Intro: DIY SRAM - The RAM in your Microcontroller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 Step 1: Get The Stuff . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 Step 2: The Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 Step 3: What On Earth is CMOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Step 4: The Enable Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Step 5: Our Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 Step 6: Let's Start the Fun Part . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 Step 7: Connect Them Together . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Step 8: Add the Enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Step 9: The Full Cell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Step 10: Buttons and Input Inverters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Step 11: It's Finished . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Step 12: More Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 Related Instructables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Author:gigavolt Teslaling I'm interested in everything electronics, high voltage, computers, and robotics. I am also interested in chemistry. Intro: DIY SRAM - The RAM in your Microcontroller Static Random-Access Memory. What is it? SRAM is a type of memory that will store information, but lose it when power is disconnected, which is why it is RAM. It is called static RAM because it doesn't need to be refreshed, unlike Dynamic RAM (DRAM) which has to be refreshed every few milliseconds to keep its data. DRAM is common in computer memory, because of fast access times and it only requires 1 transistor and 1 capacitor per bit making it high density. SRAM is common among microcontroller memory and some low power applications because it doesn't need to be refreshed, and uses less power. It is slower than DRAM and has a lower density at 6 transistors per cell. This instructable will show you how you can make a SRAM bit using the real design, not the register versions I previously demonstrated. The SRAM is the 6t circuit, meaning that this version uses 6 transistors per bit (in reality, ours will need 8 per bit). Why build such a device, when you can get an IC with a few thousand times more storage? Because its cool to see how those little chips actually work. Plus you can say that you made your own RAM... and maybe tell all your friends that your computer is running off of homemade RAM... Image Notes 1. The Core of the SRAM 2. The ~BL Enable 3. The BL Enable 4. The Heart of the SRAM: 2 COMS Inverters Image Notes 1. Full Circuit 2. Bit is low 3. Ignore!!! This is from another project Image Notes 1. Bit set to 1. Like the pink? :) http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Step 1: Get The Stuff The parts list for this is nice and small. 8 2N7000 transistors - These are N-channel MOSFETs 4 BS250 transistors - These are P-channel MOSFETs 1 LED 1 Resistor to match LED current - 220 - 1K will be fine. http://led.linear1.org/1led.wiz is a good calculator if you aren't sure 2 Buttons 2 Resistors 1k to 10k will work Wires A breadboard A 5-ish Volt Power Supply Image Notes 1. Full Circuit 2. Bit is low 3. Ignore!!! This is from another project Step 2: The Circuit The 6t SRAM Circuit is relatively simple. It is 2 CMOS inverters with an enable circuit on both sides. The output of one inverter is connected to the input of the other and vice versa. This creates a very simple latch because when one of the inputs is low, that inverter's output goes high, this makes the other inverter's input high, so its output is now low. To change the inverters' states, you would pulse a high current on the low side AND a low current on the high side. This pulse is enough to change the input of that inverter, so the output changes, and the circuit latches again, but in the opposite state. It is bi-stable, and won't freely oscillate. The enables connect and disconnect it from the rest of the circuit, so that it can't be accidentally changed when a bunch of them are connected together. Image Notes 1. Enable 2. Enable 3. Inverter 4. Inverter 5. Word Line (Enable) 6. Not Bit Line. The inverse input/output 7. Bit line. Input/output Image Notes 1. This is a lot easier to read and understand 2. This was created by me in Paint http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ 8. This came from Wikipedia Step 3: What On Earth is CMOS CMOS (see-moss) does NOT grow in water. It is a type of logic that uses MOSFETs and it uses very little current. CMOS stands for complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (The MOS part is also the same for the first part of MOSFET) This doesn't mean that the transistors compliment each other, but that they complement, as in the opposite, each other. CMOS uses both an N-channel MOSFET and a P-channel MOSFET. How does it work? The N-channel MOSFET will turn on when it's gate is brought up to the supply voltage, typically 3.3v or 5v, and turn off when the gate it brought down to ground. The P-channel MOSFET will turn on when it's gate is brought down to ground and turn off when it's gate is brought up to the supply. What is neat is that when one is on, the other is off. The pictures above demonstrate how this works for the humble inverter (also known as a NOT gate) Image Notes 1. Input is low (logic 0) 2. P-channel MOSFET is on when its gate voltage is low. This makes ~A go high. 3. N-channel MOSFET is off when its gate voltage is low. 4. Output is high (logic 1) Image Notes 1. Input is logic 1. 