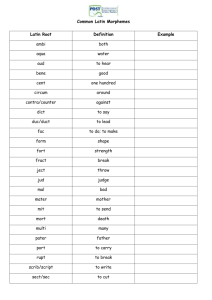
Historical linguistics Language change & Semantic change Language change • Speakers constantly need to communicate with each other in different circumstances. • For this purpose they have to adapt language to changing communicative needs in a changing environment. • These changes occur in the sound, grammar. And modifications also occur in vocabulary and in the meaning of the words. Language change • Through the basic process of word formation of word formation all people are capable of producing words. • Such words result from the combination of morphemes. • speaker is seldom aware that he or she has used language creatively. • Language is, by its nature, productive. • there are also the cases when truly new words appear, words that no speaker of the language has ever produced before. • Words may be added or lost in conjunction with cultural changes. Vocabulary changes • Vocabulary changes occur through three main factors. vocabulary change • Coinage Compounding & affixation Conversion Coinage • Languages also make or coin new words, entirely original creation, utilizing neither words from another language nor morphemes nor words already in use in one’s own language. • Examples are jazz, quiz, fun, and snob. • Morphemes are the smallest meaningful unit of a language. coinage • New words are also formed by combining existing words and morphemes into new, complex words. For example teacher. • Onomatopoeia is a modified type of coining words. Compounding and affixation • Compounds are the combination of two independent words, i.e. free morphemes. For example 'guesthouse‘. • In affixation a bound morpheme is added to a base as a prefix or as a suffix. For example unlike, likeness. Conversion • This is the change of word class without the addition of a formal suffix, for example from verb 'to cheat' to noun 'a cheat‘. • A word changes its class i.e. undergoes a functional change such as adv or adj to v e.g. up > to up shortening Process Example Acronym Radar, unesco, tevta Blends Clipping Smoke + fog > smog Motor + hotel > motel Prof, phone Abbreviations Ms, Mr. Initialism BBC, RP Back formations or reanalysis • A process where by which a word is formed by cutting off an imagined suffix from an existing word, owing to the morphological reinterpretation. • In back formation, a short word is created from a larger word on the basis of similarities between the longer word and other words in the language. For example, the word editor existed in lexicon of English long before the word edit. Semantic changes • Words and morphemes change their meanings in various ways, which shows the social context. • As we have example of the word pen. • Words have their individual history. • Semantic change is classified in two main types. • Extension and narrowing of meaning • Grammaticalization