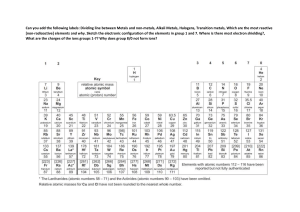
Name: Chemistry | Unit 1: Valence Electrons and properties of elements | Valence electrons and reactivity Materials: Videos below of alkali metals and halogens reactivity. Periodic table Objectives: ● Explain the reactivity trends of alkali metals and halogens Procedure: Watch the demonstrations below Alkali Metals and Water Sodium and Halogens Lithium and water Sodium and chlorine Sodium and water Sodium and bromine Potassium and water Sodium and iodine Write down your observations and ‘I wonder’ questions: Observations Questions: Use this atom builder website to answer the questions below. 1) What do the red spheres represent? 2) What do the blue spheres represent? 3) What do the up and down arrows represent? 4) What color is the 4th shell? 5) How many subshells does the 3rd shell have? I wonder questions Build Neon and sodium, take a snapshot of each, and put them into the table below. Neon Sodium 6) Which of the two elements (neon or sodium) has a full outer shell? 7) Which of the two elements (neon or sodium) is completely unreactive? 8) Using the observations from sodium and water and your answers from the previous two questions, explain why sodium is so reactive. A complete answer will discuss energy levels and electrons. 9) Explain how lithium and potassium follow the same pattern. 10) Do you think that magnesium would be more reactive or less reactive than sodium? Justify your answer. Build Neon and chlorine, take a snapshot of each, and put them into the table below. Neon Chlorine 11) You explained earlier why sodium is so reactive. Why does it make sense that even though chlorine is on the other side of the periodic table, it is also very reactive. 12) Explain how bromine and iodine fits the same pattern. 13) Do you think that oxygen would be more reactive or less reactive than chlorine. Justify your answer. Build the Dot Diagrams for each of the elements below using the periodic table, your knowledge of valence electrons, the dots, and element symbols. (Note: If you are putting a dot on the top or bottom of the element symbol and it shifts the element symbol, move the dot further away. See this video for help. Li Na K Cl Br I Putting things together! 14) What are valence electrons? 15) Why are valence electrons important? 16) How many valence electrons does each of the alkali metals have? 17) How many valence electrons does each of the halogens have? 18) How many valence electrons does each of the noble gases have (except helium)? 19) Why does helium only have 2 valence electrons? 20) Alkali metals need to ____________ (gain/lose) 1 electron to have a _________ outer shell. 21) Halogens need to ____________ (gain/lose) 1 electron to have a _________ outer shell. Reactivity within a group. Go back to the gifs of the alkali metals reacting with water before answering the following. 22) What happens to the reactivity of the alkali metals as you go down the group? (On the periodic table) Build lithium, sodium, and potassium using the atom builder. Take screenshots and put them in the table below. Lithium Sodium Potassium 23) What kind of charge do protons have? 24) What kind of charge do electrons have? 25) If there are __________ (positive/negative) things in the nucleus and ___________ (positive/negative) things in the electron cloud, there are _____________ (attractive/repulsive) forces. 26) What do you notice about the valence electron(s) of the alkali metals in relation to the nucleus as you compare lithium, sodium, and potassium? 27) Use the diagrams of the alkali metals and your answers to the previous questions to explain why the reactivity of alkali metals increases as you go down the periodic table. Go back to the gifs of the alkali metals reacting with water before answering the following. 28) What happens to the reactivity of the halogens as you go down the group? (On the periodic table) Build chlorine, bromine, and iodine using the atom builder. Take screenshots and put them in the table below. Chlorine Bromine Iodine 29) Use the diagrams of the halogens and your answers above to explain why the reactivity of halogens _____________ (increases/decreases) as you down the group? Summing it all up! 30) Write a paragraph comparing and contrasting the reactivity trends of the alkali metals and halogens. A complete answer will include information about valence electrons, electron shells, losing/gaining electrons, attractive forces between the valence electrons and nucleus.