2. Output is logic 0. 3. P-channel MOSFET is off when its gate voltage is high. 4. N-channel MOSFET is on when its gate voltage is high. This makes ~A go low Step 4: The Enable Circuit The first thing we have to tackle is the Enable Transistor. The schematic shows that all you need is one N-channel MOSFET to be the enable. That, however, is an ideal MOSFET. An ideal MOSFET is a symmetrical device that can switch currents in both directions. The 2N7000* is not an ideal MOSFET, there is a small diode built into it that is parallel with the actual FET. This means that current can be switched on and off when flowing in one direction, but it will flow freely through the other direction whether the FET is on or off. I don't know why the MOSFETs are made that way, it is probably a manufacturing thing. My guess is that for some reason, it is easier to make MOSFETs with a diode than without. To counter this, we put 2 FETs together with their diodes facing opposite directions. That way, current can't flow in either direction freely UNLESS the MOSFET is switched on. This is why our SRAM will need 8 transistors instead of 6. *It should be noted that most discrete MOSFETs have a body diode, as its called, in them. http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Image Notes 1. The diodes cancel each other out, so no current can flow 2. When enabled, Current can flow from A to B or from B to A. 3. My Enable Circuit Image Notes 1. Current can flow from A to B or from B to A when the transistor is switched on. 2. Ideal MOSFET Image Notes 1. 2N7000 Step 5: Our Circuit Ok, so we have the SRAM circuit in the middle, but what the heck is all of the rest of that stuff? The LED is simple, it is the output, so we know what the bit is set to. The write enable switch turns on the enables, allowing you to write to the SRAM. The Bit Line Switch is used to write the data to the SRAM. These switches need the pull-down resistors because the gates of MOSFETs are slightly capacitive, meaning that if you disconnect them from anything, they may hold their charge and stay switched on. The ~BL inverter is used to invert the signal to go to the NOT Bit Line. Then the BL inverter reverts the signal to its original state. The reason for this second inverter is that the Pull-Down resistor doesn't draw enough current to switch the SRAM latch (more on this in step 13) so to counter this, we just use another inverter. http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Image Notes 1. Write Enable switch with pull down resistor 2. Bit Line switch with pull down resistor 3. Inverter for the ~BL 4. Inverter for the BL 5. Output LED Step 6: Let's Start the Fun Part Ok, well the fun part also happens to be the tricky part. I took a lot of pictures so, hopefully, it won't be a scary, daunting task. The circuit starts out simple, but gets scary rather quickly. A picture is worth a thousand words (actually a 10MP picture is about 10 million 32-bit words), so I plan on a few words and a lot of pictures. To start we are going to make the two inverters. They are simply a BS250 and a 2N7000 with their drains connected together. To do this, the BS250 goes on the left, and the 2N7000 goes on the right. Both should have the rounded side facing you. WARNING: if the rounded side is facing away, then the body diodes will short the supply and ground, and the transistors will release their blue smoke! Also, the rightmost pin (pin 3) of the BS250 and the leftmost pin (pin 1) of the 2N7000 should be connected together. Image Notes 1. BS250 2. 2N7000 Image Notes 1. BS250 connected to 5v 2. 