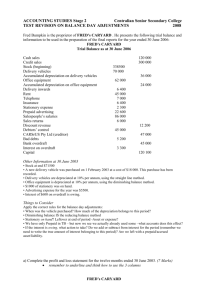
TWIKATANE COMBINED SCHOOL BUSINESS STUDIES DEPARTMENT LESSON PLAN FORM TEACHER: CHIKOPO R. GRADE: . 806232 DATE: ……………………………… SUBJECT: BUSINESS STUDIES NUMBER OF PUPILS: …………….. TOPIC: ADJUSTMENTS IN THE FINAL ACCOUNTS GENDER: GIRLS: SUB TOPIC: Adjustments to final accounts DURATION: ………………………. TS NO: BOYS: . OUTCOME(S): At the end of lesson pupils should prepare the final accounts with adjustments without difficulties. RATIONALE: In this lesson, learners will be able to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. Through demonstration and participatory method by learners, it is expected that the learners will acquire the knowledge of preparing the final accounts with adjustments. In this lesson, using the demonstration approach I intend to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. This lesson is the 1st lesson of 4 lessons for the topic of Adjustments to final accounts. Reference: Senior Secondary Principles of Accounts 10 – 12 by Lovemore Chibuye (2017) PART INTRO TIME 5 min 40 min D E V E L LESSON CONTENT Recap of the previous terms work. Preview of the lesson The following trial balance was extracted from the books of R. Gambo at the close of business on 28 February 2007 Dr Cr K’000 K’000 Purchases and Sales 92,800 157,165 Cash at bank 4,100 Cash in hand 324 Capital 11,400 Drawings 17,100 Office furniture 2,900 Rent 3,400 Wages and Salaries 31,400 Discounts 820 160 Debtors and Creditors 12,316 5,245 Stock 1 March 2006 4,120 Provision for doubtful debts 405 Delivery Van 3,750 Van running costs 615 Bad debts written off 730 174,375 174,375 The following additional information as at 28 February 2007 is available: a) Stock 28 February 2007 K2,400,000 b) Wages and Salaries accrued at 28 February 2007 K340,000 c) Rent prepaid at 28 February 2007 K230,000 d) Van running costs owing at 28 February 2007 K72,000 e) Increase the provision for doubtful debts by K91,000 f) Provide for depreciation as follows: Office furniture K380,000; Delivery Van K1,250,000 Required: Draw up the trading, profit and loss account for the year ending 28 February 2007 together with a balance sheet as at that date. R. Gambo Trading, Profit and Loss account for the year ended 28 February 2007 Sales 157,165,000 Opening stock 4,120,000 Purchases 92,800,000 96,920,000 Less: Closing stock (2,400,000) Cost of goods sold (94,520,000) Gross profit 62,645,000 Add: Discount received 160,000 METHODOLOGY QPN/VE Illustration LEARNER ACTIVITY Answering questions Observation REF/AIDS Business Accounting by F. Wood Chalkboard Total income Less: Expenses Rent Less: Rent prepaid O 62,805,000 Discount allowed Increase in provision for bad debts Van running costs Add: Van costs owing E Fixed Assets Office Furniture Delivery Van Cash at bank Cash in hand Prepaid expenses Total Current Assets Less: Current Liabilities Creditors Expenses Owing T Working Capital Net Assets Financed by: Capital Add: Net Profit Less: Drawings Net Worth Observation 31,740,000 820,000 91,000 615,000 72,000 687,000 730,000 380,000 1,250,000 (38,868,000) 24,937,000 NBV 2,520,000 2,500,000 5,020,000 2,400,000 12,316,000 (496,000) 11,820,000 4,100,000 324,000 230,000 18,874,000 Chalkboard 5,245,000 412,000 (5,657,000) 13,217,000 18,237,000 11,400,000 24,937,000 35,337,000 (17,100,000) 18,237,000 1. A 30 min P L I C A T I O N CONC Demonstration Chalkboard 3,170,000 R. Gambo Balance Sheet as at 28 February 2007 Cost Accumulated Dep’n 2,900,000 380,000 3,750,000 1,250,000 6,650,000 1,630,000 Current Assets Stock Debtors Less: Provision for bad debts N P 31,400,000 340,000 Bad debts written off Depreciation: Office Furniture Delivery Van Total Expenses Net Profit M Observation 3,400,000 (230,000) Wages and Salaries Add: Wages & Salaries accrued P Demonstration 5 min J. Wakunuma, a sole trader, extracted the following trial balance from his books at the close of business on 31 March 2010 Dr Cr K’000 K’000 Purchases and Sales 61,420 127,245 Stock 1 April 2009 7,920 Capital 25,200 Bank overdraft 2,490 Cash 140 