Communication, Language and Culture: The Form of the Message
advertisement

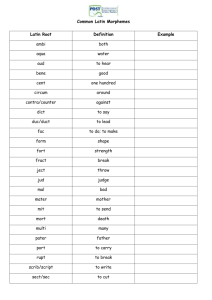
Communication, Language and Culture: The Form of the Message In order for social scientists to understand how people organize their lives, carry out work, practice religions, and the like, they need to be aware of how people talk to each other (Bnvillain 2003, 2) Communicative interactions Types of meanings transmitted through language: • Situational • Social • cultural The act of speaking is action • Creation of particular meanings • Creating expectations Why is communication(language) important for anthropology? • Links of language and culture • Understand social organization --religion, law, etc. • Social patterns and structures Language needs to be understood within cultural contexts: social, situational, cultural Cultural Model Is a construction of reality that is created, shared, and transmitted by members of a group (ideology) Speech community Consists of people who are united in numerous ways: norms and shared rules Characteristics of Human Communication • Productivity: the ability to communicate many messages efficiently • Displacement: the ability to think in the past, the future and the present Properties of languages • Sounds • --Phoneme: a minimal unit of sound that functions to differentiate the meaning of words • Vocabulary • Grammar: rules for combining sounds into sequences that carry meaning Grammar • Morphology • Syntax • Semantics Morphology • Is concerned with how phonemes are combined by language into larger units • Words: one or more morphemes Morphological examples • Cow • Cow- boy • Affixes: bound morphemes: • dis --- dis-like Syntax • rules that determine how words should be combined to make sense to speakers of a language • (English) word order critical for meaning (you, are, and there) • There you are • You are there • Are you there? Morphological Typologies (classification system) • Classification of languages according to how they structure words out of morphemes • Isolating languages: few morphemes, simple method: prefix and suffix (English) • Agglutinating languages: words containing many morphemes, highly regular rules (Turkish) • Synthetic or polysynthetic: Words containing many morphemes, very complex rules (Inuktitut Origins of Language • 50,000 • Stated as paralanguage: non-verbal communication (body posture, voice tone, touch, smell and facial movements) • All languages equally efficient (semantically and grammatically) • Semantics: the study of meaning in language, including the analysis of meaning of words and sentences Discussion Question • Why do you think it is important to understand the relationship between language, communication and cultural contexts?