2N7000 connected to ground 3. Gates are connected together http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Step 7: Connect Them Together Now we are going to connect the inverters together. The output of one is connected to the input of the other. To do this, connect a wire to pin 2 of a transistor on the left inverter and connect it to the output of the other transistor. The output of the inverter is where pin 3 of the BS250 and pin 1 of the 2N7000 are connected together. Repeat this, but with the input of the right inverter and the output of the left one. If you are confused, refer to the picture. Image Notes 1. These 2 wires connect the inverters together Step 8: Add the Enable The enable is simple. One 2N7000 has its rounded side facing you, the other has its flat side facing you. The right-most pin of the left transistor is connected to the leftmost pin of the right transistor. Confused? The picture says it all, and then some. Next, the gates get connected together via a wire. Lastly, we need to connect the enable to the SRAM bit. To do this, put a wire on either the very left or very right pin. Next, put the other end of the wire on the gate of the closest inverter. Image Notes 1. Gate connection 2. Wire connecting enable to SRAM Step 9: The Full Cell Make another enable on the other side of the circuit, and connect it up (if you connect both enables to the gate on both sides, you will guarantee that they aren't connected to the same side of the circuit). Now you have a full SRAM cell. Connect the gates of the enables together then connect another wire from ground to one of the gates. Add the LED and resistor by putting a resistor on the output or gate of one inverter then to the positive lead of the LED and ground the negative lead of the LED. Now you may want to test in. Plug in your power supply and watch for the blue smoke! Actually, a better idea is to keep one hand on the switch, and touch the transistors with the other to make sure they don't get hot. If it passes that test, set one enable input to ground and the other to +5v (or whatever you are using) turn the supply on, and enable the circuit by disconnecting the gates from ground and setting to +5v. The LED should turn on, or off. If it hold its state, disable the circuit and switch the wires around, as in the input that was grounded should be set high and vice versa. If the LED still doesn't change, check your circuit. http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Image Notes 1. Inverters 2. Enable 3. Enable Step 10: Buttons and Input Inverters Wiring up the buttons is fairly straight forward. One pin gets tied to +5v and the other is tied to ground through a resistor. The output of the button is the pin that is tied to ground. The Write Enable button output connected to the enable gates. The output of the Bit Line button is connected to the first inverter's input. It's output goes to the enable and to the second inverter's gate. It's output goes to the other enable. I'm not going into detail on building the inverters, because I already covered that. Image Notes 1. Buttons 2. First inverter Image Notes 1. Second inverter Step 11: It's Finished Now, its time to turn the power supply on again and try out your new RAM! If all goes well, you should be able to change the LED's state when the write enable is high, but it should latch when the write enable it low. Build a few thousand more of these, add some decoding logic and you have your own SRAM chip! http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Image Notes 1. Bit set to 1. Like the pink? :) Image Notes 1. Full Circuit 2. Bit is low 3. Ignore!!! This is from another project Step 12: More Information This is a very efficient circuit and is what is used in most SRAM chips, but I found out that it isn't a perfect circuit. Remember how I said earlier that the resistor wasn't enough to change the circuit's state? Well, as it turns out, there is a very brief current spike when the circuit is switched. This spike lasts for less than a millisecond, but it is as high as 100 milliamps. This spike is caused by current rushing in through the enable and to ground through the output of the inverter. This spike is very brief because once the inverter is switched, no more current flows. This spike can be reduced by using smaller MOSFETs (like on an IC) that have lower capacities and by grouping everything closer together which further reduces the capacitance. This is the least complex memory circuit I've built so far. I have made a TTL RAM using an SR Flip Flop, and I made a CMOS RAM that used a D Latch, and I implemented that into a 1 Byte RAM for your favorite microcontroller. Eventually I'm going to attempt a DRAM circuit and if I can find a few ferrite cores cheaply (<$5 for 100+), I might try to make a Core Memory!!! Image Notes 1. Enable 2. Enable 3. Inverter 4. Inverter 5. Word Line (Enable) 6. Not Bit Line. The inverse input/output 7. Bit line. Input/output 8. This came from Wikipedia http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ Related Instructables DIY RAM MemoryRegister Style by gigavolt DIY CMOS RAM Memory by gigavolt Single CMOS NOT Gate/Inverter by andy70707 DIY RAM for Your Micro by gigavolt Semi Conducting - A Guide by Inducktion http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SRAM-The-RAM-in-your-Microcontroller/ LOGIC GATES by Jimmy Proton