Discounts 2,480 62 Returns inwards 3,480 Returns outwards 1,356 Carriage outwards 3,210 Rent and Insurance 8,870 Provision for bad debts 630 Fixtures and fittings 1,900 Van 5,600 Debtors and Creditors 12,418 11,400 Drawings 21,400 Wages and Salaries 39,200 General office expenses 319 168,383 168,383 The following additional information as at 31 March 2010 is available: a) Stock 31 march 2010 K6,805,000 b) Wages and Salaries accrued at 31 March 2009 K3,500,000; Office expenses owing K16,000 c) Rent prepaid 31 March 2009 K600,000 d) Increase the provision for doubtful debts by K110,000 to K740,000 e) Provide for depreciation as follows: Fixtures and fittings K190,000; Van K1,400,000 Required: Prepare the trading profit and loss account for the year ending 31 March 2010 together with the balance sheet as at date Recap of the main points Class exercises Answering exercises VE Listening Chalkboard LESSON CRITIQUE: ............................................................................................................ HOD’S COMMENT: ................................................................................................................ TWIKATANE COMBINED SCHOOL BUSINESS STUDIES DEPARTMENT LESSON PLAN FORM TEACHER: CHIKOPO R. GRADE: . 806232 DATE: ……………………………… SUBJECT: BUSINESS STUDIES NUMBER OF PUPILS: …………….. TOPIC: ADJUSTMENTS IN THE FINAL ACCOUNTS GENDER: GIRLS: SUB TOPIC: Adjustments to final accounts DURATION: ………………………. TS NO: BOYS: . OUTCOME(S): At the end of lesson pupils should prepare the final accounts with adjustments without difficulties. RATIONALE: In this lesson, learners will be able to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. Through demonstration and participatory method by learners, it is expected that the learners will acquire the knowledge of preparing the final accounts with adjustments. In this lesson, using the demonstration approach I intend to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. This lesson is the 2nd lesson of 4 lessons for the topic of Adjustments to final accounts. Reference: Senior Secondary Principles of Accounts 10 – 12 by Lovemore Chibuye (2017) PART INTRO TIME 5 min 20 min D E V E L LESSON CONTENT Recap of the previous terms work. Preview of the lesson The following trial balance was extracted from the ledger of Mrs. Mapalo, a Sole trader. Dr Cr K’000 K’000 Sales 138,078 Purchases 82,350 Carriage 5,144 Drawings 7,800 Rent, Rates and Insurance 6,622 Postage and Stationery 3,001 Advertising 1,330 Salaries and Wages 26,420 Bad debts 877 Provision for doubtful debts 130 Debtors 12,120 Creditors 6,471 Cash in hand 177 Cash at bank 1,002 Stock 1 June 2008 11,927 Equipment At cost 58,000 Accumulated depreciation 19,000 Capital 53,091 216,770 216,770 The following additional information as at 31 May 2009 a) Rent is accrued by K210,000 b) Rates have been prepaid by K880,000 c) K2,211,000 of carriage represents carriage inwards on purchases d) Equipment is to be depreciated at 15% p.a. using straight line method e) The provision for doubtful debts to be increased by K40,000 f) Stock at the close of the business has been valued at K13,551,000 Required: Prepare a trading, profit and loss account for the year ended 31 May 2009 and a balance sheet as at that date. Mrs. Mapalo Trading, Profit and Loss account for the year ended 31 May 2009 Sales 138,078,000 Opening stock 11,927,000 Purchases 82,350,000 Add: Carriage inwards 2,211,000 84,561,000 96,488,000 Less: Closing Stock (13,551,000) Cost of goods sold 82,937,000 Gross Profit 55,141,000 Less: Expenses Carriage outwards 2,933,000 Rent, Rates and Insurance 6,622,000 METHODOLOGY QPN/VE LEARNER ACTIVITY Answering questions Illustration Observation Demonstration Observation REF/AIDS Business Accounting by F. Wood Chalkboard Chalkboard O Add: Rent accrued Less: Rates prepaid P Postage and Stationery Advertising Salaries and Wages Bad debts Increase in provision for bad debts Depreciation: Equipment Total Expenses Net profit E N T P 10 min P L I C A T I O N CONC 5,952,000 3,001,000 