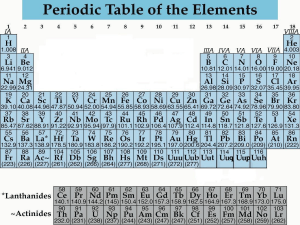
Periodic Table Organization: Worksheet
advertisement

How is the periodic table E.Q. organized? All notes must be in the student’s own handwriting. Chunk the information on the right to form questions in this column. The periodic table is an arrangement of known elements based on atomic # and chemical & physical properties. 3 main categories 1. Metals 2. Nonmetals 3. Metalloids Organized base on 3 things: Atomic structure (number of valence electrons) Atomic number (number of protons) Chemical & Physical properties (reactivity level) Reactivity is a chemical property; if an element reacts, it will change to a different substance. The Valence (group number) determines the level of reactivity. Groups 1 & 2 are “givers” because they only have a few valence electrons. They will give their electrons when reacting with other elements. Metals- most are metals, middle and left side (except hydrogen) Hard and shiny Conduct heat and electricity Few valence electrons Malleable- can be hammered and flattened “ping! ping!” Ductile- can be stretched into wire Nonmetals- upper right and hydrogen Generally gases and brittle solids Dull surface Insulators (block heat and cold energy) Have more valence electrons Receive electrons or share when reacting with other elements Metalloids- near staircase line Have properties of both metals & nonmetals Semiconductors of electricity Group 1A are called Alkali metals (except hydrogen)- highly reactive Group 8a are called Noble gases - nonreactive Summary Write a summary about the organization of the periodic table here. Make sure to use complete sentences and write a full paragraph, not just a few sentences.