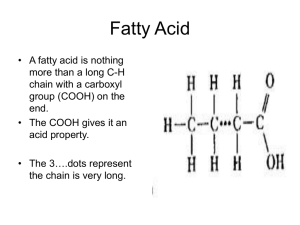
FATS & OILS FATS •SOLID AT ROOM TEMPERATURE OILS •LIQUID AT ROOM TEMPERATURE • CARBON HYDROGEN OXYGEN TRIGLYCERIDES ONE FAT MOLECULE = • 3 FATTY ACIDS + 1 GLYCEROL TYPES OF FATS • SATURATED FATS • Solid at room temperature • Found in animal foods/products • UNSATURATED FATS • Liquid at room temperature • Found in plant foods SATURATED FATTY ACIDS (all carbon atoms are filled with hydrogen) • BUTYRIC ACID—Milk, Butter • PALMITIC ACID—palm oil, beef, eggs, poultry, seafood • LAURIC ACID—Dairy foods, Coconut milk • STEARIC ACID—Beef fat, meat, eggs, chocolate UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS TWO TYPES OF UNSATURATED • MONOUNSATURATED • =ONLY ONE DOUBLE BOND POLYUNSATURATED TWO OR MORE DOUBLE BONDS MONOUNSATURATED • OLEIC ACID • Olive oil, sesame seeds, safflower oil, canola oil, peanuts, avocado POLYUNSATURATED (PUFA) Types of PUFAs • Omega-3 • • • • • • • Sources: Green leaves and algae and fish because they eat them Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Omega 6 Linoleic Acid Linolenic Acid Arachidonia Acid ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS (EFA) • • • • LINOLEIC ACID—Breast milk LINOLENIC ACID OMEGA 3—Oily fish OMEGA 6 TRANS FAT • Trans fats are the result of a process called hydrogenation. To make vegetable oils solid at room temperature, the hydrogen atoms are rearranged at the point of the double bonds. • The process creates trans double bonds by moving the hydrogen atom to the other side of the carbon chain at the point of the double bond. These two hydrogen atoms then balance eachother and the fatty acid becomes straight and the fat becomes more solid. Partially hydrogenated oil