1,330,000 26,420,000 877,000 40,000 8,700,000 Mrs. Mapalo’s Balance Sheet as at 31 May 2009 Fixed Assets Cost Accumulated Dep’n Equipment 58,000,000 27,700,000 Current Assets Stock 13,551,000 Debtors 12,120,000 Less: Provision for doubtful debts (170,000) 11,950,000 Cash at bank 1,002,000 Cash in hand 177,000 Prepaid expenses 880,000 Total Current Assets 27,560,000 Less: Current Assets Creditors 6,471,000 Accrued expenses 210,000 (6,681,000) Working Capital Net Assets Financed by: Capital 53,091,000 Add: Net Profit 5,888,000 58,979,000 Less: Drawing 7,800,000 M A 210,000 (880,000) 5 min 49,253,000 5,888,000 NBV 30,300,000 Demonstration Observation Chalkboard Class exercises Answering exercises Chalkboard VE Listening 20,879,000 51,179,000 51,179,000 The following trial balance was extracted from the books of Mr. Chico, a business man based in Ndola. Dr Cr K’000 K’000 Sales 430,000 Purchases 293,500 Carriage inwards 2,100 Drawings 31,000 Rent 5,200 Business Rates 2,600 Insurance 550 Postage 250 Stationery 986 Advertising 250 Wages 10,500 Bad debts 400 Provision for doubtful debts 400 Debtors 5,120 Creditors 3,600 Cash in hand 120 Cash at bank 3,257 Stock 6,520 Equipment at cost 150,000 Accumulated depreciation – equipment 35,000 Capital 43,353 512,353 512,353 Following a discussion with Mr. chico, the following points have come to light: a) Accruals are necessary for rent K150,000), business rates (K200,000), and stationery (K16,000) b) Insurance has been prepaid by K150,000, advertising by K50,000 c) Stock at the year end is K7,000,000 d) Depreciation is to be charged on equipment at a rate of 10% on cost e) The doubtful debt provision is to be increased to 10% of the year end balance f) Purchases invoices to the value of K12,000,000 were found in the desk drawer the day before meeting with Mr. Chico. Half of them have been paid by cheque (but no record made in the cash book) and the rest are outstanding. Required: Prepare a trading and profit and loss account for the year ending on the date of extraction of the trial balance together with a balance sheet as at that date Recap of the main points LESSON CRITIQUE: ............................................................................................................. HOD’S COMMENT: ............................................................................................................... TWIKATANE COMBINED SCHOOL BUSINESS STUDIES DEPARTMENT LESSON PLAN FORM TEACHER: CHIKOPO R. GRADE: . 806232 DATE: ……………………………… SUBJECT: BUSINESS STUDIES NUMBER OF PUPILS: …………….. TOPIC: ADJUSTMENTS IN THE FINAL ACCOUNTS GENDER: GIRLS: SUB TOPIC: Adjustments to final accounts DURATION: ………………………. TS NO: BOYS: . OUTCOME(S): At the end of lesson pupils should prepare the final accounts with adjustments without difficulties. RATIONALE: In this lesson, learners will be able to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. Through demonstration and participatory method by learners, it is expected that the learners will acquire the knowledge of preparing the final accounts with adjustments. In this lesson, using the demonstration approach I intend to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. This lesson is the 3rd lesson of 4 lessons for the topic of Adjustments to final accounts. Reference: Senior Secondary Principles of Accounts 10 – 12 by Lovemore Chibuye (2017) PART INTRO TIME 5 min 40 min D E V E L LESSON CONTENT Recap of the previous work. Preview of the lesson The trial balance for a Accounts Ltd a small business at 31 August 2008 is as follows: Dr Cr K’000 K’000 Stock 1 Sept 2007 8,200 Purchases and Sales 26,000 40,900 Rent 4,400 Business rates 1,600 Sundry expenses 340 Motor vehicle at cost 9,000 Debtors and Creditors 1,160 2,100 Bank 1,500 Provision for depreciation on motor vehicle 1,200 Capital 19,700 Drawings 11,700 63,900 63,900 The following additional information as at 31 August 2008 is available: a) Stock valued at cost price K9,100,000 b) Accrued rent of K400,000 c) Prepaid business rates of K300,000 d) The motor vehicle is to be depreciated at 20% per annum Required: Prepare the trading, profit and loss account for the year ending 31 August 2008 together with a balance sheet as at that date. Solution Accounts Ltd’s Trading, Profit and Loss account for the year ended 31 May 2009 Sales 40,900,000 Opening stock 8,200,000 Purchases 26,000,000 34,200,000 Less: Closing Stock (9,100,000) Cost of goods sold 25,100,000 Gross Profit 15,800,000 METHODOLOGY QPN/VE Illustration LEARNER ACTIVITY Answering questions Observation REF/AIDS Business Accounting by F. Wood Chalkboard O P Less: Expenses Business Rates Less: Rates prepaid 1,600,000 300,000 Rent Add: Rent accrued 4,400,000 400,000 Sundry expenses Depreciation: Motor van Total Expenses Net profit E N A P P I 30 min C A T I O N CONC Demonstration Observation Chalkboard 4,800,000 340,000 1,800,000 8,240,000 7,560,000 NBV 6,000,000 9,560,000 15,560,000 Chalkboard 15,560,000 T L Observation 1,300,000 Accounts Ltd’s Balance Sheet as at 31 May 2009 Fixed Assets Cost Accumulated Dep’n Motor van 9,000,000 3,000,000 Current Assets Stock 9,100,000 Debtors 1,160,000 Cash at bank 1,500,000 Prepaid expenses 300,000 Total Current Assets 12,060,000 Less: Current liabilities Creditors 2,100,000 Accrued expenses 400,000 (2,500,000) Working Capital Net Assets Financed by: Capital 19,700,000 Add: Net Profit 7,560,000 27,260,000 Less: Drawing 11,700,000 M Demonstration 5 min Mr. Musonda has been trading for some years as a wine merchant. The following list of balances has been extracted from his ledger as at 30 April 2007, the end of his most recent financial years. K’000 Capital 83,887 Sales 259,870 Trade creditors 19,840 Returns outwards 13,407 Provision for doubtful debts 512 Discounts allowed 2,306 Discount received 1,750 Purchases 135,680 Returns inwards 5,624 Carriage outwards 4,562 Drawings 18,440 Carriage inwards 11,830 Rent, rates and insurance 25,973 Postage, stationery and telephone 2,410 Heating and lighting 1,101 Advertising 5,980 Salaries and wages 38,521 Bad debts 2,008 Cash in hand 534 Cash at bank 4,440 Stock as at 1 May 2006 15,654 Trade debtors 24,500 Fixtures and fittings – at cost 120,740 Provision for dep’n on fixtures and fittings – as at 30 April 2007 63,020 Depreciation 12,074 The following additional information as at 30 April 2007 is available. a) Stock at the close of business was valued at K17,750,000 b) Insurance have been prepaid by K1,120,000 c) Heating and lighting is accrued by K1,360,000 d) Rates have been prepaid by K5,435,000 e) The provision for doubtful debts is to be adjusted so that it is 3% of trade debtors Recap of the main points Class exercises Answering exercises VE Listening Chalkboard LESSON CRITIQUE: .............................................................................................................. HOD’S COMMENT: ................................................................................................................ TWIKATANE COMBINED SCHOOL BUSINESS STUDIES DEPARTMENT LESSON PLAN FORM TEACHER: CHIKOPO R. GRADE: . 806232 DATE: ……………………………… SUBJECT: BUSINESS STUDIES NUMBER OF PUPILS: …………….. TOPIC: ADJUSTMENTS IN THE FINAL ACCOUNTS GENDER: GIRLS: SUB TOPIC: Adjustments to final accounts DURATION: ………………………. TS NO: BOYS: . OUTCOME(S): At the end of lesson pupils should prepare the final accounts with adjustments without difficulties. RATIONALE: In this lesson, learners will be able to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. Through demonstration and participatory method by learners, it is expected that the learners will acquire the knowledge of preparing the final accounts with adjustments. In this lesson, using the demonstration approach I intend to prepare the final accounts with adjustments. This lesson is the 4th lesson of 4 lessons for the topic of Adjustments to final accounts. Reference: Senior Secondary Principles of Accounts 10 – 12 by Lovemore Chibuye (2017) PART INTRO TIME 5 min 20 min D E V E L LESSON CONTENT Recap of the previous work. Preview of the lesson From the following trial balance of John Banda, Store owner, prepare a trading, profit and loss account for the year ending 31 December 2007, and a balance sheet as at that date, taking into consideration the adjustments shown below: Dr Cr K’000 K’000 Sales 400,000 Purchases 350,000 Sales returns 5,000 Purchases returns 6,200 Stock 1 Jan 2007 100,000 Provision for doubtful debts 800 Wages and Salaries 30,000 Rates 6,000 Telephone 1,000 Shop fittings at cost 40,000 Van at cost 30,000 Debtors and Creditors 9,800 7,000 Bad debts 200 Capital 179,000 Bank 3,000 Drawings 18,000 593,000 593,000 The following additional information as at 31 December 2007 is available. a) Stock at 31 December 2007 K120,000,000 b) Accrued wages K5,000,000 c) Rates prepaid K500,000 d) Provision for doubtful debts to be increased to 10% of debtors e) Telephone account outstanding K220,000 f) Depreciate Shop fittings at 10% per annum, and Van at 20% per annum on cost John Banda’s Trading, Profit and Loss account for the year ended 31 December 2007 Sales 400,000,000 METHODOLOGY QPN/VE Illustration LEARNER ACTIVITY Answering questions Observation REF/AIDS Business Accounting by F. Wood Chalkboard Chalkboard Less: Returns inwards Turnover Opening stock Purchases Less: Purchases returns O P M E 5,000,000 395,000,000 350,000,000 6,200,000 Less: Closing Stock Cost of goods sold Gross Profit Less: Expenses Increase in Provision Wages and Salaries Add: Wage accrued 30,000,000 5,000,000 Rates Less: Rates prepaid 6,000,000 500,000 Telephone Add: Telephone outstanding 1,000,000 220,000 Chalkboard Class exercises Answering exercises Chalkboard 35,000,000 5,500,000 1,220,000 200,000 6,000,000 4,000,000 52,100,000 19,100,000 John Banda’s Balance Sheet as at 31 December 2007 Cost Accumulated Dep’n 40,000,000 4,000,000 30,000,000 6,000,000 70,000,000 10,000,000 Bank Prepaid expenses Total Current Assets Less: Current Assets Creditors Accrued expenses Less: Drawing Observation 343,800,000 443,800,000 (120,000,000) 180,000 Current Assets Stock Debtors Less: Provision for doubtful debts Working Capital Net Assets Financed by: Capital Add: Net Profit Demonstration 100,000,000 N T Observation 323,800,000 71,200,000 Bad debts Depreciation: Van Shop Fittings Total Expenses Net profit Fixed Assets Shop Fittimgs Van Demonstration 9,800,000 (980,000) NBV 36,000,000 24,000,000 60,000,000 120,000,000 8,820,000 3,000,000 500,000 132,320,000 7,000,000 5,220,000 (12,220,000) 120,100,000 180,100,000 179,000,000 19,100,000 198,100,000 18,000,000 180,100,000 A P P L I C A T I O N 10 min Fanny Mulombe, a sole trader had the following Trial Balance extracted from business accounts on 31 October, 2006 the end of the financial year. K K Bad debts written off 400,000 Cash in hand 250,000 Cash at bank 6,250,000 Purchases/Sales 23,500,000 80,000,000 Rent and rates 1,250,000 Motor vehicles 12,500,000 Light and heat 600,000 Carriage outwards 350,000 Opening stock (1 Nov. 2005) 18,750,000 Commission received 1,350,000 Capital 75,740,000 Drawings 8,500,000 Returns 1,650,000 2,000,000 Office salaries 25,000,000 Debtors/Creditors 23,600,000 5,650,000 Provision for bad debts 1,860,000 Furniture and fittings 8,000,000 Land and buildings 46,000,000 Bank loan 10,000,000 A senior accounting officer requests you to prepare the Trading and Profit and Loss Account to show how the business fared that year and the Balance Sheet to reflect its financial position as at 31 October, 2006. Take the following into consideration: The closing stock was valued at K19,500,000 K800,000 was owing on office salaries K150,000 rates had been paid in advance The motor vehicles were to be depreciated by 10% Provision for bad debts to be increased to 10% of the debtors K800,000 interest on loan was not yet paid CONC 5 min Recap of the main points [35] VE Listening LESSON CRITIQUE: ................................................................................................................... HOD’S COMMENT: .....................................................................................................................